|
Jean-Bernard Caron
Jean-Bernard Caron is a French and Canadian palaeontologist currently working as a curator of invertebrate palaeontology at the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto. Caron is also cross-appointed at the University of Toronto as an associate professor in the Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Earth Sciences. He is known for his work on the Burgess Shale. Education Caron completed a bachelor's degree in natural history at the Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand in 1997 and his Diplôme d'études approfondies in palaeontology, sedimentology and chronology from the University Claude-Bernard, Lyon in 1999. His thesis focused on the problematic Burgess Shale animal ''Banffia constricta''. Jean-Bernard Caron volunteered as a field assistant at the Burgess Shale in 1998 and, in 1999 and 2000, participated in the last two seasons led by Desmond Collins, then Curator of Invertebrate Palaeontology at the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM). He also spent several months at the RO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years. After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown, the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrónos'', "time"; and , '' -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".Memidex/WordNet, "chronology,memidex.com (accessed September 25, 2010). Chronology is a part of periodization. It is also a part of the discipline of history including earth history, the earth sciences, and study of the geologic time scale. Related fields Chronology is the science of locating historical events in time. It relies upon chronometry, which is also known as timekeeping, and historiography, which examines the writing of history and the use of historical methods. Radiocarbon dating estimates the age of formerly living things by measuring the proportion of carbon-14 isotope in their carbon content. Dendrochronology estimates the age of trees by corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
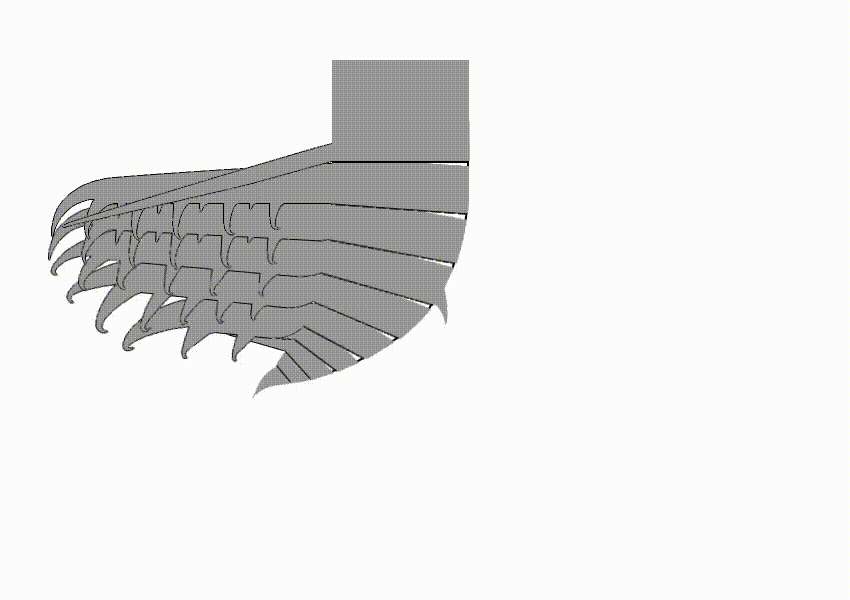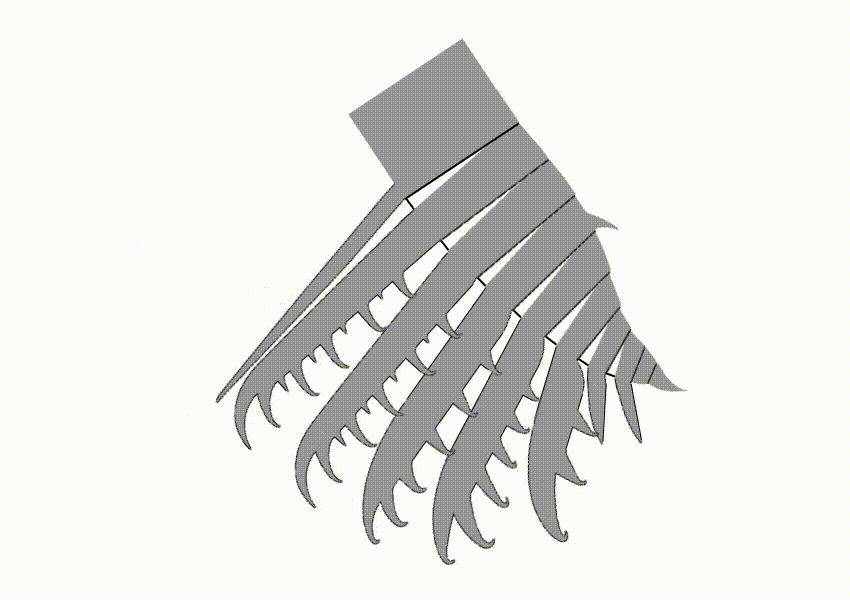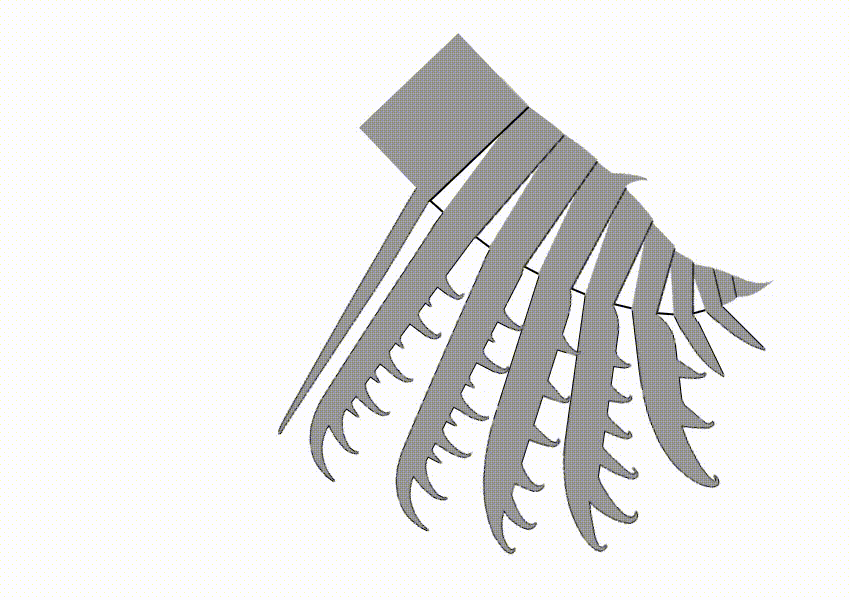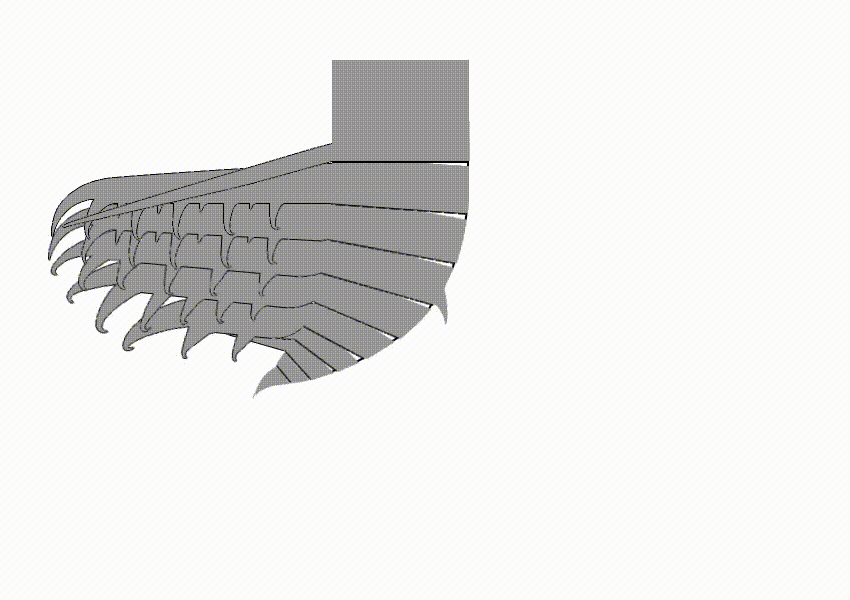
Hurdia
''Hurdia'' is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. As a radiodont like ''Peytoia'' and ''Anomalocaris'', it is part of the ancestral lineage that led to euarthropods. Description ''Hurdia'' was one of the largest organisms in the Cambrian oceans, ''H. victoria'' reached approximately in length, while ''H. triangulata'' reached up to just . Its head bore a pair of rake-like frontal appendages which shovelled food into its pineapple-ring-like mouth (oral cone). Like other hurdiids, ''Hurdia'' bore a large frontal carapace protruding from its head composed of three sclerites: a central component known as the H-element and two lateral components known as P-elements. The function of this organ remains mysterious; it cannot have been protective as there was no underlying soft tissue. Originally, it is estimated that body flaps ran along the sides of the organisms, from which large gills were suspended. However, anatomy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yawunik
''Yawunik'' is an extinct genus of Cambrian megacheiran ("Great appendage" arthropod) known from the Burgess Shale in Canada (Marble Canyon locality). The type species has been named ''Yawunik kootenayi'' after the Kootenay, both a geographic area (and National Park, where the fossil was found) and North American First Nation, also known as the Ktunaxa. Yawunik is the name of a primordial sea monster in Ktunaxa mythology. The fossil dates back to 508 million years ago. Description ''Yawunik'' had large size for megacheiran, up to long not including great appendage. It had four eyes, in the anteriormost position of the head, and lateral eyes are larger. ''Yawunik'' differs from other leanchoilid such as ''Leanchoilia ''Leanchoilia'' is an megacheiran arthropod known from Cambrian deposits of the Burgess Shale in Canada and the Chengjiang biota of China. It was about long and had long, whip-like feelers mounted on frontal arm-like appendages. Its internal o ...'' by havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphusauctum
''Siphusauctum'' is an extinct genus of filter-feeding animals that lived during the Middle Cambrian about 510 million years ago. Attached to the substrate by a holdfast, it had a tulip-shaped body, called the calyx, into which it actively pumped water that entered through pores and filtered out and digested organic contents. It grew to a length of only about . ''Siphusauctum gregarium'' was described in 2012 from numerous fossils recovered from the "Tulip Beds" strata of the Burgess Shale of Yoho National Park, British Columbia, Canada. The generic name comes Latin ' ("cup" or "goblet") and ' ("large"), referring to the general shape and size of the animal. The specific epithet comes from Latin ' ("flock" or "herd") referring to the large numbers of specimens recovered. It is the only species classified under the genus ''Siphusauctum'' and the family Siphusauctidae. The seeming presence of a digestive tract and anus suggest that it is a member of Bilateria, but it cannot be ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthrozanclus
''Orthrozanclus'' (from Greek + ( + ), "dawn scythe") is a genus of sea creatures known from two species, ''O. reburrus'' from the Middle Cambrian (~) Burgess shale and ''O. elongata'' from Early Cambrian (~) Maotianshan Shales. Animals in this genus were one to two centimeters long, with spikes protruding from their armored bodies. The placement of this genus into a specific family is not universally accepted. History of discovery Jean-Bernard Caron and Donald A. Jackson found a specimen in the Burgess Shale and in 2006 referred to it as "scleritomorph C" without a detailed description. In 2007 Caron and Simon Conway Morris published a description and named the fossil ''Orthrozanclus reburrus''. The genus name means "Dawn scythe" and derives from Greek, with the species name meaning "bristling hair" in Latin. The two known specimens of ''O. elongata'' were discovered from Maotianshan Shale in 2015 and 2016 and formally described the following year. Description ''Orthrozancl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpetogaster
''Herpetogaster'' is an extinct cambroernid genus of animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China, Pioche Formation of Nevada and Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of Canada containing the species ''Herpetogaster collinsi'' and ''Herpetogaster haiyanensis''. Description '' H. collinsi'' is known from over 101 specimens. It possessed a pair of branching tentacles and a tough but flexible body that curved helically to the right like a ram's horn and was divided into at least 13 segments. A flexible, extensible stolon emerged from the body at about the ninth segment and secured the animal to the sea floor, often by attaching to the sponge '' Vauxia.'' It is not known whether the attachment was permanent. A mouth opened between the tentacles, leading internally to a pharynx, a large lentil-shaped stomach, a narrower straight intestine, and an anus at the end of the "tail." The tentacles were softer than the body and probably extensible. A dark line running down the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. In a ''rooted'' phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the inferred most recent common ancestor of those descendants, and the edge lengths in some trees may be interpreted as time estimates. Each node is called a taxonomic unit. Internal nodes are generally called hypothetical taxonomic units, as they cannot be directly observed. Trees are useful in fields of biology such as bioinformatics, systematics, and phylogenetics. ''Unrooted'' trees illustrate only the relatedness of the leaf nodes and do not require the ancestral root to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maotianshan Shales
The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Cambrian, Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their ''Lagerstätte, Konservat Lagerstätten'', deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill (, Literal meaning: Hat Sky Mountain) in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China. The most famous assemblage of organisms are referred to as the Chengjiang biota for the multiple scattered fossil sites in Chengjiang. The age of the Chengjiang Lagerstätte is locally termed Qiongzhusian, a stage correlated to the late Atdabanian Stage in Siberian sequences of the middle of the Early Cambrian. The shales date to ≤. The shales also contain the slightly younger Guanshan biota from Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoecology
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs a variety of fields including paleontology, ecology, climatology and biology. Paleoecology emerged from the field of paleontology in the 1950s, though paleontologists have conducted paleoecological studies since the creation of paleontology in the 1700s and 1800s. Combining the investigative approach of searching for fossils with the theoretical approach of Charles Darwin and Alexander von Humboldt, paleoecology began as paleontologists began examining both the ancient organisms they discovered and the reconstructed environments in which they lived. Visual depictions of past marine and terrestrial communities have been considered an early form of paleoecology. Overview of paleoecological approaches * Classic paleoecology uses data from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
