|
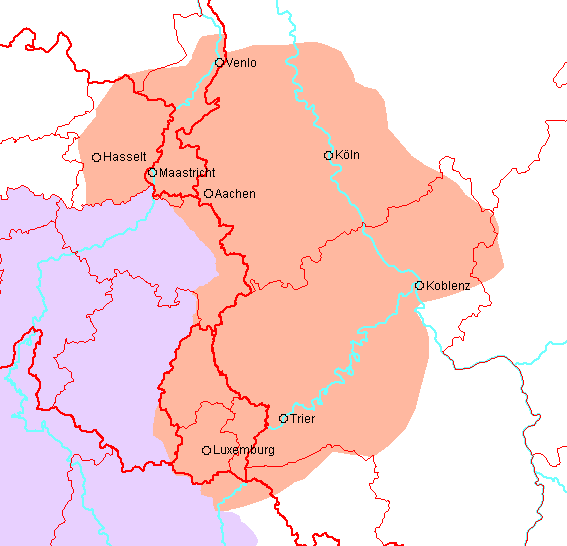
Jaun Valley Dialect
The Jaun Valley dialect ( sl, podjunsko narečje, ''podjunščina'') is a Slovene dialect in the Carinthian dialect group. It is primarily spoken in the Jaun Valley (german: Jauntal, sl, Podjuna) of Austria as well as in Strojna and Libeliče, Slovenia. It is spoken west of a line from Diex to Völkermarkt to Eberndorf, east of Sittersdorf, and north of the Ebriach dialect. Major settlements in the dialect area are Griffen, Kühnsdorf, Globasnitz, Bleiburg, and Lavamünd.Toporišič, Jože. 1992. ''Enciklopedija slovenskega jezika''. Ljubljana: Cankarjeva založba, p. 183. Phonological and morphological characteristics The Jaun Valley dialect has pitch accent and there has been accentual retraction from final circumflexes. It lacks Slovenian palatalization, has partially preserved the Proto-Slavic nasal vowels, long ''ə'' > ''a'', Proto-Slavic ''a'' > ''ɔ'', ''ła'' > ''wa'', the phoneme /w/ is preserved, and ''šč'' > ''š''. The addition of ''š-'' before deictics In lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovene Dialects
In a purely dialectological sense, Slovene dialects ( sl, slovenska narečja , ) are the regionally diverse varieties that evolved from old Slovene, a South Slavic language of which the standardized modern version is Standard Slovene. This also includes several dialects in Croatia, most notably the so-called Western Goran dialect, which is actually Kostel dialect. In reality, speakers in Croatia self-identify themselves as speaking Croatian, which is a result of a ten centuries old country border passing through the dialects since the Francia. In addition, two dialects situated in Slovene (and the speakers self identify as speaking Slovene) did not evolve from Slovene (left out in the map on the right). The Čičarija dialect is a chakavian dialect and parts of White Carniola were populated by Serbs during the Turkish invasion and therefore Shtokavian is spoken there. Spoken Slovene is often considered to have at least 48 dialects () and 13 subdialects (). The exact number of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffen, Austria
Griffen ( sl, Grebinj) is a market town in the district of Völkermarkt in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Geography Griffen lies in the wide ''Jauntal'' valley of the Drava River, between the Klagenfurt basin in the west and the Lavant Valley in the north. The municipal area comprises the cadastral communities of Griffnerthal, Großenegg (''Tolsti Vrh''), Haberberg (''Gabrje''), Kaunz (''Homec''), Kleindörfl (''Mala vas''), Pustritz (''Pustrica''), Sankt Kollmann (''Šentkolman''), Wölfnitz (''Golovica''), and Wriesen (''Brezje''). It is further subdivided into 35 villages and hamlets. History From the 7th century onwards, the ''Jauntal'' (Slovene: ''Podjuna'') area was a centre of the Slavic settlement of the Eastern Alps and part of the early medieval principality of Carantania. Up to today it remains a core territory of the Carinthian Slovenes. The settlement was first mentioned in an 822 deed, after Carantania had been incorporated into the Carolingian Empire and evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced without nasalization. Nasalized vowels are vowels under the influence of neighbouring sounds. For instance, the [] of the word ''hand'' is affected by the following nasal consonant. In most languages, vowels adjacent to nasal consonants are produced partially or fully with a lowered velum in a natural process of assimilation and are therefore technically nasal, but few speakers would notice. That is the case in English: vowels preceding nasal consonants are nasalized, but there is no phonemic distinction between nasal and oral vowels, and all vowels are considered phonemically oral. The nasality of nasal vowels, however, is a distinctive feature of certain languages. In other words, a language may contrast oral vowels and nasalized vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the Attested language, unattested, linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium B.C. through the 6th century A.D. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages. Rapid development of Slavic speech occurred during the Proto-Slavic period, coinciding with the massive expansion of the Slavic-speaking area. Dialectal differentiation occurred early on during this period, but overall linguistic unity and mutual intelligibility continued for several centuries, into the 10th century or later. During this period, many sound changes diffused across the entire area, often uniformly. This makes it inconvenient to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Accent
A pitch-accent language, when spoken, has word accents in which one syllable in a word or morpheme is more prominent than the others, but the accentuated syllable is indicated by a contrasting pitch ( linguistic tone) rather than by loudness (or length), as in many languages, like English. Pitch-accent also contrasts with fully tonal languages like Vietnamese and Standard Chinese, in which each syllable can have an independent tone. Some have claimed that the term "pitch accent" is not coherently defined and that pitch-accent languages are just a sub-category of tonal languages in general. Languages that have been described as pitch-accent languages include: most dialects of Serbo-Croatian, Slovene, Baltic languages, Ancient Greek, Vedic Sanskrit, Tlingit, Turkish, Japanese, Norwegian, Swedish (but not in Finland), Western Basque,Hualde, J.I. (1986)"Tone and Stress in Basque: A Preliminary Survey"(PDF). ''Anuario del Seminario Julio de Urquijo'' XX-3, 1986, pp. 867-896. Yaq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavamünd
Lavamünd ( sl, Labot) is a market town in the district of Wolfsberg in the Austrian state of Carinthia. The Lavamünd hydroelectric power plant on the Drava River and the Koralpe power plant are located in or near Lavamünd. Geography Lavamünd lies in the southeast of Carinthia, close to the border with Slovenia ( Slovene Carinthia). It is situated at the confluence of the Lavant and Drava rivers. In the northeast, the Soboth Pass leads across the Koralpe range to Eibiswald in Styria. At an elevation of AA, the area is the lowest part of Carinthia. The municipal area consists of the cadastral communities of Ettendorf, Großlamprechtsberg, Hart (''Dobrova''), Lamprechtsberg-Hartneidstein, Lavamünd proper, Lorenzenberg (''Šentlovrenc''), Magdalensberg, Rabenstein (''Rabštajn pri Labotu''), Weißenberg, and Wunderstätten (''Drumlje pri Labotu''). History The region in the Drava valley was already settled in Roman times. The estates at the confluence with the Lavant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleiburg
Bleiburg ( sl, Pliberk) is a small town in the south Austrian state of Carinthia (''Koroška''), south-east of Klagenfurt, in the district of Völkermarkt, some four kilometres (2.5 miles) from the border with Slovenia. The municipality consists of the twelve ''Katastralgemeinden'' Aich (''Dob''), Bleiburg, Grablach (''Grablje''), Kömmel (''Komelj''), Moos (''Blato''), Oberloibach (''Libuče''), Rinkenberg (''Vogrče''), Sankt Margarethen (''Šmarjeta''), Schattenberg (''Senčni kraj''), Unterloibach (''Libuče''), Weißenstein (''Belšak'') and Woroujach (''Borovje''). According to a 2001 census, 30.4% of the population are Carinthian Slovenes (in 1971, they were 52.8%). Geography The border town is located in the valley of the Feistritz creek, a right tributary of the Drava, north of the Peca massif of the Karavanke mountain range. It is home to a district court, military barracks and to the local productive and services industry. The name of Bleiburg, literally meaning 'Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globasnitz
Globasnitz ( Slovene: ''Globasnica'') is a town in the district of Völkermarkt in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Population A considerable percentage (42.1%) of the population are Carinthian Slovenes, and Slovene is a second official language of the municipality. History In the Carinthian Plebiscite of 1920, Sankt Jakob was one of the 17 Carinthian municipalities, where the majority of the population (52%) voted for the annexation to the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...). References External links * Reconstruction of an Ostrogoth woman from a skull, discovered in Globasnitz (her skull was intentionally deformed at birth) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebriach Dialect
The Ebriach dialect ( sl, obirsko narečje, ''obirščina'') is a Slovene dialect in the Carinthian dialect group. It is spoken in Austrian Carinthia around Bad Eisenkappel, in the watershed of the Vellach River ( sl, Bela) and Ebriach Creek (german: Ebriachbach, sl, Obirski potok), and Jezersko.Toporišič, Jože. 1992. ''Enciklopedija slovenskega jezika''. Ljubljana: Cankarjeva založba, p. 152. Phonological and morphological characteristics The Ebriach dialect has uvular stops in place of velars, it has close reflexes of the nasal vowel A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced wit ...s, and varying reflexes of the old acute and neoacute on short syllables. There has been accentual retraction from circumflected long vowels (e.g., ''vèčer'' vs. standard Slovene ''večêr''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carinthian Dialect Group
The Carinthian dialect group (''koroška narečna skupina'', ''koroščina''Logar, Tine. 1996. ''Dialektološke in jezikovnozgodovinske razprave''. Ljubljana: SAZU.) is a group of closely related dialects of Slovene, a South Slavic language. The Carinthian dialects are spoken by Carinthian Slovenes in Austria, in Slovenian Carinthia, and in the northwestern parts of Slovenian Styria along the upper Drava Valley, in the westernmost areas of Upper Carniola on the border with Italy, and in some villages in the Province of Udine in Italy. Phonological and morphological characteristics Among other features, this group is characterized by late denasalization of *''ę'' and *''ǫ'', a close reflex of long yat and open reflex of short yat, lengthening of old acute syllables and short neo-acute syllables, and an ''e''-like reflex of the long semivowel and ''ə''-like reflex of the short semivowel.Toporišič, Jože. 1992. ''Enciklopedija slovenskega jezika''. Ljubljana: Cankarjeva zalo� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sittersdorf
Sittersdorf ( sl, Žitara vas) is a town in the district of Völkermarkt in Carinthia in south-central Austria. Geography Sittersdorf lies about 10 km as the crow flies from the Slovenian border. The Vellach and the Suchabach flow through it. The largest bodies of water in the municipality are the Gösselsdorfer See and the Sonnegger Reservoir. Population According to the 2001 census, 19.8% of the population were Carinthian Slovenes Carinthian Slovenes or Carinthian Slovenians ( sl, Koroški Slovenci; german: Kärntner Slowenen) are the indigenous minority of Slovene ethnicity, living within borders of the Austrian state of Carinthia, neighboring Slovenia. Their status of t .... Gallery Image:Tichoja, kerk foto2 2011-07-21 13.49.jpg, Tichoja, church Image:Sittersdorf Kirche Heilige Helena 17112006 02.jpg, St. Helena, church Image:Sittersdorf Altendorf Bildstock und Filialkirche Heiliger Andreas 08122007 05.jpg, Altendorf, Wayside shrine and succursal church St. Andrew Imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eberndorf
Eberndorf ( sl, Dobrla vas, archaically ''Dobrla ves'') is a market town of the Völkermarkt District in Carinthia, Austria. Geography It is the main settlement in the Jaun (''Podjuna'') Valley of the Drava River, east of the Carinthian capital Klagenfurt. Here the road from Völkermarkt leads uphill to the Karawanks mountain range and across the Seebergsattel Pass to Slovenia. The nearby lake Gösselsdorfer See is a popular destination for day-trippers in summer. The municipal area includes the Katastralgemeinden Buchbrunn (''Bukovje''), Gablern (''Lovanke''), Gösselsdorf (''Goselna vas''), Kühnsdorf (''Sinča vas''), Loibegg (''Belovče''), Mittlern (''Metlova''), Mökriach (''Mokrije'') and Pribelsdorf (''Priblja vas''). At the 2001 census 8.6% of the population were Carinthian Slovenes. History In the late 11th century the Aribonid count Kazelin (''Chazelinus'') founded Eberndorf Abbey within the Duchy of Carinthia. Patriarch Ulrich von Aquileia confirmed the estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)