|
Jaso State
Jaso or Jassu, formerly known as Yashogarh was a princely state of the Bundelkhand Agency in British India located in present-day Nagod tehsil, Satna district, Madhya Pradesh. It was surrounded in the north, east and south by Nagod State and in the east by Ajaigarh. History Jaso State was founded in 1732 by Bharti Chand, younger brother of Raja Hrideshah of Panna. Around 1750, it was split into Bandhora and Jaso, being reunited later in the eighteenth century. In 1816 Jaso State became a British protectorate. The last ruler of the state signed the accession of Jaso State to the Indian Union in 1948. Rulers Rulers bore the title of Diwan * 1732 – 1750 Bharti Chand * 1750 – 1775 Hari Singh * 1775 – 1786 Chet Singh * 1786 – 1830 Murat Singh * 1830 – 1860 Ishri Singh (b. ... – d. 1860) * 1860 – 1865 Ram Singh (b. ... – d. 1860) * 1860 – 1869 Shatarjit Singh (adopted son and descendant of Dewan Chet Singh) * 1869 – 1876 Bhopal Singh * 1876 – 1888 Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
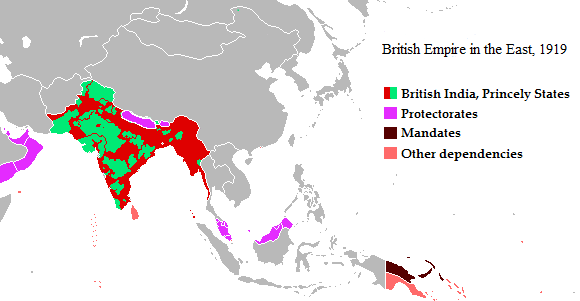
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajputs
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Rajput covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities. Over time, the Rajputs emerged as a social class comprising people from a variety of ethnic and geographical backgrounds. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the membership of this class became largely hereditary, although new claims to Rajput status continued to be made in the later centuries. Several Rajput-ruled kingdoms played a significant role in many regions of central and northern India from seventh century onwards. The Rajput population and the former Rajput states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Madhya Pradesh
The history of the Indian state Madhya Pradesh is divided into three periods - the ancient period, the medieval period and modern period. During the ancient period, the region was dominated by the Nanda Empire, the Maurya Empire, and the Gupta Empire. The medieval period saw the rise of Rajput clans including the Paramara and Chandela clans, the latter is known for constructing the temples of Khajuraho. The Malwa Sultanate also ruled during this period. The modern period in Madhya Pradesh saw the rise of the Mughal and Maratha empires, and later, the British Empire. The British princely states of Gwalior, Indore, and Bhopal, were a part of modern Madhya Pradesh. The British rule continued until the middle of the 20th century, when India gained independence in 1947. The state of Madhya Pradesh was formed in 1956, and Chhattisgarh was carved out from the state in 2000. Ancient History The Bhimbetka caves show evidence of paleolithic settlements in present-day Madhya Prades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of India
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large ( Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates and jagirs. In 1947, princely states covered 40% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Indian Princely States
Before the Partition of India in 1947, about 584 princely states, also called "native states", existed in India, which were not fully and formally part of British India, the parts of the Indian subcontinent which had not been conquered or annexed by the British but under indirect rule, subject to subsidiary alliances. Things moved quickly after the partition of British India in 1947. By the end of 1949, all of the states had chosen to accede to one of the newly independent states of India or Pakistan or else had been conquered and annexed. Outline In principle, the princely states had internal autonomy, while by treaty the British Crown had suzerainty and was responsible for the states' external affairs. In practice, while the states were indeed ruled by potentates with a variety of titles, such as Maharaja, Raja, Nizam, Raje, Deshmukh, Nawab, Mirza, Baig, Chhatrapati, Khan, Thakur Sahab, Darbar saheb or specially Jam for Jadeja/Samma, the British still had considerable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagelkhand Agency
The Bagelkhand Agency was a British political unit which managed the relations of the British with a number of autonomous princely states existing outside British India, namely Rewa and 11 minor states, of which the most prominent were Maihar, Nagod and Sohawal. Other principalities included Jaso, Kothi, Baraundha (aka Patharkachhar) as well as the Kalinjar Chaubes, consisting of the princely estates of Paldeo, Kamta-Rajaula, Taraon, Pahra and Bhaisaunda.Malleson, G. B. ''An historical sketch of the native states of India,'' London 1875, Reprint Delhi 1984 History The Agency was established in March 1871 and was named after the Bagelkhand region. From 1871 to 1933 the Agency was under the political supervision of the Governor-General of India's Agent for Central India, and under the direct supervision of a political Agent residing ordinarily at Satna The total area was , and the population in 1901 was 1,555,024, a decrease of 11% over the previous census ten years before, large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewan
''Dewan'' (also known as ''diwan'', sometimes spelled ''devan'' or ''divan'') designated a powerful government official, minister, or ruler. A ''dewan'' was the head of a state institution of the same name (see Divan). Diwans belonged to the elite families in the history of Mughal and post-Mughal India and held high posts within the government. Etymology The word is Persian in origin and was loaned into Arabic. The original meaning was "bundle (of written sheets)", hence "book", especially "book of accounts," and hence "office of accounts," "custom house," "council chamber". The meaning of the word, ''divan'' "long, cushioned seat" is due to such seats having been found along the walls in Middle Eastern council chambers. It is a common surname among Sikhs in Punjab. Council The word first appears under the Caliphate of Omar I (A.D. 634–644). As the Caliphate state became more complicated, the term was extended over all the government bureaus. The ''divan of the Sublime P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and Newfoundland were afforded the designation in September of that same year, followed by South Africa in 1910. These were the only British possessions recognized as Dominions at the outbreak of war. In 1922, the Irish Free State was given Dominion status, followed by the short-lived inclusion of India and Pakistan in 1947 (although India was officially recognized as the Union of India). The Union of India became the Republic of India in 1950, while the became the Islamic Republic of Pakistan in 1956.” was an independent dominion in the British Commonwealth of Nations existing between 15 August 1947 and 26 January 1950. Until its independence, India had been ruled as an informal empire by the United Kingdom. The empire, also called the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajaigarh State
Ajaigarh State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The state was ruled by Bundela clan of Rajput. The state was founded in 1785 and its capital was located in Ajaigarh, Madhya Pradesh Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco .... Ajaigarh's last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1950. References Sources * Princely states of Bundelkhand 1950 disestablishments in India Rajputs Panna district {{India-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the the Crown, British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They Instrument of accession, acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagod State
Nagod State (also known as 'Nagode' and 'Nagodh') was a princely state of colonial India, located in modern Satna district of Madhya Pradesh. The state was known as 'Unchahara' from the name of Unchehara its original capital until the 18th century. History In 1344, the city of Uchchakalpa, present-day Unchahara, was founded by Rajput Raja Veerraj Judeo when he seized the fort of Naro from "the others". In 1720 the state was renamed Nagod after its new capital. In 1807 Nagod was a tributary to Panna and was included in the sanad granted to that state. In 1809, however, Lal Sheoraj Singh was recognized and confirmed in his territory by a separate sanad granted to him. Nagod State became a British protectorate after the treaty of Bassein in 1820. Raja Balbhadra Singh was deposed in 1831 for murdering his brother. The state fell into debt and in 1844 the administration was taken over by the British owing to economic mismanagement. The ruler was loyal during the Indian Mutiny in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |