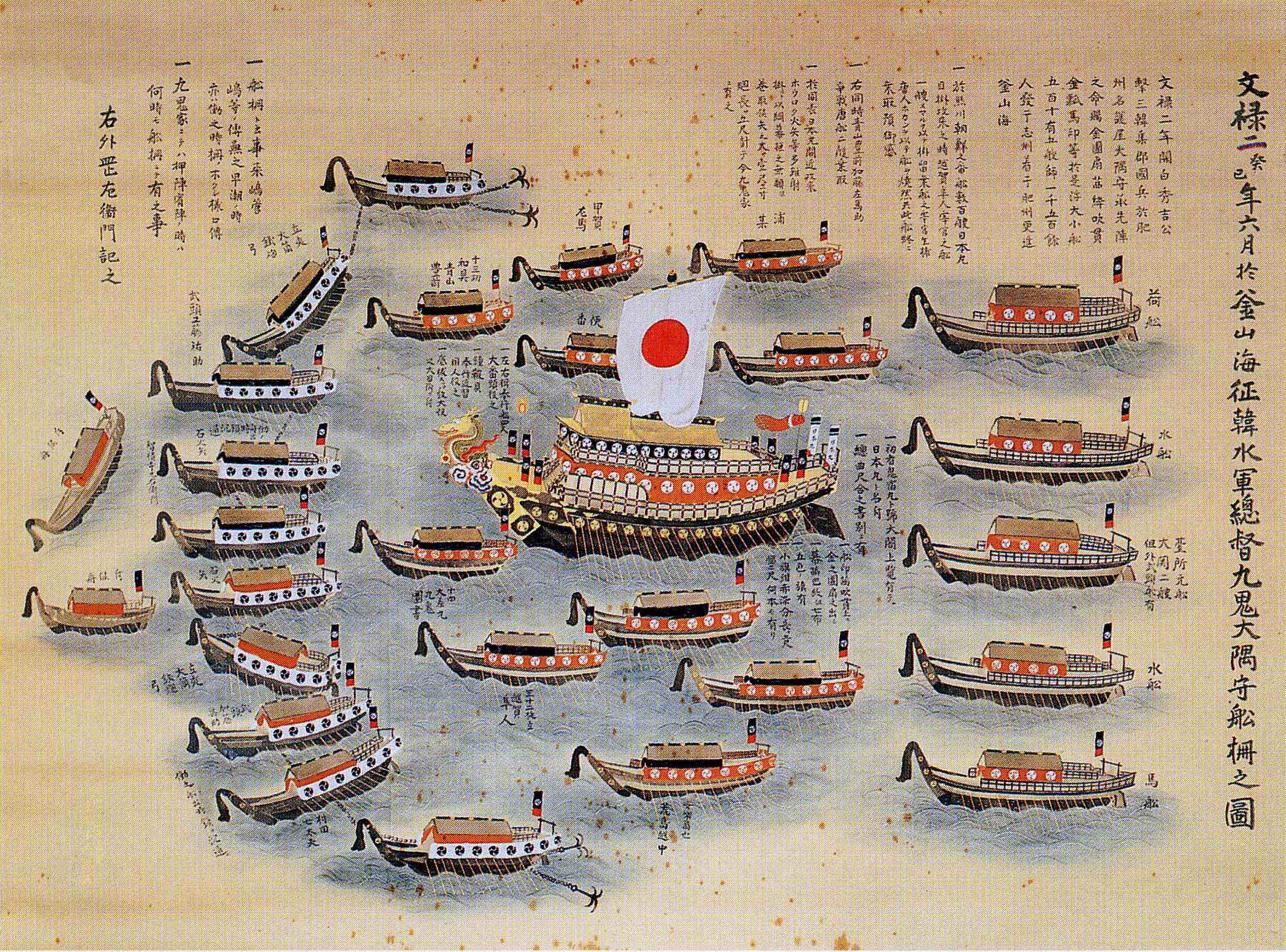
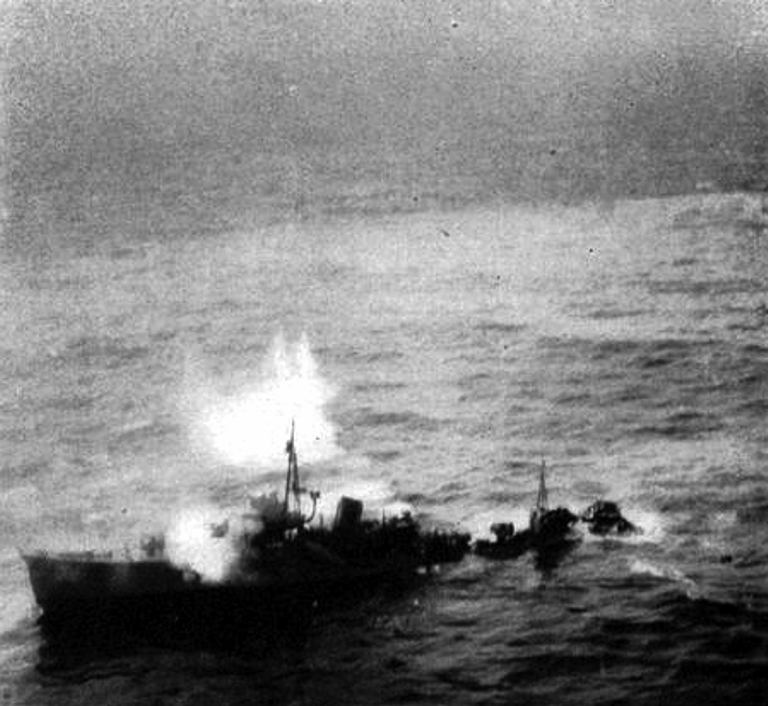
|
Japanese Submarine Tender Jingei
,Nelson. ''Japanese-English Character Dictionary''. pages 872, 984 was the lead vessel of the s operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, from the 1920s through World War II. She was the first purpose-built submarine tender in the Imperial Japanese Navy.Jentsura, ''Warships of the Imperial Japanese Navy'', p. 237 Background Under the Eight-eight fleet plan, the Imperial Japanese Navy planned to acquire 100 submarines for long-distance scouting operations, which would also be used to conduct attrition warfare against any enemy fleet approaching Japan. ''Jingei'' was intended to serve as a flagship for the Submarine Division Commander and as a depot ship for the nine submarines in a submarine division. Initially, ''Jingei'' was planned as a 14,500-ton vessel; however, her specifications were scaled down to 8,500-tons due to restrictions imposed by the Washington Naval Treaty. Design ''Jingei'' was built by Mitsubishi Yards in Nagasaki, and the contractor was given an unusually free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ensign Of Japan
The national flag of Japan is a rectangular white banner bearing a crimson-red circle at its center. This flag is officially called the , but is more commonly known in Japan as the . It embodies the country's sobriquet: the Land of the Rising Sun. The ''Nisshoki'' flag is designated as the national flag in the Act on National Flag and Anthem, which was promulgated and became effective on 13 August 1999. Although no earlier legislation had specified a national flag, the sun-disc flag had already become the ''de facto'' national flag of Japan. Two proclamations issued in 1870 by the Daijō-kan, the governmental body of the early Meiji period, each had a provision for a design of the national flag. A sun-disc flag was adopted as the national flag for merchant ships under Proclamation No. 57 of Meiji 3 (issued on 27 February 1870), and as the national flag used by the Navy under Proclamation No. 651 of Meiji 3 (issued on 27 October 1870). Use of the ''Hinomaru'' was severely restric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomozuru Incident
was one of four s of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). It capsized in a storm on 12 March 1934, shortly after its completion. This incident forced the IJN to review the stability of all recently completed, under construction and planned ships. It was salvaged and put back into service after extensive modifications. During World War II, the ''Tomozuru'' fought in the Battle of the Philippines and in the Dutch East Indies campaign as an escort, and it continued to play that role for the rest of the war. The ''Tomozuru'' Incident In February 1934, ''Tomozuru'' joined the 21st Torpedo Flotilla at Sasebo. *01:00, 12 March 1934, ''Tomozuru'' departed from Sasebo for a night torpedo exercise with the light cruiser and torpedo boat . *03:25, because of stormy weather, ''Tatsuta'' ordered the other two boats to return to base. *03:58, radio contact lost with ''Tomozuru''. Possible loss of power or radio capability. *04:12, ''Tomozuru''s lights disappeared, presumably this is when it c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Fleet (Imperial Japanese Navy)
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) established during World War II. History The 8th Fleet was established on 14 July 1942 and was given an operational title of Outer South Seas Force, which reflected its mission of guarding conquests in the South Pacific. In this respect it essentially replaced the 4th Fleet, which was then given an operation title of Outer South Seas Force, and was primarily tasked with defending the Mandates. Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa was appointed as the first commander of the 8th Fleet. Initially, the 8th Fleet included the ''Takao''-class heavy cruiser ''Chōkai'' as its flagship, Cruiser Division 6 (CruDiv6) with the entire ''Furutaka'' and ''Aoba'' classes of four older and somewhat smaller heavy cruisers ( ''Aoba'', ''Kinugasa'', ''Kako'' and ''Furutaka''), Cruiser Division 18 (CruDiv18) with three old light cruisers ( ''Tenryū'', ''Tatsuta'' and ''Yūbari''), eight old destroyers, and Submarine Squadron 7 (SubDiv7) wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilian personnel) often use the shortened name, Kwaj . The total land area of the atoll amounts to just over . It lies in the Ralik Chain, southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii. The US Navy has hosted a naval base on Kwajalein Island since World War II. It was the final resting place of the German cruiser '' Prinz Eugen'' after it survived the Operation Crossroads nuclear test in 1946. In the late 1950s, the US Army took over the base as part of their Nike Zeus anti-ballistic missile efforts, and since then the atoll has been widely used for missile tests of all sorts. Today it is part of the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site, with various radars, tracking cameras, missile launchers, and many support systems spread across many islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wake Island
The Battle of Wake Island was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on Wake Island. The assault began simultaneously with the attack on Pearl Harbor naval and air bases in Hawaii on the morning of 8 December 1941 (7 December in Hawaii), and ended on 23 December, with the surrender of American forces to the Empire of Japan. It was fought on and around the atoll formed by Wake Island and its minor islets of Peale and Wilkes Islands by the air, land, and naval forces of the Japanese Empire against those of the United States, with Marines playing a prominent role on both sides. The island was held by the Japanese for the duration of the Pacific War theater of World War II; the remaining Japanese garrison on the island surrendered to a detachment of United States Marines on 4 September 1945, after the earlier surrender on 2 September 1945 on the battleship in Tokyo Bay to General Douglas MacArthur. Prelude In January 1941, the United States Navy constructed a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawanishi E7K
The Kawanishi E7K was a Japanese three-seat reconnaissance seaplane mainly in use during the 1930s. It was allocated the reporting name Alf by the Allies of World War II. Design and development In 1932 the Imperial Japanese Navy requested the Kawanishi Aircraft Company produce a replacement for the company's Kawanishi E5K. The resulting design, designated the Kawanishi E7K1, was an equal span biplane powered by a 462 kW (620 hp) Hiro Type 91 W-12 liquid-cooled inline engine. The first aircraft flew on 6 February 1933 and was handed over to the navy for trials three months later. It was flown in competition with the Aichi AB-6 which was designed to meet the same 7-''Shi'' requirement. The E7K1 was ordered into production as the Navy Type 94 Reconnaissance Seaplane () and entered service in early 1935. It became a popular aircraft, but was hindered by the unreliability of the Hiro engine. Later production E7K1s were fitted with a more powerful version of the Hiro 91, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Fleet (Imperial Japanese Navy)
The 4th Fleet was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The Fourth Fleet designation was used during three separate periods. The initial designation was for a group of ships that were assigned to work together during the Russo-Japanese conflict and the period of its immediate aftermath. The second time the designation was used was during the Sino-Japanese conflict, and the third time was as a South Pacific area of command during the middle of the Pacific War. History Russo-Japanese War First established on June 14, 1905, the 4th Fleet was created after the Battle of Tsushima in the Russo-Japanese War specifically to support and cover the landings of Japanese forces in Sakhalin. Afterwards, it was sent to the United States with the Japanese delegation negotiating the Treaty of Portsmouth ending the war, and was disbanded on December 20, 1905. The Fourth Fleet incident The Fourth Fleet was temporarily resurrected during a war game exercise executed in 1935, playing the role of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
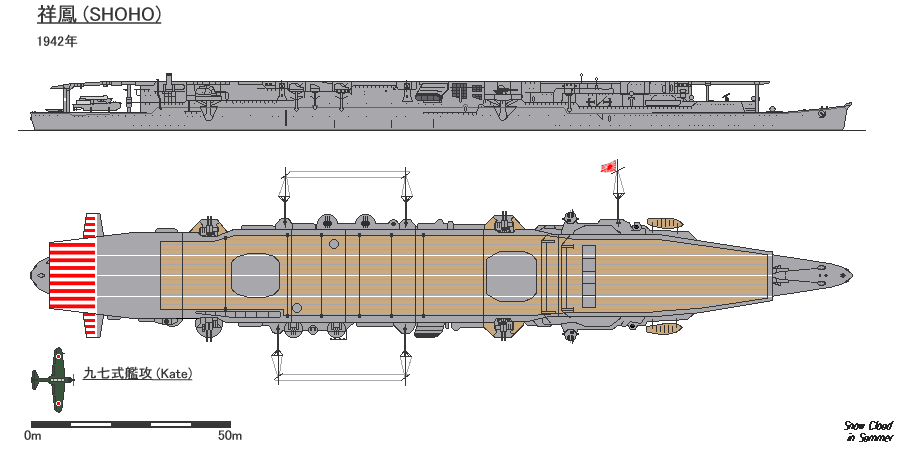
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Shōhō
''Shōhō'' (Japanese: 祥鳳, "Auspicious Phoenix" or "Happy Phoenix") was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Originally built as the submarine support ship ''Tsurugizaki'' in the late 1930s, she was converted before the Pacific War into an aircraft carrier and renamed. Completed in early 1942, the ship supported the invasion forces in Operation MO, the invasion of Port Moresby, New Guinea, and was sunk by American carrier aircraft on her first combat operation during the Battle of the Coral Sea on 7 May. ''Shōhō'' was the first Japanese aircraft carrier to be sunk during World War II. Design, construction and conversion ''Shōhō'' and her sister were designed to be easily modified as an oil tanker, submarine tender, or aircraft carrier as needed. ''Shōhō'' was laid down by the Yokosuka Naval Arsenal on 3 December 1934 as the submarine tender ''Tsurugizaki''. She was launched on 1 June 1935 and completed on 15 January 1939. Not long after the ship w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Zuihō
was the name ship of her class of two light aircraft carriers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Originally laid down as the submarine tender ''Takasaki'', she was renamed and converted while under construction into an aircraft carrier. The ship was completed during the first year of World War II and played a minor role in the Battle of Midway in mid-1942. She participated in the Guadalcanal Campaign during the rest of 1942. Significantly damaged during the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands in that campaign, after repairs ''Zuihō'' covered the evacuation of Japanese forces from Guadalcanal in early 1943. Her aircraft were disembarked several times in mid- to late-1943 and used from land bases in a series of battles in the Southwest Pacific. ''Zuihō'' participated in the Battles of the Philippine Sea and Leyte Gulf in mid-1944. In this last engagement, she mainly served as a decoy for the main striking forces and was sunk by American aircraft. In between battles, the ship se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. Some Chinese historians believe that the Japanese invasion of Manchuria on 18 September 1931 marks the start of the war. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia. China fought Japan with aid from Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States. After the Japanese attacks on Malaya and Pearl Harbor in 1941, the war merged with other conflicts which are generally categorized under those conflicts of World War II a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |