|
Japanese Destroyer Okinami
was a of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Design and description The ''Yūgumo'' class was a repeat of the preceding with minor improvements that increased their anti-aircraft capabilities. Their crew numbered 228 officers and enlisted men. The ships measured overall, with a beam of and a draft of . They displaced at standard load and at deep load.Whitley, p. 203 The ships had two Kampon geared steam turbines, each driving one propeller shaft, using steam provided by three Kampon water-tube boilers. The turbines were rated at a total of for a designed speed of . The main armament of the ''Yūgumo'' class consisted of six Type 3 guns in three twin-gun turrets, one superfiring pair aft and one turret forward of the superstructure. The guns were able to elevate up to 75° to increase their ability against aircraft, but their slow rate of fire, slow traversing speed, and the lack of any sort of high-angle fire-control system meant that they were virtually useless as anti-ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-tube Boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam passes through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater) to become superheated. Superheated steam is defined as steam that is heated above the boiling point at a given pressure. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines, since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower drum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
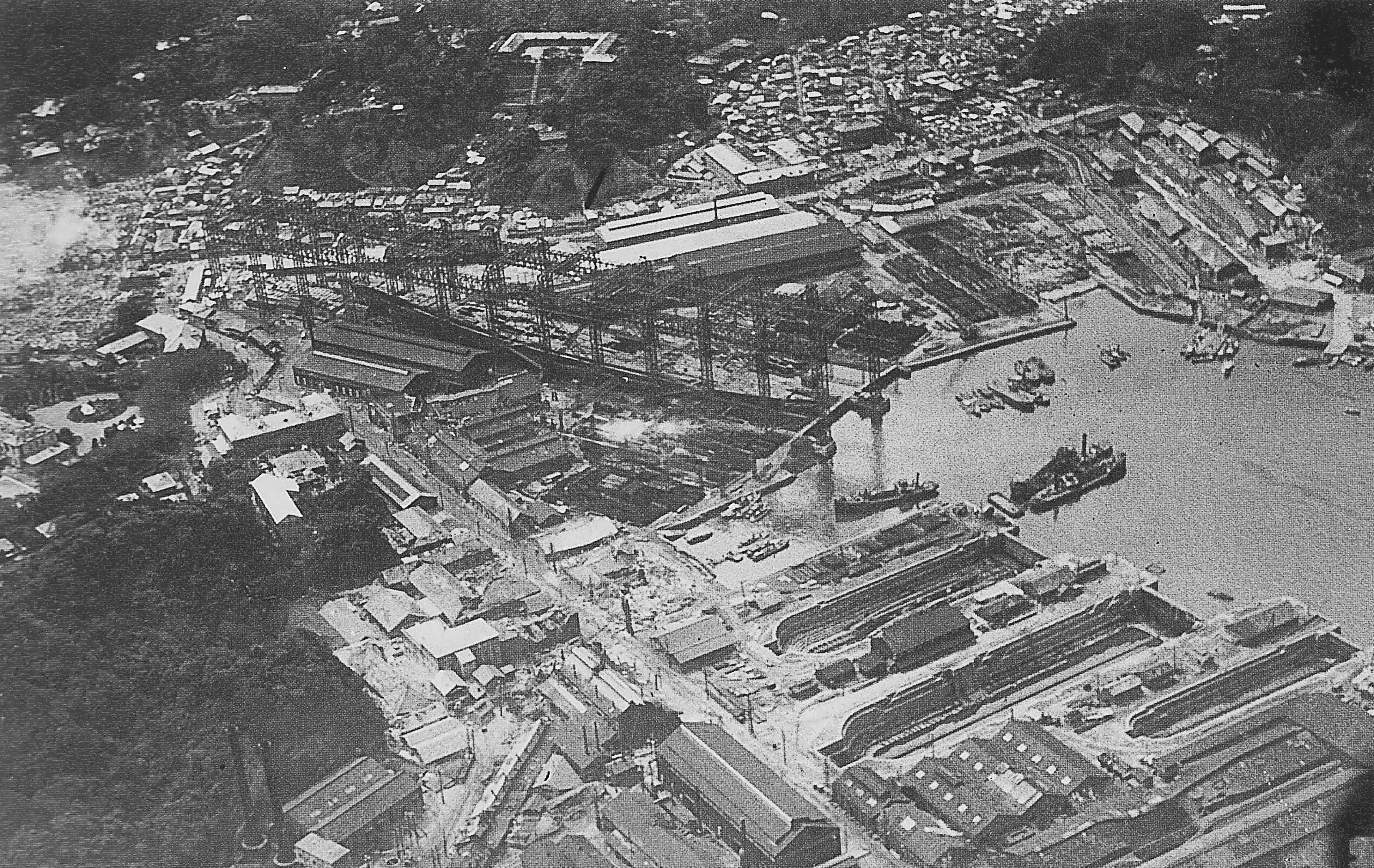
Yokosuka Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, and was located at Yokosuka, Kanagawa prefecture on Tokyo Bay, south of Yokohama. History In 1866, the Tokugawa shogunate government established the ''Yokosuka Seisakusho'', a military arsenal and naval base, with the help of foreign engineers, including the French naval architect Léonce Verny. The new facility was intended to produce modern, western-style warships and equipment for the Tokugawa navy. The construction of the arsenal was an important first step for the modernization of Japan's industry. Modern buildings, an aqueduct, foundry, brick factories, technical schools to train Japanese technicians were established. After the Boshin War and the Meiji Restoration, the new Meiji government took over control of the facility in 1871, renaming it the ''Yokosuka Zosenjo'' (Yokosuka Shipyards). The first dry dock was opened in 1871, and is still in operation today. Japan's first d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Infantry Regiment (Imperial Japanese Army)
The was an infantry regiment in the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA). Its call sign and unit code was . The unit was formed in 1884 and based in the city of Toyohashi as a branch of the Nagoya Garrison. Throughout its history, the majority of its soldiers came from the Mikawa region, or eastern Aichi prefecture. The regiment first deployed for the First Sino-Japanese War in 1894. In 1904, it deployed again for the Russo-Japanese War where it fought in several major battles. Between 1928 and 1936, the regiment was deployed to China where it engaged in two military operations in China, though it spent most of the time on garrison and occupation duty. With the start of the Second Sino-Japanese War in the summer of 1937, the regiment participated in the Battle of Shanghai and then participated in the major campaigns of central China. In 1944, the 18th Regiment was sent to the Pacific theater as part of the 29th Division. On the way to Saipan, the transport ship that was carryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Destroyer Asashimo
was a of the Imperial Japanese Navy. She was among the several ships sunk during Operation Ten-Go by attacking US aircraft in 1945. Service career and fate On 29 February 1944, while escorting a large convoy en route to Truk, ''Asashimo'' detected the submarine making a night surface approach on the convoy. ''Rock'' fired a spread of four torpedoes from her stern tubes at the closing ''Asashimo'' without scoring a hit. Illuminated by the destroyer's searchlight, and under fire from the ship's 5-inch (130 mm) guns, ''Rock'' dived. For four hours ''Asashimo'' continued depth charge attacks, without success. That night ''Rock'' surfaced and found that her periscopes were excessively damaged and that her bridge had been riddled with shrapnel. The damage necessitated a return to Pearl Harbor for repairs. Later that night, the busy ''Asashimo'' sank the submarine . Japanese records indicate that one of their convoys, Matsu No. 1, was attacked by a submarine on 29 February 1944 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Trout (SS-202)
USS ''Trout'' (SS-202) was the fifth ''Tambor''-class submarine commissioned in the United States Navy, serving in the Pacific from 1941 to 1944. She received 11 battle stars for World War II service and three Presidential Unit Citations, for her second, third, and fifth war patrols. ''Trout'' also delivered ammunition to the besieged American forces on Corregidor and brought out 20 tons of gold bars and silver pesos from the Philippine currency reserve to Pearl Harbor. During 1941, she was used as a target by a series of tests determining the vulnerability of submarines to depth charge attacks. ''Trout'' is credited with sinking 12 enemy ships for 37,144 tons according to JANAC records. During her first ten war patrols she made 32 torpedo attacks, firing 85 torpedoes, including 34 hits, 5 confirmed premature detonations, 5 confirmed duds, and 25 suspected duds. She was also involved in six battle surface actions and was attacked with depth charges eight times. She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakito Maru
''Sakito Maru'' ( ja, 崎戸丸) was a 7,126-ton Japanese troop transport that operated during World War II. She was sunk on 1 March 1944 with great loss of life. Construction ''Sakito Maru'' was built in 1939 by the Mitsubishi Zosen Kaisha in Nagasaki for the Nippon Yusen shipping company. She was the lead ship of seven ships of the ''Sakito Maru''-class of high speed transports: ''Sakito Maru'' (崎戸丸), ''Sanuki Maru'' (讃岐丸), Sado Maru'' (佐渡丸), ''Sagami Maru'' (相模丸), '' Sagara Maru'' (相良丸), ''Sasako Maru'' (笹子丸), and ''Sakura Maru'' (佐倉丸). Early service On the foggy morning of 4 September 1940, ''Sakito Maru'' collided with the 1,514- gross register ton fishing barge ''Olympic II'', which was anchored on the Horseshoe Kelp fishing bank at the entrance of Los Angeles Harbor off Los Angeles, California. ''Olympic II'' sank in of water with the loss of seven or eight lives. On 24 September 1941, ''Sakito Maru'' took the Japanese car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic center of the U.S.); its capital Hagåtña (144°45'00"E) lies further west than Melbourne, Australia (144°57'47"E). In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. People born on Guam are American citizens but have no vote in the United States presidential elections while residing on Guam and Guam delegates to the United States House of Representatives have no vote on the floor. Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamoru, historically known as the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples of Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Taiwan, Micronesia, and Polynesia. As of 2022, Guam's population is 168, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Census Bureau, the population of Saipan was 43,385, a decline of 10% from its 2010 count of 48,220. The legislative and executive branches of Commonwealth government are located in the village of Capitol Hill, Saipan, Capitol Hill on the island while the judicial branch is headquartered in the village of Susupe. Since the entire island is organized as a single municipality, most publications designate Saipan as the Commonwealth's capital. As of 2015, Saipan's mayor is David M. Apatang and the governor of the Northern Mariana Islands is Ralph Torres. History Prehistory Traces of human settlements on Saipan have been found by archaeologists ranging over 4,000 years, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aircraft Gun
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
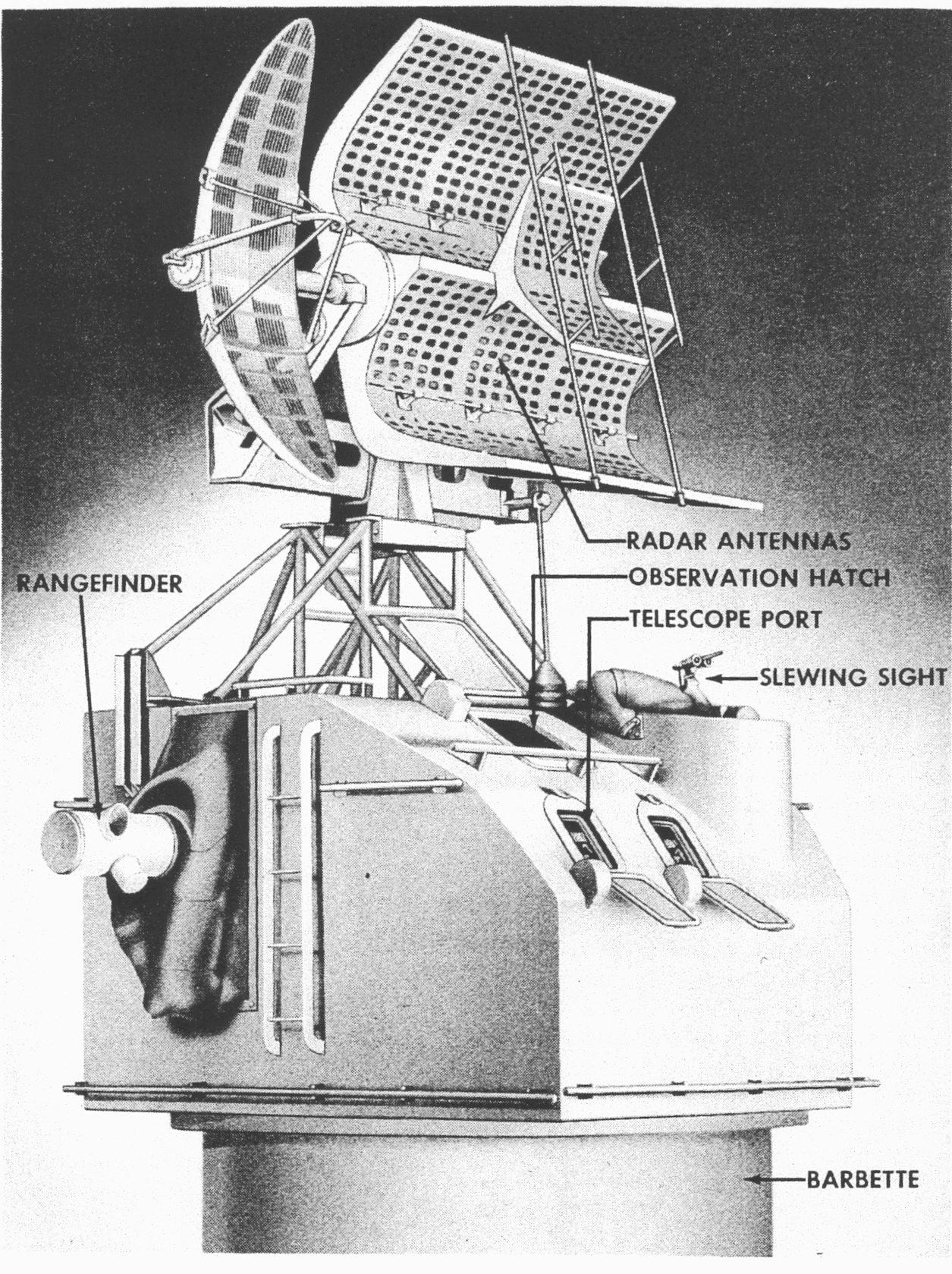
Ship Gun Fire-control System
Ship gun fire-control systems (GFCS) are analogue fire-control systems that were used aboard naval warships prior to modern electronic computerized systems, to control targeting of guns against surface ships, aircraft, and shore targets, with either optical or radar sighting. Most US ships that are destroyers or larger (but not destroyer escorts except Brooke class DEG's later designated FFG's or escort carriers) employed gun fire-control systems for and larger guns, up to battleships, such as . Beginning with ships built in the 1960s, warship guns were largely operated by computerized systems, i.e. systems that were controlled by electronic computers, which were integrated with the ship's missile fire-control systems and other ship sensors. As technology advanced, many of these functions were eventually handled fully by central electronic computers. The major components of a gun fire-control system are a human-controlled director, along with or later replaced by radar or te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |