|
January 2037 Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse will take place on Saturday, January 31, 2037. The Moon will be plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 3 minutes 41 seconds, in a moderately deep total eclipse which will see the Moon 20.74% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may be stained a deep red colour for observers in north and west North America, most of Asia, Australia and New Zealand. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 17 minutes 28 seconds in total. It occurs during a supermoon (perigee), and blue moon (second full moon of month), just like the eclipse of January 2018 lunar eclipse, January 31, 2018, one metonic cycle (19 years) previous. Visibility Related lunar eclipses Lunar year series See also *List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses Notes External links * 21st-century lunar eclipses, 2037-01 Future lunar eclipses, 2037-01 2037 in science {{lunar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse Chart Close-2037Jan31
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon". Lunar may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * Lunar (series), ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games * Lunar (song), "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta * "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album ''Prior to the Fire'' * Lunars, a fictional race in the series ''The Lunar Chronicles'' by Marissa Meyer Other uses * Lunar Magic, Super Mario World level editor * Lunar Design, or LUNAR, a San Francisco-based design consultancy * Hasselblad Lunar, a digital camera * Lunar, a brandname of Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate, a birth control pill * Lunar C (Jake Brook, born 1990), English rapper See also * * * Lunar calendar, based upon the monthly cycles of the Moon's phase ** Lunar day, in such calendars ** Lunar month, in such calendars * Moon (other) * Luna (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saros Cycle
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, approximately 6585.3211 days, or 18 years, 10, 11, or 12 days (depending on the number of leap years), and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. One saros period after an eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and Moon return to approximately the same relative geometry, a near straight line, and a nearly identical eclipse will occur, in what is referred to as an eclipse cycle. A sar is one half of a saros. A series of eclipses that are separated by one saros is called a ''saros series''. It corresponds to: *6,585.321347 solar days *18.029 years *223 synodic months *241.999 draconic months *18.999 eclipse years (38 eclipse seasons) *238.992 anomalistic months The 19 eclipse years means that if there is a solar eclipse (or lunar eclipse), then after one saros a new moon will take place at the same node of the orbit of the Moon, and under these circumstances another eclipse can occur. History The earliest d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma (eclipse)
Gamma (denoted as γ) of an eclipse describes how centrally the shadow of the Moon or Earth strikes the other body. This distance, measured at the moment when the axis of the shadow cone passes closest to the center of the Earth or Moon, is stated as a fraction of the equatorial radius of the Earth or Moon. Sign The sign of gamma defines, for a solar eclipse, if the axis of the shadow passes north or south of the center of the Earth; a positive value means north. The Earth is defined as that half which is exposed to the Sun (this changes with the seasons and is not related directly to the Earth's poles or equator; thus, the Earth's center is wherever the Sun is directly overhead). For a lunar eclipse, it defines whether the axis of the Earth's shadow passes north or south of the Moon; a positive value means south. Gamma changes monotonically throughout any single saros series. The change in gamma is larger when Earth is near its aphelion (June to July) than when it is near pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude Of Eclipse
The magnitude of eclipse is the fraction of the angular diameter of a celestial body being eclipsed. This applies to all celestial eclipses. The magnitude of a partial or annular solar eclipse is always between 0.0 and 1.0, while the magnitude of a total solar eclipse is always greater than or equal to 1.0. This measure is strictly a ratio of diameters and should not be confused with the covered fraction of the apparent area (disk) of the eclipsed body. Neither should it be confused with the astronomical magnitude scale of apparent brightness. Effect of the magnitude on a solar eclipse The apparent sizes of the Moon and Sun are both approximately 0.5°, or 30', but both vary because the distance between Earth and Moon varies. (The distance between Earth and Sun also varies, but the effect is slight in comparison.) In an annular solar eclipse, the magnitude of the eclipse is the ratio between the apparent angular diameters of the Moon and that of the Sun during the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timing
Timing is the tracking or planning of the spacing of events in time. It may refer to: * Timekeeping, the process of measuring the passage of time * Synchronization, controlling the timing of a process relative to another process * Time metrology, the measurement of time Timing in different fields * Timing (comedy), use of rhythm, tempo and pausing to enhance comedy and humour * Timing (linguistics), rhythmic division of time into equal portions by a language * Timing (music), ability to "keep time" accurately and to synchronise to an ensemble * Color timing, photochemical process of altering and enhancing the color of an image * Ignition timing, timing of piston and crankshaft so that a spark will occur near the end of the compression stroke * Market timing, by attempting to predict future market price movements * Memory timings (or RAM timings), measure of the performance of DRAM memory * Valve timing In a piston engine, the valve timing is the precise timing of the opening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can happen only on the night of a full moon when the Moon is near either lunar node. The type and length of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to the lunar node. When the moon is totally eclipsed by the Earth, it takes on a reddish color that is caused by the planet when it completely blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon surface, as only the light reflected from the lunar surface has been refracted by Earth's atmosphere. This light appears reddish due to the Rayleigh scattering of blue light, the same reason sunrise and sunsets are more orange than during the day. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermoon
A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon that nearly coincides with perigee—the closest that the Moon comes to the Earth in its elliptic orbit—resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual apparent size of the lunar disk as viewed from Earth. The technical name is a perigee syzygy (of the Earth–Moon–Sun system) or a full (or new) Moon around perigee. Because the term ''supermoon'' is astrological in origin, it has no precise astronomical definition. The real association of the Moon with both oceanic and crustal tides has led to claims that the supermoon phenomenon may be associated with increased risk of events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, but no such link has been found. The opposite phenomenon, an apogee syzygy or a full (or new) Moon around apogee, has been called a micromoon. Definitions The term ''supermoon'' is attributed to astrologer Richard Nolle ''while reading "Strategic Role Of Perigean spring tides in Nautical History and Coastal flooding"'' publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g., f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Moon
A blue moon is an additional full moon that appears in a subdivision of a year: the third of four full moons in a season. The phrase in modern usage has nothing to do with the actual color of the Moon, although a visually blue Moon (the Moon appearing with a bluish tinge) may occur under certain atmospheric conditions—for instance, if volcanic eruptions or fires release particles in the atmosphere of just the right size to preferentially scatter red light. Definition The term has traditionally, in the ''Maine Farmer's Almanac'', referred to an "extra" full moon, where a year which usually has 12 full moons has 13 instead. The "blue moon" reference is applied to the third full moon in a season with four full moons, thus correcting the timing of the last month of a season that would have otherwise been expected too early. This happens every two to three years (seven times in the Metonic cycle of 19 years). The author of a March 1946 article in ''Sky & Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
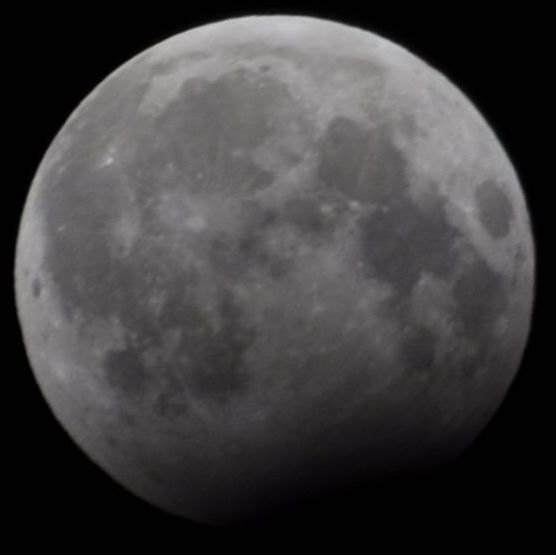
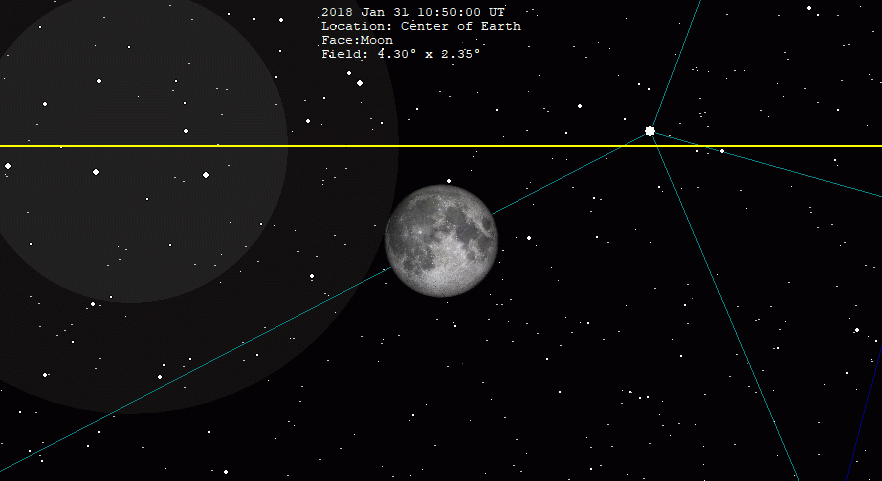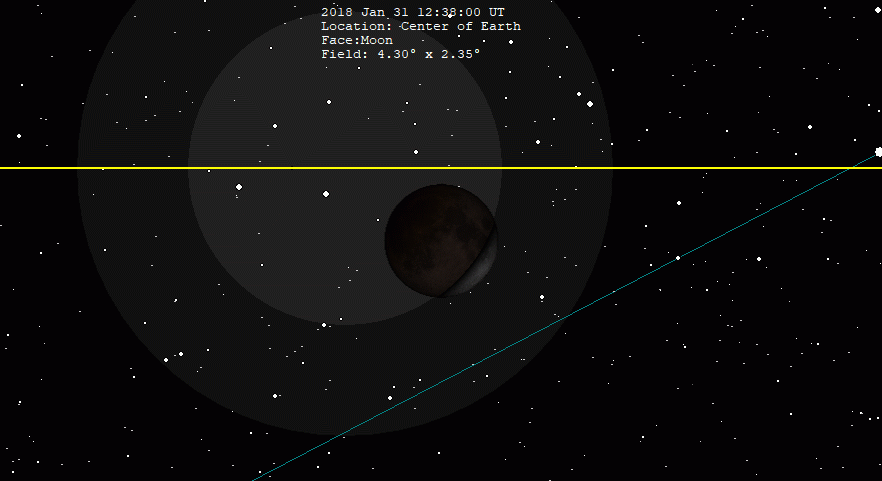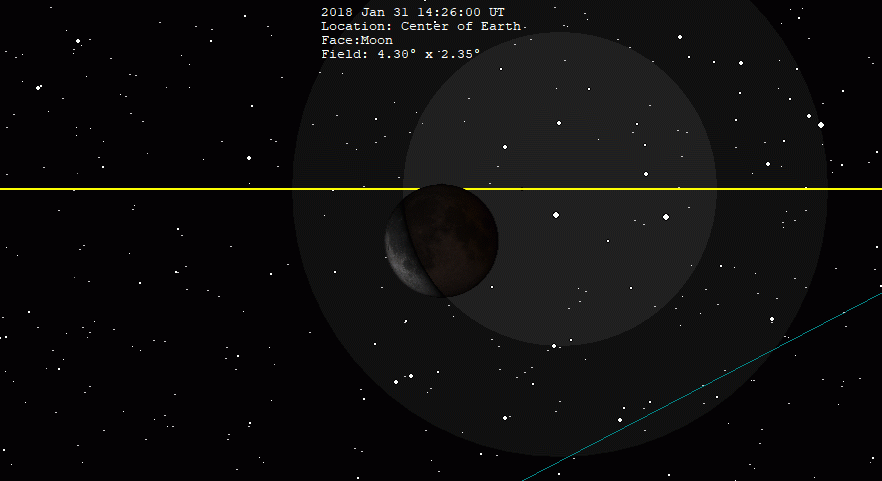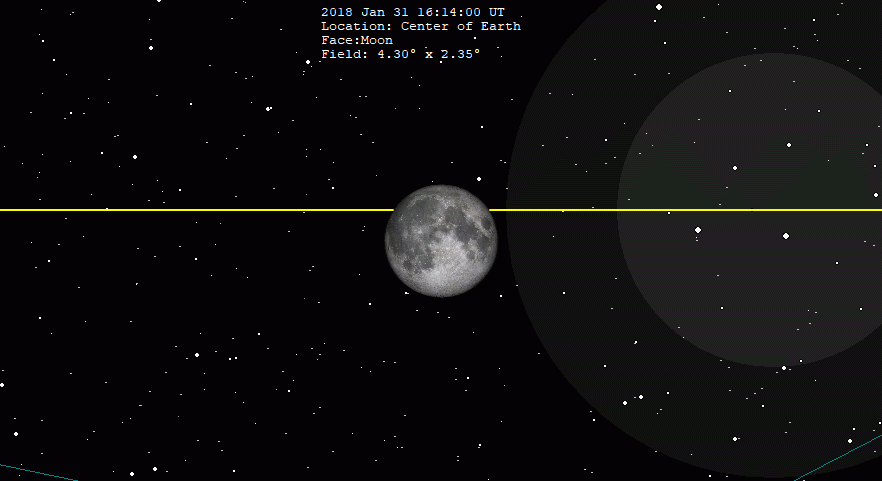
January 2018 Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 31 January 2018. The Moon was near its perigee on 30 January and as such may be described as a "supermoon", when the Moon's distance from the Earth is less than 360,000 km (223,694 miles). The previous supermoon lunar eclipse was in September 2015. During the total lunar eclipse of Wednesday, 31 January 2018, the Moon was 360,202 km (only 202 km to be a Super Full Moon) (223,819 mi) from the Earth. A blue moon occurs because there are 2 full moons in the same calendar month, or if there are 4 full moons in the same season (third of four is blue moon). As this supermoon was also a blue moon (the second full moon in a calendar month), it was referred to as a "super blue blood moon"; "blood" refers to the typical red color of the Moon during a total lunar eclipse. The 31 January, 2018 lunar event was called 'Trifecta'. This coincidence last occurred on 30 December 1982 for the eastern hemisphere, and otherwise before that on 31 March 1866. The ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metonic Cycle
The Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris (from grc, ἐννεακαιδεκαετηρίς, from ἐννεακαίδεκα, "nineteen") is a period of almost exactly 19 years after which the lunar phases recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise observation the Metonic cycle defined as 235 lunar month, synodic months is just 2 hours, 4 minutes and 58 seconds longer than 19 tropical year, tropical years. Meton of Athens, in the 5th century BC, judged the cycle to be a whole number of days, 6,940. Using these whole numbers facilitates the construction of a lunisolar calendar. A tropical year is longer than 12 lunar months and shorter than 13 of them. The arithmetic identity 12×12 + 7×13 = 235 shows that a combination of 12 "short" years (12 months) and 7 "long" years (13 months) will be almost exactly equal to 19 solar years. Application in traditional calendars In the Babylonian calendar, Babylonian and Hebrew calendar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse From Moon-2037Jan31
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon". Lunar may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games * "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta * "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album ''Prior to the Fire'' * Lunars, a fictional race in the series ''The Lunar Chronicles'' by Marissa Meyer Other uses * Lunar Magic, Super Mario World level editor * Lunar Design, or LUNAR, a San Francisco-based design consultancy * Hasselblad Lunar, a digital camera * Lunar, a brandname of Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate, a birth control pill * Lunar C (Jake Brook, born 1990), English rapper See also * * * Lunar calendar, based upon the monthly cycles of the Moon's phase ** Lunar day, in such calendars ** Lunar month, in such calendars * Moon (other) * Luna (other) Luna commonly refers to: * Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin * Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon Luna may also refer to: Places ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)