|
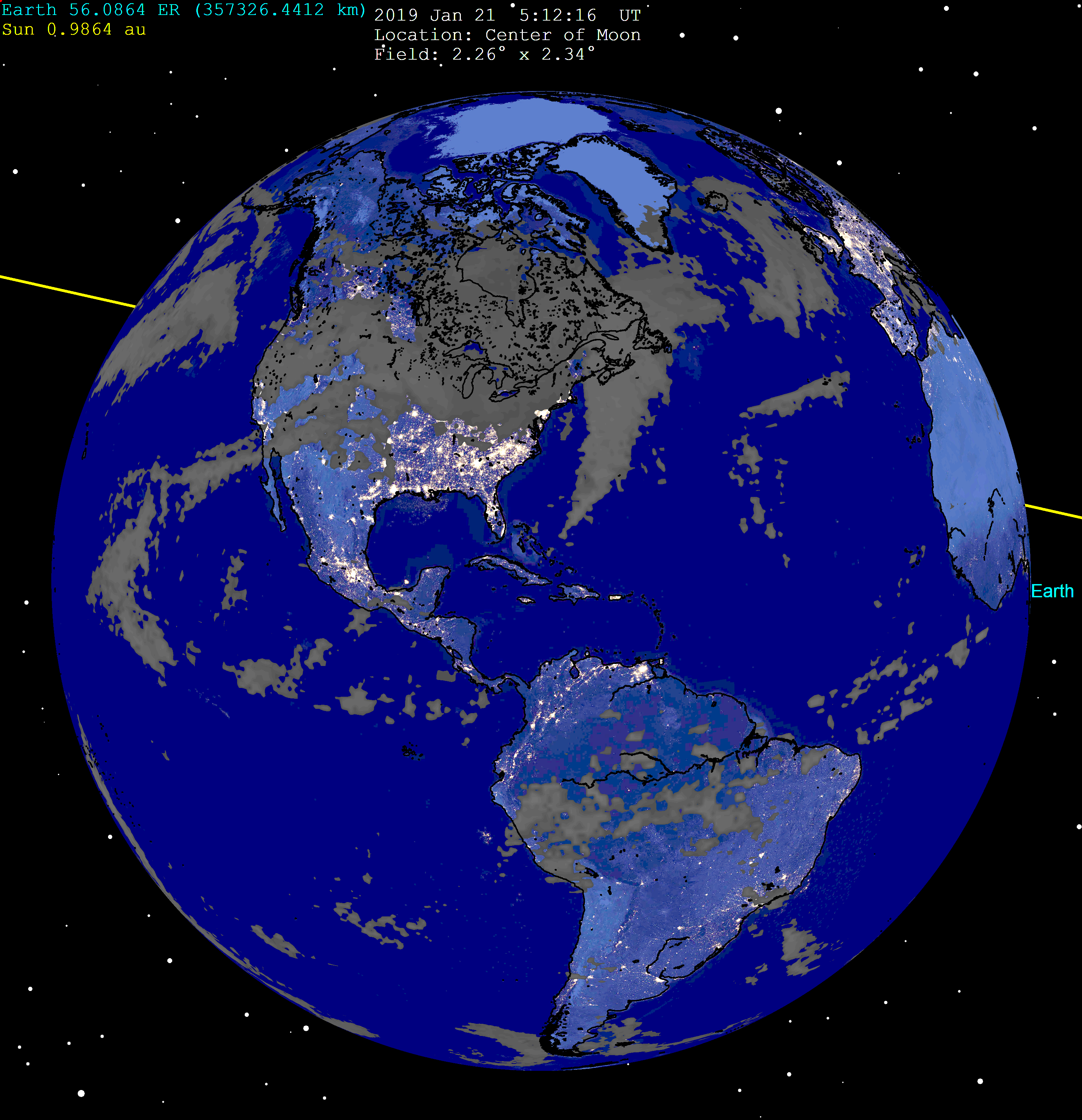
January 2019 Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 21 January 2019 UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). For observers in the Americas, the eclipse took place between the evening of Sunday, 20 January and the early morning hours of Monday, 21 January. For observers in Europe and Africa, the eclipse occurred during the morning of 21 January. The Moon was near its perigee on 21 January and as such can be described as a "supermoon". As this supermoon was also a wolf moon (the first full moon in a calendar year), it was referred to as a "super blood wolf moon"; Lunar eclipse#Blood moon, blood refers to the typical red color of the Moon during a total lunar eclipse. This was the last total lunar eclipse until May 2021 lunar eclipse, May 2021. This was a Super Full Moon because occurred less than a day before perigee and the Moon was less than exactly 360,000 km (223,694 mi). The Griffith Observatory in Los Angeles, California captured video showing a meteor between the size of an acorn and tennis ball i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oria, Italy
Oria (or ''Orra'', la, Uria; grc, Ὑρία, translit=Huría or , '; he, אוריה, translit=uriya) is a town and ''comune'' in the Apulia region, in the province of Brindisi, in southern Italy. It is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Oria. History In classical times, Oria was known as ''Hyria (Uria)'' or ''Hyrium'', a city in ancient Messapii, Messapia and one of the principal Messapian cities. It was just north of the ancient town Manduria, at some distance southwest of Brundisium, and southeast of Taranto, Taras/Taranto, Tarentum; corresponding to the location of the modern town. According to Herodotus (7.170), it was founded by the Messapians (who according to Herodotus were originally Crete, Cretans) sometime after the abortive siege of the Sicanian city Camicus. Messapians were probably of Illyrians, Illyrian origin. Between 217 and 84 BC the city was Mint (coin), minting its own coins. The coins often feature ''Iapagus'', the Iapgyes, Iapygian national hero. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Standard Time
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00). During daylight saving time, a time offset of UTC−07:00 is used. In the United States and Canada, this time zone is generically called the Pacific Time Zone. Specifically, time in this zone is referred to as Pacific Standard Time (PST) when standard time is being observed (early November to mid-March), and Pacific Daylight Time (PDT) when daylight saving time (mid-March to early November) is being observed. In Mexico, the corresponding time zone is known as the ''Zona Noroeste'' (Northwest Zone) and observes the same daylight saving schedule as the U.S. and Canada. The largest city in the Pacific Time Zone is Los Angeles, whose metropolitan area is also the largest in the time zone. The zone is two hours ahead of the Hawaii–Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Further-eastern European Time
UTC+03:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +03:00. In areas using this time offset, the time is three hours later than the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Following the ISO 8601 standard, a time with this offset would be written as, for example, 2019-02-08T23:36:06+03:00. As standard time (year-round) :''Principal cities: Moscow, Saint Petersburg, Doha, Riyadh, Baghdad, Nairobi, Dire Dawa, Addis Ababa, Manama, Sana'a, Aden, Minsk, Kuwait City, Asmara, Antananarivo, Kampala, Amman, Damascus'' Africa East Africa *Comoros *Djibouti *Eritrea *Ethiopia *France **French Southern and Antarctic Lands ***Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean ****Bassas da India, Europa Island and Juan de Nova Island **Mayotte *Kenya *Madagascar *Somalia *Somaliland ''(disputed territory)'' *South Africa **Prince Edward Islands *Tanzania *Uganda Antarctica *Some bases in Antarctica. See also Time in Antarctica **Japan *** Showa Station Asia Arabia Standard Time Arabia Standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad Time
Kaliningrad Time is the time zone two hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+02:00) and one hour behind Moscow Time (MSK−1). It is used in Kaliningrad Oblast. Until 2011, Kaliningrad Time was identical to Eastern European Time (UTC+02:00; UTC+03:00 with daylight saving time). On 27 March 2011, Russia moved to permanent DST, switching Kaliningrad time permanently to UTC+03:00. On 26 October 2014, this law was reversed but daylight saving time was not reintroduced, so Kaliningrad is now permanently set to UTC+02:00. Main cities: * Kaliningrad * Sovetsk * Chernyakhovsk See also * Time in Russia There are eleven time zones in Russia (within its internationally recognized borders), which currently observe times ranging from UTC+02:00 to UTC+12:00. Daylight saving time (DST) has not been used in Russia since 26 October 2014. From 27 March ... References Time zones Time in Russia {{Standard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Time
Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer. A number of African countries use UTC+02:00 all year long, where it is called Central Africa Time (CAT), although Egypt and Libya also use the term ''Eastern European Time''. The most populous city in the Eastern European Time zone is Cairo, with the most populous EET city in Europe being Athens. Usage The following countries, parts of countries, and territories use Eastern European Time all year round: * Egypt, since 21 April 2015; used EEST ( UTC+02:00; UTC+03:00 with daylight saving time) from 1988–2010 and 16 May–26 September 2014. See also Egypt Standard Time. * Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia), since 26 October 2014; also used EET in years 1945 and 1991–2011. See also Kaliningrad Time. * Libya, since 27 October 2013; switched from Central European Time, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Summer Time
Central European Summer Time (CEST), sometimes referred to as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+02:00, which makes it the same as Eastern European Time, Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia. Names Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST), Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT), and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet). Period of observation Since 1996, European Summer Time has been observed between 01:00 UTC (02:00 CET and 03:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March, and 01:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union. There were pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Summer Time
During British Summer Time (BST), civil time in the United Kingdom is advanced one hour forward of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), in effect changing the time zone from UTC±00:00 to UTC+01:00, so that mornings have one hour less daylight, and evenings one hour more. BST begins at 01:00 GMT every year on the last Sunday of March and ends at 01:00 GMT (02:00 BST) on the last Sunday of October. The starting and finishing times of daylight saving were aligned across the European Union on 22 October 1995, and the UK retained this alignment after it left the EU; both BST and Central European Summer Time begin and end on the same Sundays at 02:00 Central European Time, 01:00 GMT. Between 1972 and 1995, the BST period was defined as "beginning at two o'clock, Greenwich mean time, in the morning of the day after the third Saturday in March or, if that day is Easter Day, the day after the second Saturday in March, and ending at two o'clock, Greenwich mean time, in the morning of the da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Time
Central European Time (CET) is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. It is used in most parts of Europe and in a few North African countries. CET is also known as Middle European Time (MET, German: MEZ) and by colloquial names such as Amsterdam Time, Berlin Time, Brussels Time, Madrid Time, Paris Time, Rome Time, Warsaw Time or even Romance Standard Time (RST). The 15th meridian east is the central axis for UTC+01:00 in the world system of time zones. As of 2011, all member states of the European Union observe summer time ( daylight saving time), from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. States within the CET area switch to Central European Summer Time (CEST, UTC+02:00) for the summer. In Africa, UTC+01:00 is called West Africa Time (WAT), where it is used by several countries, year round. Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia also refer to it as ''Central Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Summer Time
Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC+01:00) is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in: * the Canary Islands * Portugal (including Madeira but not the Azores) * the Faroe Islands The following countries also use the same time zone for their daylight saving time but use a different title: *United Kingdom, which uses British Summer Time (BST) *Ireland, which uses Irish Standard Time (IST) ( (ACÉ)). Also sometimes erroneously referred to as "Irish Summer Time" (). The scheme runs from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October each year. At both the start and end of the schemes, clock changes take place at 01:00 UTC+00:00. During the winter, Western European Time (WET, GMT+0 or UTC±00:00) is used. The start and end dates of the scheme are asymmetrical in terms of daylight hours: the vernal time of year with a similar amount of daylight to late October is mid-February, well before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Time
Western European Time (WET, UTC±00:00) is a time zone covering parts of western Europe and consists of countries using UTC±00:00 (also known as Greenwich Mean Time, shortly called GMT). It is one of the three standard time zones in the European Union along with Central European Time and Eastern European Time. The following Western European countries and regions use UTC±00:00 in winter months: *Portugal, since 1912 with pauses (except Azores, UTC−01:00) *United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies, since 1847 in England, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, and since 1916 in Northern Ireland, with pauses *Ireland, since 1916, except between 1968 and 1971 *Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, UTC+01:00) *Faroe Islands, since 1908 *Madeira islands, since 1912 with pauses * North Eastern Greenland (Danmarkshavn and surrounding area) *Iceland, since 1968, without summer time changes All the above countries except Iceland implement daylight savi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich Mean Time
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. The term 'GMT' is also used as one of the names for the time zone UTC+00:00 and, in UK law, is the basis for civil time in the United Kingdom. English speakers often use GMT as a synonym for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). For navigation, it is considered equivalent to UT1 (the modern form of mean solar time at 0° longitude); but this meaning can differ from UTC by up to 0.9s. The term GMT should thus not be used for purposes that require precision. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt, noon (12:00:00) GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian and reaches its highest po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Standard Time
The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America and some Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to result in UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In Canada, the provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island are in this zone, though legally they calculate time specifically as an offset of four hours from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT–4) rather than from UTC. Small portions of Quebec (eastern Côte-Nord and the Magdalen Islands) also observe Atlantic Time. Officially, the entirety of Newfoundland and Labrador observes Newfoundland St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |