|
Jamo (company)
Klipsch Audio Technologies (also referred to as Klipsch Speakers or Klipsch Group, Inc.) is an American loudspeaker company based in Indianapolis, Indiana. Founded in Hope, Arkansas, in 1946 as 'Klipsch and Associates' by Paul W. Klipsch, the company produces loudspeaker drivers and enclosures, as well as complete loudspeakers for high-end, high-fidelity sound systems, public address applications, and personal computers. On January 6, 2011, Audiovox announced that the company had signed a "term sheet to purchase all the shares of Klipsch Group Inc". The sale was completed March 1, 2011. Horn loading Since its inception, Klipsch has promoted the use of horn-loaded speakers as part of its goal to produce speakers featuring: *High efficiency (more formally called "sensitivity"), meaning that they can be driven by relatively low-powered amplifiers *Low modulation distortion, which Paul Klipsch believed was very important *Wide dynamic range, meaning that they accurately reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidiary
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a same management being substantially controlled by same entity/group are called sister companies. The subsidiary can be a company (usually with limited liability) and may be a government- or state-owned enterprise. They are a common feature of modern business life, and most multinational corporations organize their operations in this way. Examples of holding companies are Berkshire Hathaway, Jefferies Financial Group, The Walt Disney Company, Warner Bros. Discovery, or Citigroup; as well as more focused companies such as IBM, Xerox, and Microsoft. These, and others, organize their businesses into national and functional subsidiaries, often with multiple levels of subsidiaries. Details Subsidiaries are separate, distinct legal entities f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
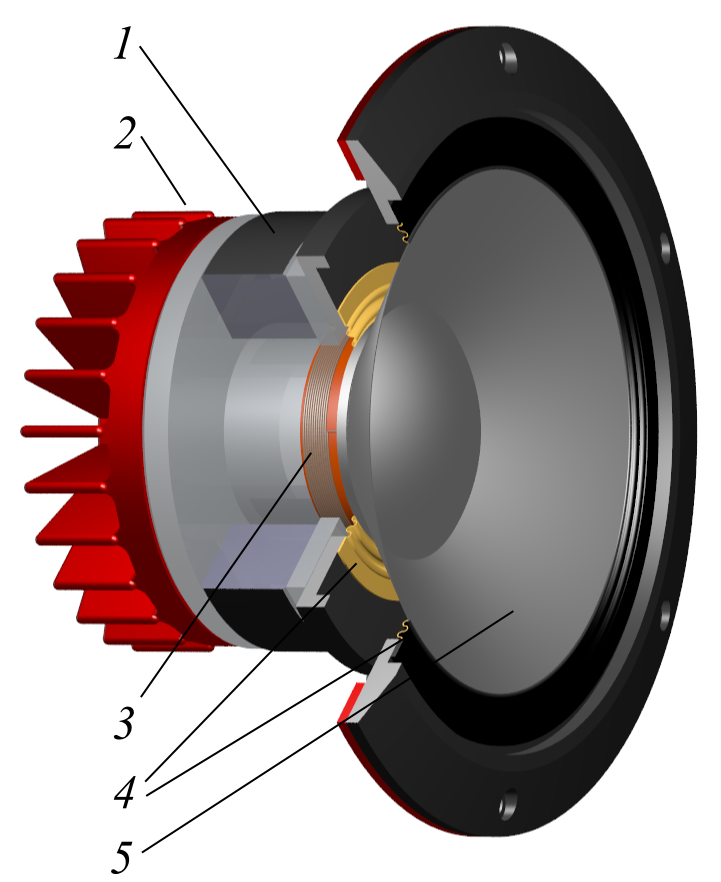
Woofer
A woofer or bass speaker is a technical term for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from 50 Hz up to 1000 Hz. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's bark, " woof" (in contrast to the name used for loudspeakers designed to reproduce high-frequency sounds, ''tweeter''). The most common design for a woofer is the electrodynamic driver, which typically uses a stiff paper cone, driven by a voice coil surrounded by a magnetic field. The voice coil is attached by adhesives to the back of the loudspeaker cone. The voice coil and the magnet form a linear electric motor. When current flows through the voice coil, the coil moves in relation to the frame according to Fleming's left hand rule for motors, causing the coil to push or pull on the driver cone in a piston-like way. The resulting motion of the cone creates sound waves, as it moves in and out. At ordinary sound pressure levels (SPL), most humans can hear down to about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
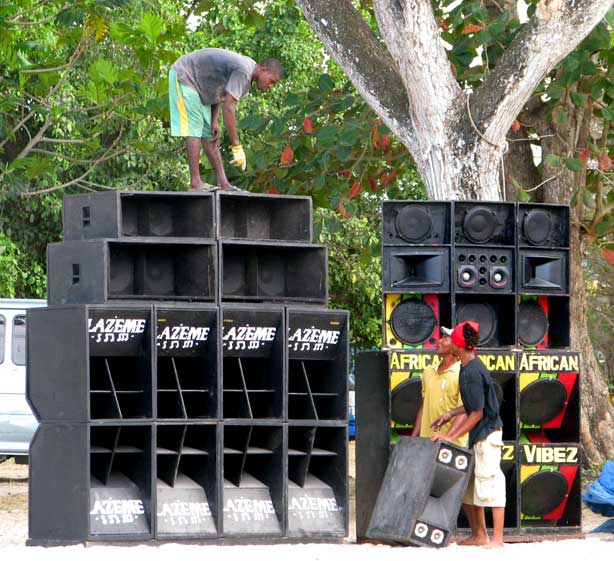
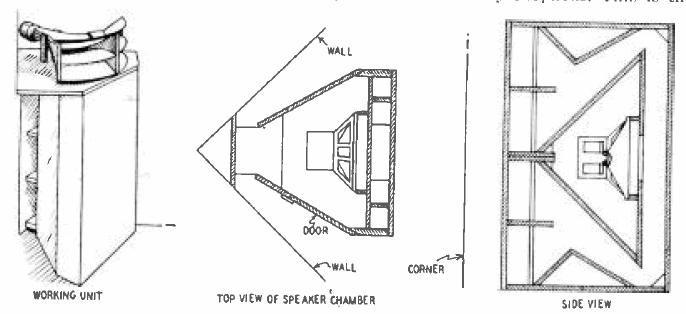
Klipschorn Speaker Drawing 1948
Klipsch Audio Technologies (also referred to as Klipsch Speakers or Klipsch Group, Inc.) is an American loudspeaker company based in Indianapolis, Indiana. Founded in Hope, Arkansas, in 1946 as 'Klipsch and Associates' by Paul W. Klipsch, the company produces loudspeaker drivers and enclosures, as well as complete loudspeakers for high-end, high-fidelity sound systems, public address applications, and personal computers. On January 6, 2011, Audiovox announced that the company had signed a "term sheet to purchase all the shares of Klipsch Group Inc". The sale was completed March 1, 2011. Horn loading Since its inception, Klipsch has promoted the use of horn-loaded speakers as part of its goal to produce speakers featuring: *High efficiency (more formally called "sensitivity"), meaning that they can be driven by relatively low-powered amplifiers *Low modulation distortion, which Paul Klipsch believed was very important *Wide dynamic range, meaning that they accurately reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by multinational company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. Researchers working at Bell Laboratories are credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Nine Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telephone conglomerate. In the late 19th century, the laboratory began as the Western Electric Engineering Department, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tractrix
In geometry, a tractrix (; plural: tractrices) is the curve along which an object moves, under the influence of friction, when pulled on a horizontal plane by a line segment attached to a pulling point (the ''tractor'') that moves at a right angle to the initial line between the object and the puller at an infinitesimal speed. It is therefore a curve of pursuit. It was first introduced by Claude Perrault in 1670, and later studied by Isaac Newton (1676) and Christiaan Huygens (1693). Mathematical derivation Suppose the object is placed at (or in the example shown at right), and the puller at the origin (mathematics), origin, so is the length of the pulling thread (4 in the example at right). Then the puller starts to move along the axis in the positive direction. At every moment, the thread will be tangent to the curve described by the object, so that it becomes completely determined by the movement of the puller. Mathematically, if the coordinates of the object are , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Resonance
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration (its ''resonance frequencies''). The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to narrow mechanical resonance to the frequency range of human hearing, but since acoustics is defined in general terms concerning vibrational waves in matter, acoustic resonance can occur at frequencies outside the range of human hearing. An acoustically resonant object usually has more than one resonance frequency, especially at harmonics of the strongest resonance. It will easily vibrate at those frequencies, and vibrate less strongly at other frequencies. It will "pick out" its resonance frequency from a complex excitation, such as an impulse or a wideband noise excitation. In effect, it is filtering out all frequencies other than its resonance. Acoustic resonance is an important consideration for instrument builders, as most acoustic i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
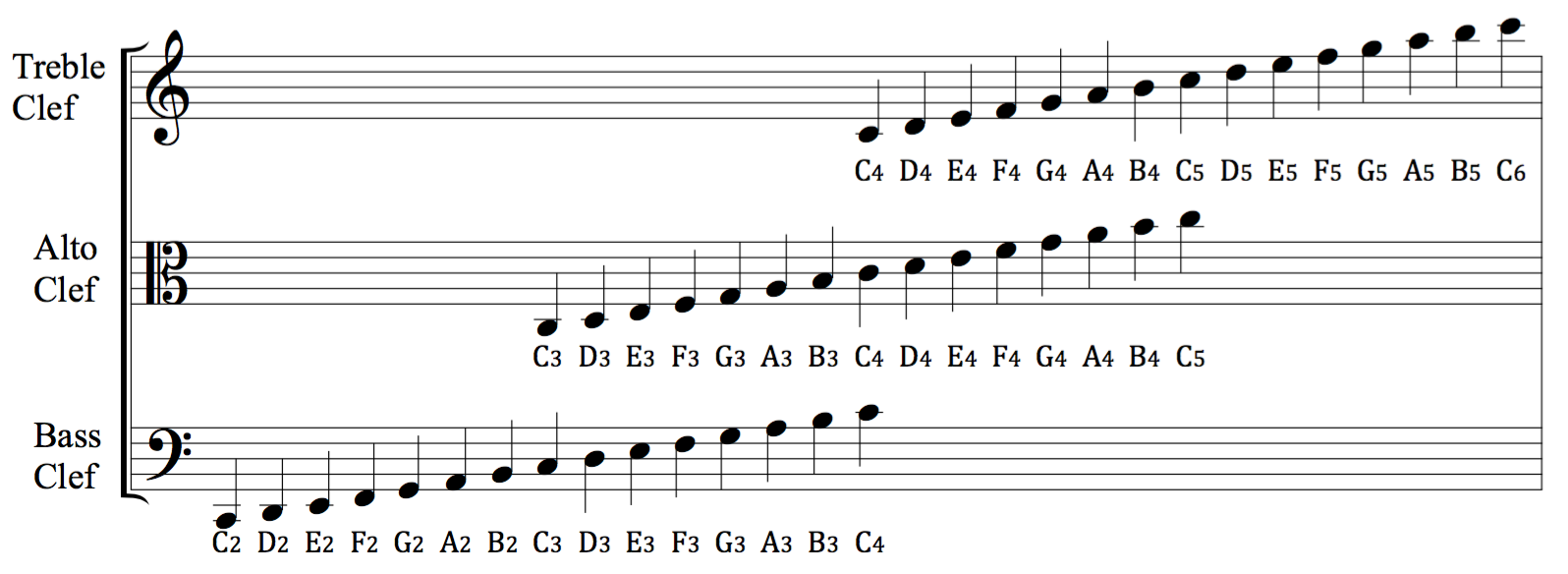
Treble Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a Musical notation, musical symbol used to indicate which Musical note, notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff (music), stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the #G-clefs, G-clef, #F-clefs, F-clef, and #C-clefs, C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing Scientific pitch notation, G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-range Speaker
A mid-range speaker is a loudspeaker driver that reproduces sound in the frequency range from 250 to 2000 Hz. It is also known as a squawker. Mid-range drivers are usually cone types or, less commonly, dome types, or compression horn drivers. The radiating diaphragm of a cone mid-range unit is a truncated cone, with a voice coil attached at the neck, along with the spider portion of the suspension, and with the cone surround at the wide end. Cone mid-range drivers typically resemble small woofers. The most common material used for mid-range cones is paper, occasionally impregnated and/or surface-treated with polymers or resins in order to improve vibrational damping. Other mid-range cone materials include plastics such as polypropylene, Cobex, Bextrene, woven Kevlar, fiberglass, carbon fiber, or light metal alloys based on aluminium, magnesium, titanium, or other alloys. The radiating surface of a dome mid-range is typically a 90-degree section of a sphere, made from cloth, metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass (sound)
Bass ( ) (also called bottom end) describes tones of low (also called "deep") frequency, pitch and range from 16 to 256 Hz (C0 to middle C4) and bass instruments that produce tones in the low-pitched range C2-C4. They belong to different families of instruments and can cover a wide range of musical roles. Since producing low pitches usually requires a long air column or string, and for stringed instruments, a large hollow body, the string and wind bass instruments are usually the largest instruments in their families or instrument classes. Use in composition In musical compositions, such as songs and pieces, these are the lowest-pitched parts of the harmony. In choral music without instrumental accompaniment, the bass is supplied by adult male bass singers. For an accompanied choir, the bass is typically provided by pipe organ or piano (or if a choir can afford to hire one, by orchestra). In an orchestra, the basslines are played by the double bass and cellos, bassoon o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and analysis of systems, such as audio and control systems, where they simplify mathematical analysis by converting governing differential equations into algebraic equations. In an audio system, it may be used to minimize audible distortion by designing components (such as microphones, amplifiers and loudspeakers) so that the overall response is as flat (uniform) as possible across the system's bandwidth. In control systems, such as a vehicle's cruise control, it may be used to assess system stability, often through the use of Bode plots. Systems with a specific frequency response can be designed using analog and digital filters. The frequency response characterizes systems in the frequency domain, just as the impulse response characterizes systems in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: “Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd ed. 1982 David K Cheng: “Field and Wave Electromagnetics”, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Edition 2, 1998. Edward C. Jordan & Keith G. Balmain; “Electromagnetic Waves and Radiating Systems” (2nd ed. 1968) Prentice-Hall. Particularly in the fields of fiber optics, lasers, and integrated optics, the term radiation pattern may also be used as a synonym for the near-field pattern or Fresnel pattern.Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |