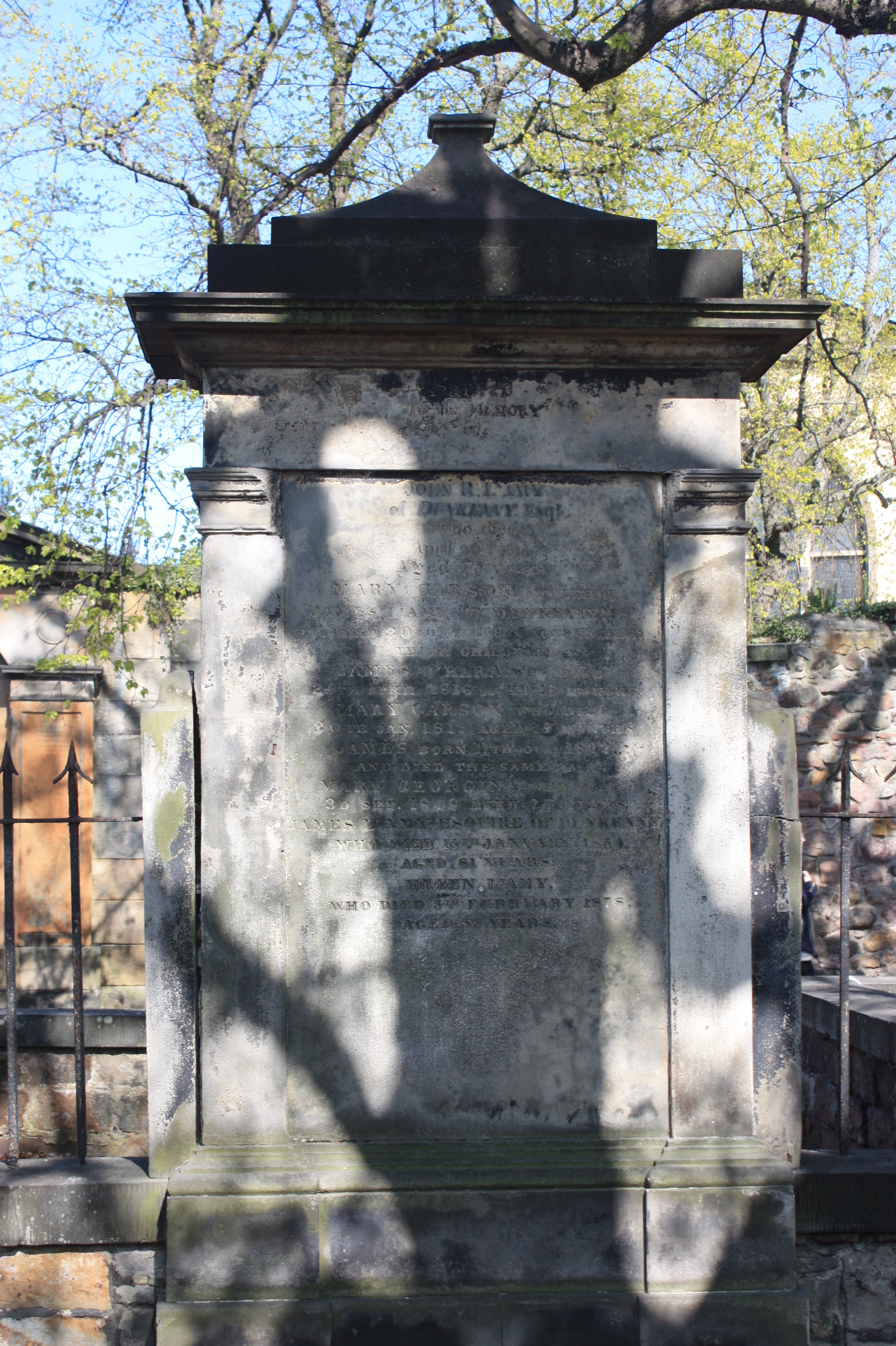|
James L'Amy
James L'Amy of Dunkenny (8 July 1772- 15 January 1854) was a Scottish advocate and amateur phrenologist. He served as Sheriff of Forfar from 1819 until death. Life L'Amy was born on 8 July 1772 the son of Agnes (née) Hamilton and John Ramsay L'Amy of Dunkenny, Forfarshire. His older sister was the Scottish poet Agnes Lyon. He studied law and qualified as an advocate in 1794. In the 1820s he was living at 27 Northumberland Street next to the "father of phrenology" and fellow-lawyer, George Combe, at 25 Northumberland Street. Combe may have introduced L'Amy to phrenological thinking. In 1830 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposer was George Augustus Borthwick. He was Vice President of the Royal Scottish Society of Arts. In 1852 he is listed as a director of the Scottish Naval and Military Academy on Lothian Road, Edinburgh.Edinburgh Post Office Directory 1852 He died on 15 January 1854 in Edinburgh and is buried with his wife and family in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenology
Phrenology () is a pseudoscience which involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits.Wihe, J. V. (2002). "Science and Pseudoscience: A Primer in Critical Thinking." In ''Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience'', pp. 195–203. California: Skeptics Society.Hines, T. (2002). ''Pseudoscience and the Paranormal''. New York: Prometheus Books. p. 200 It is based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. It was said that the brain was composed of different muscles, so those that were used more often were bigger, resulting in the different skull shapes. This led to the reasoning behind why everyone had bumps on the skull in different locations. The brain "muscles" not being used as frequently remained small and were therefore not present on the exterior of the skull. Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology generalized beyond empirical knowledge in a way that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyfriars Kirkyard
Greyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building. History Greyfriars takes its name from the Franciscan friary on the site (the friars of which wear grey habits), which was dissolved in 1560. The churchyard was founded in August 1562 after Royal sanction was granted to replace the churchyard at St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The latter burial ground was not used after around 1600. The Kirkyard was involved in the history of the Covenanters. The Covenanting movement began with signing of the National Cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenologists
Phrenology () is a pseudoscience which involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits.Wihe, J. V. (2002). "Science and Pseudoscience: A Primer in Critical Thinking." In ''Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience'', pp. 195–203. California: Skeptics Society.Hines, T. (2002). ''Pseudoscience and the Paranormal''. New York: Prometheus Books. p. 200 It is based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. It was said that the brain was composed of different muscles, so those that were used more often were bigger, resulting in the different skull shapes. This led to the reasoning behind why everyone had bumps on the skull in different locations. The brain "muscles" not being used as frequently remained small and were therefore not present on the exterior of the skull. Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology generalized beyond empirical knowledge in a way that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Lawyers
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English * Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland *Scots language Scots ( endonym: ''Scots''; gd, Albais, ) is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland (where the local dialect is known as Ulster Scots). Most commonl ..., a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland * Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also * Scotch (other) * Scotland (other) * Scots (other) * Scottian (other) * Schottische * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1854 Deaths
Events January–March * January 4 – The McDonald Islands are discovered by Captain William McDonald aboard the ''Samarang''. * January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is perhaps born. * January 9 – The Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh, U.S.A. is founded to promote German culture. * January 20 – The North Carolina General Assembly in the United States charters the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, to run from Goldsboro through New Bern, to the newly created seaport of Morehead City, near Beaufort. * January 21 – The iron clipper runs aground off the east coast of Ireland, on her maiden voyage out of Liverpool, bound for Australia, with the loss of at least 300 out of 650 on board. * February 11 – Major streets are lit by coal gas for the first time by the San Francisco Gas Company; 86 such lamps are turned on this evening in San Francisco, California. * February 13 – Mexican troops force William W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1771 Births
Events January– March * January 5 – The Great Kalmyk ( Torghut) Migration is led by Ubashi Khan, from the east bank of the Lower Volga River back to the homeland of Dzungaria, at this time under Qing Dynasty rule. * January 9 – Emperor Go-Momozono accedes to the throne of Japan, following his aunt's abdication. * February 12 – Upon the death of Adolf Frederick, he is succeeded as King of Sweden by his son Gustav III. At the time, however, Gustav is unaware of this, since he is abroad in Paris. The news of his father's death reaches him about a month later. * March – War of the Regulation: North Carolina Governor William Tryon raises a militia, to put down the long-running uprising of backcountry militias against North Carolina's colonial government. * March 12 – The North Carolina General Assembly establishes Wake County (named for Margaret Wake, the wife of North Carolina Royal Governor William Tryon) from portions of Cumberland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ramsay L'Amy
John Ramsay L’Amy of Dunkenny WS FRSE DL (1813-1892) was a Scottish lawyer, phrenologist and early photographer. To distinguish himself from his grandfather, of the same name, he was often styled “Younger Dunkenny”. Life He was born at 27 Northumberland Street in Edinburgh on 9 April 1813 the son of James L'Amy FRSE and his wife Mary Carson. He was apprenticed to his lawyer neighbour George Combe (it being inappropriate to be apprenticed to your father in the legal world) at 25 Northumberland Street. Through Combe he acquired an interest in phrenology. In 1845 he married Mary Riche Macleod Innes (1819-1875) at South Leith Parish Church and they appear to have emigrated to Coogee, New South Wales in Australia where their first child, Christine Ramsay L’Amy was born in 1846. They returned to Scotland around 1850, then living on the estate at Mordington in Berwickshire. He was an early member of the Edinburgh Photographic Society (established 1861) and exhibited fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Heriot's School
George Heriot's School is a Scottish independent primary and secondary day school on Lauriston Place in the Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland. In the early 21st century, it has more than 1600 pupils, 155 teaching staff, and 80 non-teaching staff. It was established in 1628 as George Heriot's Hospital, by bequest of the royal goldsmith George Heriot, and opened in 1659. It is governed by George Heriot's Trust, a Scottish charity. Architecture The main building of the school is notable for its renaissance architecture, the work of William Wallace, until his death in 1631. He was succeeded as master mason by William Aytoun, who was succeeded in turn by John Mylne. In 1676, Sir William Bruce drew up plans for the completion of Heriot's Hospital. His design, for the central tower of the north façade, was eventually executed in 1693. The school is a turreted building surrounding a large quadrangle, and built out of sandstone. The foundation stone is inscribed with the date 1628. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the highest courts in Scotland. The city's Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sciences, and engineering. It is the second-largest financial centre in the United Kingdom, and the city's historical and cultural attractions have made it the UK's second-most visited tourist d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff Of Forfar
The Sheriff of Angus (alternatively the Sheriff of Forfar) was historically the royal official responsible for enforcing law and order in Angus, Scotland and bringing criminals to justice. Prior to 1748 most sheriffdoms, was held on a hereditary basis. From that date, following the Jacobite uprising of 1745, they were replaced by salaried sheriff-deputes, qualified advocates who were members of the Scottish Bar. After the merger of sheriffdoms in 1934 the post became that of the Sheriff of Perth and Angus. Sheriffs of Forfar * William de Monte Alto * William Comyn, Lord of Badenoch (1195-1211) * Hugh Cameron (1214-1219) * Thomas Malherb (1227) * John Fenton (1261) * Robert Mowat (1261-1264) * John Fenton (1266) * Matthew le Chen (1272) * Alexander de Lamberton * David de Bethune (1290) * Henry de Prestoun (1304) * John de Pollock (1305) * William de Airth (1305) * John de Traquair (1328) * Robert Ramsay (1340) * John Octerlony (1342) * Robert Ramsay (1359) * Malcolm Ramsay (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Naval And Military Academy
The Scottish Naval and Military Academy in Edinburgh was a school opened on 8 November 1825 and closed in 1869. It catered mostly to young gentlemen intending a career with the Army, Navy or, especially, the forces of the East India Company. In 1829 the Academy moved into the three-storey building (subsequently the Caledonian Hotel, since demolished) on Lothian Road opposite Castle Terrace, which it shared with the Royal Riding Academy. A noted master at the Academy was James R. Ballantyne, later head master of the Sanskrit College in Benares (modern-day Varanasi), who from 1832 to 1845 taught " Persian, Hindoostanee and Arabic" from classical texts. Another lecturer was William Swan, who taught mathematics and physics, and conducted some notable experiments at the Academy. Other subjects taught were: Military Engineering: Fortifications, Military Drawing and Surveying; Drawing: Landscape and Perspective; Higher Mathematics; Navigation; Chemistry; Military Antiquities; Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |