|
James Alms
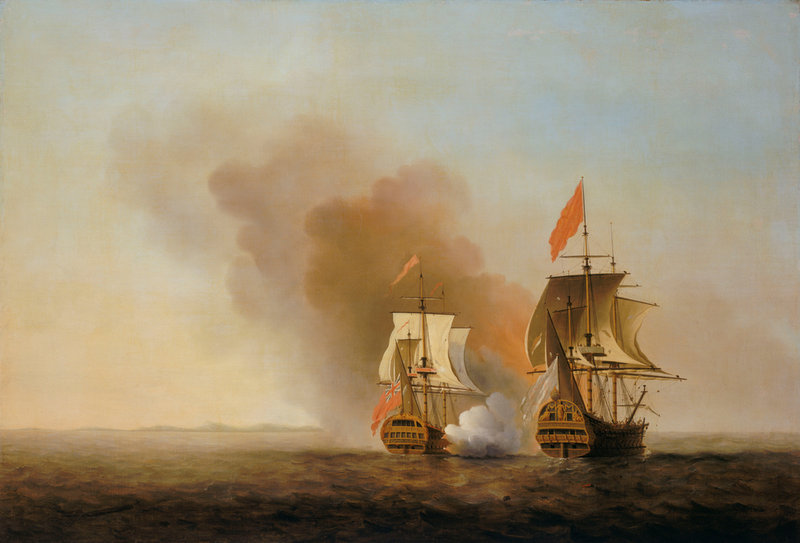
James Alms (15 July 1728 – 8 June 1791) was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the War of the Austrian Succession, the Carnatic and Seven Years' War and the American War of Independence, rising to the rank of post-captain. Alms served in the navy from an early age, seeing his first actions in the Mediterranean and off the French coast, before going out to the East Indies. He narrowly survived a shipwreck that claimed most of his shipmates, and returned to England shortly afterwards, having achieved the rank of lieutenant. He was briefly back in the East Indies for service during the early years of the Seven Years' War, before going to the West Indies in acting-command of a frigate. After being involved in a number of important actions in the Caribbean, he returned to Britain after the end of the war, and retired ashore. Returning to active service after the outbreak of the American War of Independence, he went out to the East Indies in command of his own ship. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
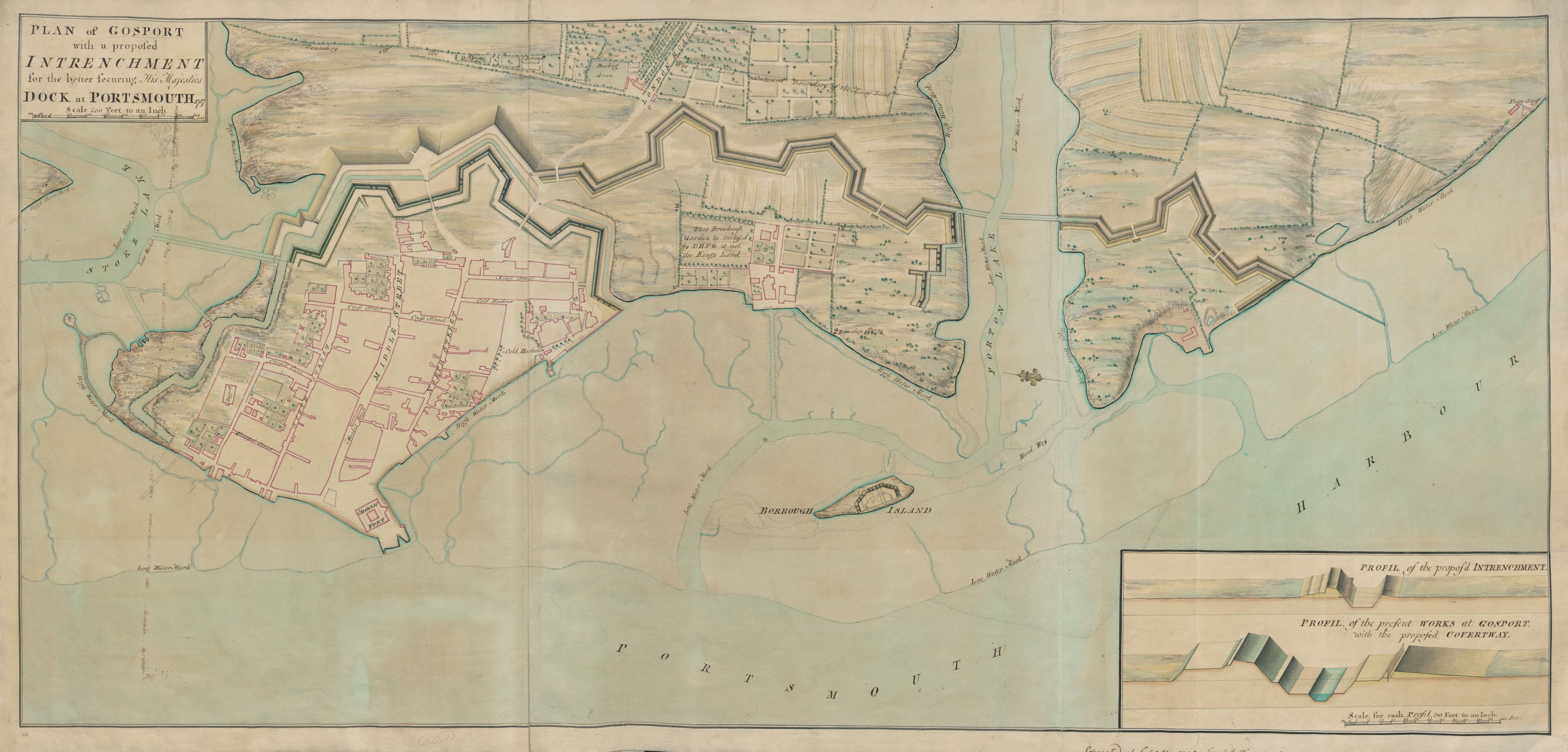
Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite the city of Portsmouth, to which it is linked by the Gosport Ferry. Gosport lies south-east of Fareham, to which it is linked by a Bus Rapid Transit route and the A32. Until the last quarter of the 20th century, Gosport was a major naval town associated with the defence and supply infrastructure of His Majesty's Naval Base (HMNB) Portsmouth. As such over the years extensive fortifications were created. Gosport is still home to and a Naval Armament Supply Facility, as well as a Helicopter Repair base. The Town area of the Borough, including Newtown, consists of the town centre, Stoke Road shopping area, Walpole Park, Royal Clarence Yard and three modern marinas: Royal Clarence, Gosport Marina and Haslar Marina. As part of the ''Renaissa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Negapatam (1782)
The Battle of Negapatam was the third in a series of battles fought between a British fleet, under Vice-Admiral Sir Edward Hughes, and a French fleet, under the Bailli de Suffren, off the coast of India during the American Revolutionary War. The battle was fought on 6 July 1782. Castex (2004), pp. 269–272 Though the battle was indecisive, Suffren was stopped in his goal by Hughes and withdrew to Cuddalore, while the British remained in control of Negapatam. Background France had entered the American Revolutionary War in 1778, and Britain declared war on the Dutch Republic in late 1780, after the Dutch refused to stop trading in military supplies with the French and the Americans. The British had rapidly gained control over most French and Dutch outposts in India when news of these events reached India, spawning the Second Anglo-Mysore War in the process. Negapatam was besieged and taken by Sir Hector Munro in November 1781. The French admiral the Bailli de Suffre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Anson, 1st Baron Anson
Admiral of the Fleet George Anson, 1st Baron Anson, (23 April 1697 – 6 June 1762) was a Royal Navy officer. Anson served as a junior officer during the War of the Spanish Succession and then saw active service against Spain at the Battle of Cape Passaro during the War of the Quadruple Alliance. He then undertook a circumnavigation of the globe during the War of Jenkins' Ear. Anson commanded the fleet that defeated the French Admiral de la Jonquière at the First Battle of Cape Finisterre during the War of the Austrian Succession. Anson went on to be First Lord of the Admiralty during the Seven Years' War. Among his reforms were the removal of corrupt defence contractors, improved medical care, submitting a revision of the Articles of War to Parliament to tighten discipline throughout the Navy, uniforms for commissioned officers, the transfer of the Marines from Army to Navy authority, and a system for rating ships according to their number of guns. Family and early ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Watson (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice Admiral Charles Watson (1714 – 16 August 1757) was an officer of the Royal Navy, who served briefly as colonial governor of Newfoundland, and died in Calcutta, India. Origins He was the son of John Watson by his wife the sister of Sir Charles Wager (1666–1743), First Lord of the Admiralty. The armorials used by his son the 1st baronet (''Argent, on a chevron engrailled azure between three martlets sable as many crescents or'') are a differenced version of the arms of the Watson family, Marquess of Rockingham, and thus the family may have been a cadet branch of the latter. Naval career Watson entered the navy as a volunteer per order on in 1728. He was promoted lieutenant in 1734 and promoted captain and given command of in 1738. He transferred to HMS ''Plymouth'' in May 1741 and to HMS ''Dragon'' in November 1742 which he commanded in the Battle of Toulon. In 1746 he transferred to HMS ''Princess Louisa'' which he commanded at the First Battle of Cape Finiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Kenya. In the 17th century, a midshipman was a rating for an experienced seaman, and the word derives from the area aboard a ship, amidships, either where he worked on the ship, or where he was berthed. Beginning in the 18th century, a commissioned officer candidate was rated as a midshipman, and the seaman rating began to slowly die out. By the Napoleonic era (1793–1815), a midshipman was an apprentice officer who had previously served at least three years as a volunteer, officer's servant or able seaman, and was roughly equivalent to a present-day petty officer in rank and responsibilities. After serving at least three years as a midshipman or master's mate, he was eligible to take the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lennox, 2nd Duke Of Richmond
Charles Lennox, 2nd Duke of Richmond, 2nd Duke of Lennox, 2nd Duke of Aubigny, (18 May 17018 August 1750) of Goodwood House near Chichester in Sussex, was a British nobleman and politician. He was the son of Charles Lennox, 1st Duke of Richmond, 1st Duke of Lennox, the youngest of the seven illegitimate sons of King Charles II. He was the most important of the early patrons of the game of cricket and did much to help its evolution from village cricket to first-class cricket. Early life Lennox was styled Earl of March from his birth in 1701 as heir to his father's dukedom. He also inherited his father's love of sports, particularly cricket. He had a serious accident at the age of 12 when he was thrown from a horse during a hunt, but he recovered and it did not deter him from horsemanship. March entered into an arranged marriage in December 1719 when he was still only 18 and his bride, Hon. Sarah Cadogan, was just 13, in order to use Sarah's large dowry to pay his considera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre André De Suffren De Saint Tropez
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word πέτρος (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translation of Aramaic כיפא (''Kefa),'' the nickname Jesus gave to apostle Simon Bar-Jona, referred in English as Saint Peter. Pierre is also found as a surname. People with the given name * Abbé Pierre, Henri Marie Joseph Grouès (1912–2007), French Catholic priest who founded the Emmaus Movement * Monsieur Pierre, Pierre Jean Philippe Zurcher-Margolle (c. 1890–1963), French ballroom dancer and dance teacher * Pierre (footballer), Lucas Pierre Santos Oliveira (born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Pierre, Baron of Beauvau (c. 1380–1453) * Pierre, Duke of Penthièvre (1845–1919) * Pierre, marquis de Fayet (died 1737), French naval commander and Governor General of Saint-Domingue * Prince Pierre, Duke of Valentinois (1895–1964), fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Hughes (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Edward Hughes (c. 17201794) was a Royal Navy officer who commanded the East Indies Station. Naval career Hughes joined the Royal Navy in 1735, and four years later, was present at the capture of Portobelo, Panama. In 1740, he was promoted to lieutenant and served in the Cartagena expedition of 1741, and at the indecisive Battle of Toulon in 1744. In HMS ''Warwick'', he participated in the action against the ''Glorioso'', but without proper support from the ''Lark'' (which was sailing with the ''Warwick''), the enemy escaped. The commander of the ''Lark'' was subsequently tried and condemned for his conduct, and Hughes received the vacated command. Captain Hughes was with Edward Boscawen at Louisburg and with Charles Saunders at Quebec. He was in continual employment during the peace, and as commodore, commanded the East Indies Station from 1773 to 1777. Before long, he returned to the East Indies Station as a rear-admiral, with an overwhelming naval force. On h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around the Indian Ocean by Portuguese explorers, soon after the Cape route was discovered. Nowadays, this term is broadly used to refer to the Malay Archipelago, which today comprises the Philippine Archipelago, Indonesian Archipelago, Malaysian Borneo, and New Guinea. Historically, the term was used in the Age of Discovery to refer to the coasts of the landmasses comprising the Indian subcontinent and the Indochinese Peninsula along with the Malay Archipelago. Overview During the era of European colonization, territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia were known as the Spanish East Indies for 333 years before the American conquest. Dutch occupied colonies in the area were known for about 300 years as the Dutch East Indies till Indonesian indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |