|
James Albus
James Sacra Albus (May 4, 1935 – April 17, 2011) was an American engineer, Senior NIST Fellow and founder and former chief of the Intelligent Systems Division of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Biography Born in Louisville, Kentucky, Albus received the B.S. degree in physics from Wheaton College, Illinois, in 1957 and the M.S. degree in electrical engineering from Ohio State University, Columbus, in 1958.IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SPACE ELECTRONICS AND TELEMETRY contributors sept 1963. Accessed August 2, 2009. In 1972 he received a Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering from the |
Louisville, Kentucky
Louisville ( , , ) is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky and the 28th most-populous city in the United States. Louisville is the historical seat and, since 2003, the nominal seat of Jefferson County, on the Indiana border. Named after King Louis XVI of France, Louisville was founded in 1778 by George Rogers Clark, making it one of the oldest cities west of the Appalachians. With nearby Falls of the Ohio as the only major obstruction to river traffic between the upper Ohio River and the Gulf of Mexico, the settlement first grew as a portage site. It was the founding city of the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, which grew into a system across 13 states. Today, the city is known as the home of boxer Muhammad Ali, the Kentucky Derby, Kentucky Fried Chicken, the University of Louisville and its Cardinals, Louisville Slugger baseball bats, and three of Kentucky's six ''Fortune'' 500 companies: Humana, Kindred Healthcare, and Yum! Brands. Muhamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairfax, Virginia
The City of Fairfax ( ), colloquially known as Fairfax City, Downtown Fairfax, Old Town Fairfax, Fairfax Courthouse, FFX, or simply Fairfax, is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. At the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census the population was 22,565, which had risen to 24,146 at the 2020 census. The City of Fairfax is an enclave surrounded by the separate political entity Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County. Fairfax City also contains an exclave of Fairfax County, the Fairfax County Court Complex. The City of Fairfax and the area immediately surrounding the historical border of the City of Fairfax, collectively designated by Fairfax County as "Fairfax", comprise the county seat of Fairfax County. The city is part of the Washington metropolitan area as well as a part of Northern Virginia. The city is west of Washington, D.C. The Washington Metro's Orange Line (Washington Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Research Magazine
Industrial may refer to: Industry * Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry * Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems * Industrial city, a city dominated by one or more industries * Industrial loan company, a financial institution in the United States that lends money, and may be owned by non-financial institutions * Industrial organization, a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure and boundaries between firms and markets * Industrial Revolution, the development of industry in the 18th and 19th centuries * Industrial society, a society that has undergone industrialization * Industrial technology, a broad field that includes designing, building, optimizing, managing and operating industrial equipment, and predesignated as acceptable for industrial uses, like factories * Industrial video, a video that targets “industry” as its primary audience * Industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
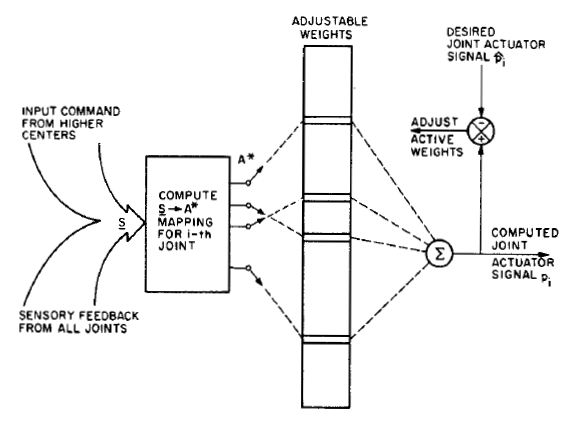
Cerebellar Model Articulation Controller
The cerebellar model arithmetic computer (CMAC) is a type of neural network based on a model of the mammalian cerebellum. It is also known as the cerebellar model articulation controller. It is a type of associative memory Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, .... The CMAC was first proposed as a function modeler for robotic controllers by James Albus in 1975 (hence the name), but has been extensively used in reinforcement learning and also as for automated classification in the machine learning community. The CMAC is an extension of the perceptron model. It computes a function for n input dimensions. The input space is divided up into hyper-rectangles, each of which is associated with a memory cell. The contents of the memory cells are the weights, which are adjusted duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Marr (neuroscientist)
David Courtenay Marr (19 January 1945 – 17 November 1980) from the ''International Encyclopaedia of Social and Behavioral Sciences'', by Shimon Edelman and Lucia M. Vaina; published 2001-01-08; archived at ; retrieved 2021-07-21 was a British and physiologist. Marr integrated results from , |
Model Of Cerebellar Perceptron
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure. Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a model plane) and abstract models (e.g. mathematical expressions describing behavioural patterns). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science, as almost every scientific theory effectively embeds some kind of model of the physical or human sphere. In commerce, "model" can refer to a specific design of a product as displayed in a catalogue or show room (e.g. Ford Model T), and by extension to the sold product itself. Types of models include: Physical model A physical model (most commonly referred to simply as a model but in this context distinguished from a conceptual model) is a smaller or larger physical copy of an object. The object being modelled may be small (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis O , names sometimes translated to English as "Louis"
{{disambiguation ...
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish-Israeli Olympic soccer player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Platform
A Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting points on a top plate. All 12 connections are made via universal joints. Devices placed on the top plate can be moved in the six degrees of freedom in which it is possible for a freely-suspended body to move: three linear movements x, y, z (lateral, longitudinal, and vertical), and the three rotations (pitch, roll, and yaw). Stewart platforms are known by various other names. In many applications, including in flight simulators, it is commonly referred to as a motion base. It is sometimes called a ''six-axis platform'' or ''6-DoF platform'' because of its possible motions and, because the motions are produced by a combination of movements of multiple actuators, it may be referred to as a ''synergistic motion platform'', due to the synergy (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robocrane
The Robocrane is a kind of manipulator resembling a Stewart platform but using an octahedral assembly of cables instead of struts. Like the Stewart platform, the Robocrane has six degrees of freedom (x, y, z, pitch, roll, & yaw). It was developed by Dr. James S. Albus of the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), using the Real-Time Control System which is a hierarchical control system. Given its unusual ability to "fly" tools around a work site, it has many possible applications, including stone carving, ship building, bridge construction, inspection, pipe or beam fitting and welding. Albus invented and developed a new generation of robot cranes based on six cables and six winches configured as a Stewart platform. The NIST RoboCraneTM has the capacity to lift and precisely manipulate heavy loads over large volumes with fine control in all six degrees of freedom. Laboratory RoboCranes have demonstrated the ability to manipulate tools such as saws, grinders, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Robot Association
The (JARA) is a trade association made up of companies in Japan that develop and manufacture robot technology. It was formed in 1971 as the Industrial Robot Conversazione and was the world's first robot association. The association was reorganized and renamed as the Japan Industrial Robot Association (JIRA) in 1972, and was formally incorporated in 1973. The name of the association was changed again in 1994 to its current one to accommodate non-industrial robots such as personal robots. Its headquarters are in Tokyo. The Japan Robot Association aims to advance the growth of the robot manufacturing industry by encouraging research and development on robots and related system products, and promoting the use of robot technology in industry and society. The activities of the Japan Robot Association include organizing the International Robot Exhibition (IREX) every two years in Tokyo, the Jisso Process Technology Exhibition every year, and hosting the ORiN (Open Robot interface for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Rabinow
Jacob Rabinow (January 8, 1910 – September 11, 1999) was an engineer and inventor. He earned a total of 229 U.S. patents on a variety of mechanical, optical and electrical devices. Biography Rabinow was born in Kharkiv, Ukraine, on January 8, 1910. In 1919, his family moved to China, then in 1921 to the United States. He graduated from the City College of New York with a Bachelor's Degree in Engineering in 1933, and a Master's Degree in Electrical Engineering in 1934. His career as an inventor began when he was hired as a mechanical engineer in 1938 by the National Bureau of Standards (now the National Institute of Standards and Technology, or NIST). He made many developments there, mainly in defense systems, and eventually became Chief of the Electro-Mechanical Ordnance Division at NBS before leaving in 1954 to form his own company. During this time, Rabinow invented and patented a number of revolutionary devices. Among them are the first disc-shaped magnetic storage media for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |