|
Jakobshavn Glacier
Jakobshavn Glacier ( da, Jakobshavn Isbræ), also known as Ilulissat Glacier ( kl, Sermeq Kujalleq), is a large outlet glacier in West Greenland. It is located near the Greenlandic town of Ilulissat (colonial name in da, Jakobshavn) and ends at the sea in the Ilulissat Icefjord. Jakobshavn Glacier drains 6.5% of the Greenland ice sheet and produces around 10% of all Greenland icebergs. Some 35 billion tonnes of icebergs calve off and pass out of the fjord every year. Icebergs breaking from the glacier are often so large (up to 1 km in height) that they are too tall to float down the fjord and lie stuck on the bottom of its shallower areas, sometimes for years, until they are broken up by the force of the glacier and icebergs further up the fjord. Studied for over 250 years, the Jakobshavn Glacier has helped develop modern understanding of climate change and icecap glaciology. Ilulissat Icefjord ( kl, Ilulissat Kangerlua) was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Calving
Ice calving, also known as glacier calving or iceberg calving, is the breaking of ice chunks from the edge of a glacier.Essentials of Geology, 3rd edition, Stephen Marshak It is a form of ice ablation or ice disruption. It is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse. The ice that breaks away can be classified as an iceberg, but may also be a growler, bergy bit, or a crevasse wall breakaway.Glossary of Glacier Terms Ellin Beltz, 2006. Retrieved July 2009. Calving of glaciers is often accompanied by a loud cracking or booming sound before blocks of ice up to high break loose and crash into the water. The entry of the ice into the water causes large, and often hazardous waves. The waves formed in locations like |
Hinrich Johannes Rink
Dr. Hinrich Johannes Rink (first name sometimes as Henrik) (26 August 1819 – 15 December 1893) was a Danish geologist, one of the pioneers of glaciology, and the first accurate describer of the inland ice of Greenland. Rink, who first came to Greenland in 1848, spent 16 winters and 22 summers in the Arctic region, and became notable for Greenland's development. Becoming a Greenlandic scholar and administrator, he served as Royal Inspector of South Greenland and went on to become Director of the Royal Greenland Trading Department. With "Forstanderskaber", Rink introduced the first steps towards Greelandic home rule. Rink carried out and printed in four volumes the first systematic collection of Greenlandic oral tradition stories. He was the founder of '' Atuagagdliutit'', the first Kalaallisut language newspaper. Early years Rink was born in Copenhagen to Holstein parents. His father was Johannes Rink (1783–1865), a Kiel, Germany merchant, and his mother was Agnese Margare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Geoscience
''Nature Geoscience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Nature Publishing Group. The Chief Editor is Tamara Goldin, who took over from Heike Langenberg in February 2020. It was established in January 2008. Scope The journal covers all aspects of the Earth sciences, including theoretical research, modelling, and field work. Significant related work in other fields, such as atmospheric sciences, geology, geophysics, climatology, oceanography, palaeontology, and space science, is also published. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed by: * '' CAB Abstracts'' * ''Chemical Abstracts Service/CASSI'' * ''Science Citation Index'' * ''Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences'' * ''GeoRef'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 16.908. See also * List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irminger Sea
The Irminger Sea is a marginal sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is bordered to the west by southern Greenland, to the north by Iceland and the Denmark Strait, to the east by the Reykjanes Ridge (a northern part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge), and to the south by open waters of the North Atlantic. It was named after Danish vice-admiral Carl Ludvig Christian Irminger (1802–1888), after whom the Irminger Current was also named.Kommandør Axel Fiedler: „Om Irminger Havets og Irmingerstrømmens navn“. ''Søværnsorientering'' Nr. 1, March 200PDF�Google-HTML-Version/ref> Geography The northern limit is the Greenland–Iceland Rise on the bottom of the Denmark Strait between Iceland and East Greenland, which connects to the Greenland Sea. To the southwest, it reaches to Cape Farvel, the southern tip of Greenland, and meets the Labrador Sea at this point. South of this point is the open North Atlantic Ocean. The sea floor of the Irminger Sea is largely part of the Irminger Basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablation
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for ascent and atmospheric reentry, ice and snow in glaciology, biological tissues in medicine and passive fire protection materials. Artificial intelligence In artificial intelligence (AI), especially machine learning, Ablation (artificial intelligence), ablation is the removal of a component of an AI system. The term is by analogy with biology: removal of components of an organism. Biology Biological ablation is the removal of a biological structure or functionality. Genetic ablation is another term for gene silencing, in which gene expression is abolished through the alteration or deletion of genetic sequence information. In cell ablation, individual cells in a population or culture are destroyed or removed. Both can be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RealClimate
''RealClimate'' is a commentary site (blog) on climatology. The site's contributors include climate scientists whose goal is to provide a response to developing stories and a context they feel is sometimes missing in mainstream commentary on climate science and climate change. The forum is moderated, and is restricted to scientific topics to avoid discussion of political or economic implications of the science. ''RealClimate'' was launched on 10 December 2004 by nine climate scientists. Recognition The creation of ''RealClimate'' was the subject of an editorial in the scientific journal ''Nature'', and was reported in the "NetWatch" news feature of the journal ''Science''. In 2005, the editors of ''Scientific American'' recognized ''RealClimate'' with a Science and Technology Web Award. In 2006, ''Nature'' compiled a list of the 50 most popular blogs written by scientists, as measured by Technorati. ''RealClimate'' was number 3 on that list. According to ''Time'', ''Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraglacial Lake
A supraglacial lake is any pond of liquid water on the top of a glacier. Although these pools are ephemeral, they may reach kilometers in diameter and be several meters deep. They may last for months or even decades at a time, but can empty in the course of hours. Lifetime Lakes may be created by surface melting during summer months, or over the period of years by rainfall, such as monsoons. They may dissipate by overflowing their banks, or creating a moulin. Effects on ice masses Lakes of a diameter greater than ~300 m are capable of driving a fluid-filled crevasse to the glacier/bed interface, through the process of hydrofracture. A surface-to-bed connection made in this way is referred to as a moulin. When these crevasses form, it can take a mere 2–18 hours to empty a lake, supplying warm water to the base of the glacier - lubricating the bed and causing the glacier to surge. The rate of emptying such a lake is equivalent to the rate of flow of the Niagara Falls. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulin (geology)
A moulin (or glacier mill) is a roughly circular, vertical (or nearly vertical) well-like shaft formed where a surface meltstream exploits a weakness in the ice. The term is derived from the French word for mill.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. They can be up to 10 meters wide and are typically found on ice sheets and flat areas of a glacier in a region of transverse crevasses. Moulins can reach the bottom of the glacier, hundreds of meters deep, or may only reach the depth of common crevasse formation (about 10–40 m) where the stream flows englacially. They are the most typical cause for the formation of a glacier cave. Moulins are parts of the internal structure of glaciers, that carry meltwater from the surface down to wherever it may go. Water from a moulin often exits the glacier at base level, sometimes into the sea, and occa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland Ice Sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equivalent, ''indlandsis''. An acronym, GIS, is frequently used in the scientific literature. It is the second largest ice body in the world, after the Antarctic ice sheet. The ice sheet is almost long in a north–south direction, and its greatest width is at a latitude of 77°N, near its northern margin. The average thickness is about and over at its thickest point. In addition to the large ice sheet, smaller ice caps (such as Maniitsoq and Flade Isblink) as well as glaciers, cover between around the periphery. The Greenland ice sheet is adversely affected by climate change. It is more vulnerable to climate change than the Antarctic ice sheet because of its position in the Arctic, where it is subject to the regional amplification o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level Rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year. Climate scientists expect further acceleration during the 21st century. Climate change heats (and therefore expands) the ocean and melts land-based ice sheets and glaciers. Between 1993 and 2018, the thermal expansion of water contributed 42% to sea level rise; melting of temperate glaciers, 21%; Greenland, 15%; and Antarctica, 8%. Over the next 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
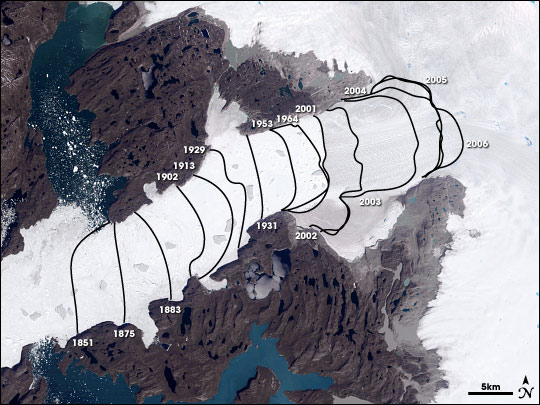
Jakobshavn Retreat-1851-2006
Ilulissat, formerly Jakobshavn or Jacobshaven, is the municipal seat and largest town of the Avannaata municipality in western Greenland, located approximately north of the Arctic Circle. With the population of 4,670 as of 2020, it is the third-largest city in Greenland, after Nuuk and Sisimiut. The city is home to almost as many sled-dogs as people. In direct translation, Ilulissat is the Kalaallisut word for "Icebergs" ( da, Isbjerge). The nearby Ilulissat Icefjord is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and has made Ilulissat the most popular tourist destination in Greenland. Tourism is now the town's principal industry. The city neighbours the Ilulissat Icefjord, where there are enormous icebergs from the most productive glacier in the northern hemisphere. History The town was established as a trading post by Jacob Severin's company in 1741 and was named in his honor.Marquardt, Ole.Change and Continuity in Denmark's Greenland Policy in ''The Oldenburg Monarchy: An Underestim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |