|
JAK2
Janus kinase 2 (commonly called JAK2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a member of the Janus kinase family and has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family (e.g. interferon receptors), the GM-CSF receptor family (IL-3R, IL-5R and GM-CSF-R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g., IL-6R), and the single chain receptors (e.g. Epo-R, Tpo-R, GH-R, PRL-R). The distinguishing feature between janus kinase 2 and other JAK kinases is the lack of Src homology binding domains ( SH2/ SH3) and the presence of up to seven JAK homology domains (JH1-JH7). Nonetheless the terminal JH domains retain a high level of homology to tyrosine kinase domains. An interesting note is that only one of these carboxy-terminal JH domains retains full kinase function (JH1) while the other (JH2), previously thought to have no kinase functionality and accordingly termed a pseudokinase domain, has since been found to be catalytically active, albeit at only 10% that of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonal Eosinophilia
Clonal hypereosinophilia, also termed primary hypereosinophilia or clonal eosinophilia, is a grouping of hematological disorders all of which are characterized by the development and growth of a pre-malignant or malignant population of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that occupies the bone marrow, blood, and other tissues. This population consists of a clone of eosinophils, i.e. a group of genetically identical eosinophils derived from a sufficiently mutated ancestor cell. The clone of eosinophils bear a mutation in any one of several genes that code for proteins that regulate cell growth. The mutations cause these proteins to be continuously active and thereby to stimulate growth in an uncontrolled and continuous manner. The expanding population of eosinophils initially formed in the bone marrow may spread to the blood and then enter into and injure various tissues and organs. Clinically, clonal eosinophilia resembles various types of chronic or acute leukemias, lymphom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
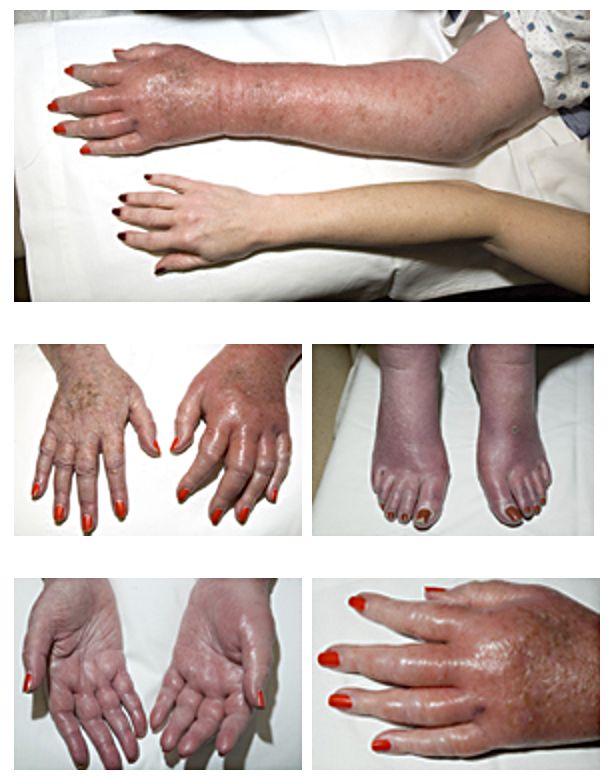
Polycythemia Vera
Polycythemia vera is an uncommon myeloproliferative neoplasm (a type of chronic leukemia) in which the bone marrow makes too many red blood cells. It may also result in the overproduction of white blood cells and platelets. Most of the health concerns associated with polycythemia vera are caused by the blood being thicker as a result of the increased red blood cells. It is more common in the elderly and may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Common signs and symptoms include itching (pruritus), and severe burning pain in the hands or feet that is usually accompanied by a reddish or bluish coloration of the skin. Patients with polycythemia vera are more likely to have gouty arthritis. Treatment consists primarily of phlebotomy. Signs and symptoms People with polycythemia vera can be asymptomatic. A classic symptom of polycythemia vera is pruritus or itching, particularly after exposure to warm water (such as when taking a bath), which may be due to abnormal histamine release o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloproliferative Disorders
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of rare blood cancers in which excess red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets are produced in the bone marrow. ''Myelo'' refers to the bone marrow, ''proliferative'' describes the rapid growth of blood cells and ''neoplasm'' describes that growth as abnormal and uncontrolled. The overproduction of blood cells is often associated with a somatic mutation, for example in the JAK2, CALR, TET2, and MPL gene markers. In rare cases, some MPNs such as primary myelofibrosis may accelerate and turn into acute myeloid leukemia. Classification MPNs are classified as blood cancers by most institutions and organizations. In MPNs, the neoplasm (abnormal growth) starts out as benign and can later become malignant. As of 2016, the World Health Organization lists the following subcategories of MPNs: * Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) * Chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) * Polycythemia vera (PV) * Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) ** PMF, Prefib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelofibrosis
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is growth of abnormal cells in the bone marrow. This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene markers. In PMF, the healthy marrow is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis), resulting in a lack of production of normal blood cells. Symptoms include anemia, increased infection and an enlarged spleen ( splenomegaly). In 2016, prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis was formally classified as a distinct condition that progresses to overt PMF in many patients, the primary diagnostic difference being the grade of fibrosis. Signs and symptoms The primary feature of primary myelofibrosis is bone marrow fibrosis, but it is often accompanied by: * Abdominal fullness related to an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly). * Bone pain * Bruising and easy bleeding due to inad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEL-JAK2
TEL-JAK2 is a gene fusion resulting from a chromosomal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 12 observed in human leukemia. The 5' moiety of ''TEL'' is fused to the 3' end of ''JAK2''. The oligomerisation domain of the TEL protein (also called ETV6) becomes juxtaposed to the tyrosine kinase In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ... domain of JAK2, and as result the TEL-JAK2 displays constitutive kinase activity. References External links * Human genes {{Improve categories, date=December 2022 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombopoietin Receptor
The thrombopoietin receptor also known as the myeloproliferative leukemia protein or CD110 (Cluster of Differentiation 110) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MPL (myeloproliferative leukemia virus) oncogene. Discovery In 1990 an oncogene, v-mpl, was identified from the murine myeloproliferative leukemia virus that was capable of immortalizing bone marrow hematopoietic cells from different lineages. In 1992 the human homologue, named, c-mpl, was cloned. Sequence data revealed that c-mpl encoded a protein that was homologous with members of the hematopoietic receptor superfamily. Presence of anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotides of c-mpl inhibited megakaryocyte colony formation. Function The ligand for c-mpl, thrombopoietin, was cloned in 1994. Thrombopoietin was shown to be the major regulator of megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet formation. The protein encoded by the c-mpl gene, CD110, is a 635 amino acid transmembrane domain, with two extracellular cytokine receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Receptor
Growth hormone receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GHR'' gene. GHR orthologs have been identified in most mammals. Structure Growth hormone receptor (GHR) is a transmembrane protein consisting of 620 amino acids. The receptor is part of the Type I cytokine receptor family of receptors. GHR exists in two forms as a full length membrane-bound receptor and as a soluble GH binding protein (GHBP). GHR contains two fibronectin type III β domains in its extracellular domain, whereas the intracellular domain contains tyrosine Kinase JAK2 binding sites for SH2 proteins. JAK2 is the primary signal transducer for growth hormone. Function This gene encodes a protein that is a transmembrane receptor for growth hormone. Binding of growth hormone to the receptor leads to reorientation of a pre-assembled receptor dimer dimerization (the receptor may however also exist as monomers on the cell surface ) and the activation of an intra- and intercellular signal transducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Thrombocythemia
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a rare chronic blood cancer (myeloproliferative neoplasm) characterised by the overproduction of platelets (thrombocytes) by megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. It may, albeit rarely, develop into acute myeloid leukemia or myelofibrosis. It is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm (blood cancers) wherein the body makes too many white or red blood cells, or platelets). Signs and symptoms Most people with essential thrombocythemia are without symptoms at the time of diagnosis, which is usually made after noting an elevated platelet level on a routine complete blood count (CBC). The most common symptoms are bleeding (due to dysfunctional platelets), blood clots (e.g., deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, visual disturbances, dizziness, fainting, and numbness in the extremities; the most common signs are increased white blood cell count, reduced red blood cell count, and an enlarged spleen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epo-R
The erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EPOR'' gene. EpoR is a 52kDa peptide with a single carbohydrate chain resulting in an approximately 56-57 kDa protein found on the surface of EPO responding cells. It is a member of the cytokine receptor family. EpoR pre-exists as dimers. These dimers were originally thought to be formed by extracellular domain interactions, however, it is now assumed that it is formed by interactions of the transmembrane domain and that the original structure of the extracellular interaction site was due to crystallisation conditions and does not depict the native conformation. Binding of a 30 kDa ligand erythropoietin (Epo), changes the receptor's conformational change, resulting in the autophosphorylation of Jak2 kinases that are pre-associated with the receptor (i.e., EpoR does not possess intrinsic kinase activity and depends on Jak2 activity). At present, the most well-established function of EpoR is to promote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Kinase
Janus kinase (JAK) is a family of intracellular, non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transduce cytokine-mediated signals via the JAK-STAT pathway. They were initially named "just another kinase" 1 and 2 (since they were just two of many discoveries in a PCR-based screen of kinases), but were ultimately published as "Janus kinase". The name is taken from the two-faced Roman god of beginnings, endings and duality, Janus, because the JAKs possess two near-identical phosphate-transferring domains. One domain exhibits the kinase activity, while the other negatively regulates the kinase activity of the first. Family The four JAK family members are: * Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) * Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) * Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) * Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) Transgenic mice that do not express JAK1 have defective responses to some cytokines, such as interferon-gamma. JAK1 and JAK2 are involved in type II interferon (interferon-gamma) signalling, whereas JAK1 and TYK2 are involved in type I interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-5 Receptor
The interleukin-5 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. It is a heterodimer of the interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit and CSF2RB. The IL-5 receptor (IL-5R) belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family and is a heterodimer composed of two polypeptide chains, one α subunit, which binds IL-5 and confers upon the receptor cytokine specificity, and one β subunit, which contains the signal transduction domains. α-subunit The IL-5Rα chain is exclusively expressed by eosinophils, some basophils and murine B1 cells or B cell precursors. Like many other cytokine receptors, alternative splicing of the α-chain gene results in expression of either a membrane bound or soluble form of the bα-chain. The soluble form does not lead to signal transduction and therefore has an antagonistic effect on IL-5 signaling. Both monomeric forms of IL-5Rα are low affinity receptors, while dimerization with the β-chain produces a high affinity receptor. In either case, the α-chain exclusively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GM-CSF-R
The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor also known as CD116 (Cluster of Differentiation 116), is a receptor for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, which stimulates the production of white blood cells. In contrast to M-CSF and G-CSF which are lineage specific, GM-CSF and its receptor play a role in earlier stages of development. The receptor is primarily located on neutrophils, eosinophils and monocytes/macrophages, it is also on CD34+ progenitor cells (myeloblasts) and precursors for erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages, but only in the beginning of their development. It is associated with Surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 4. Structure The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor is a heterodimer composed of at least two different subunits; an α chain, and a β chain which is also present in the receptors for IL-3 and IL-5. The α subunit contains a binding site for granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |