|
Jagdgeschwader III
''Jagdgeschwader III (Fighter Wing III, or JG III)'' was a fighter wing of the Imperial German Air Service during World War I. It was founded on 2 February 1918, as a permanent consolidation of four established ''jagdstaffeln'' (fighter squadrons)— 2, 26, 27, and 36. JG III was formed as a follow-on of Manfred von Richthofen's highly successful '' Jagdgeschwader I''. With a nominal strength of 56 aircraft, JG III would be under direct orders of an Armee headquarters. The German General Staff was planning a German spring offensive to begin on 21 March 1918, and wanted to assign a fighter wing to each of the three Armees involved in the assault.''Jagdgeschwader II'' was founded the same day from Jastas 12, 13, 15, and 19. An experienced flying ace with 22 victories, ''Oberleutnant'' Bruno Loerzer, was appointed to command JG III. On 12 to 15 March 1918, JG III's aircraft would be hidden near the front lines awaiting the Spring Offensive. On 21 March, the wing cleared the sky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
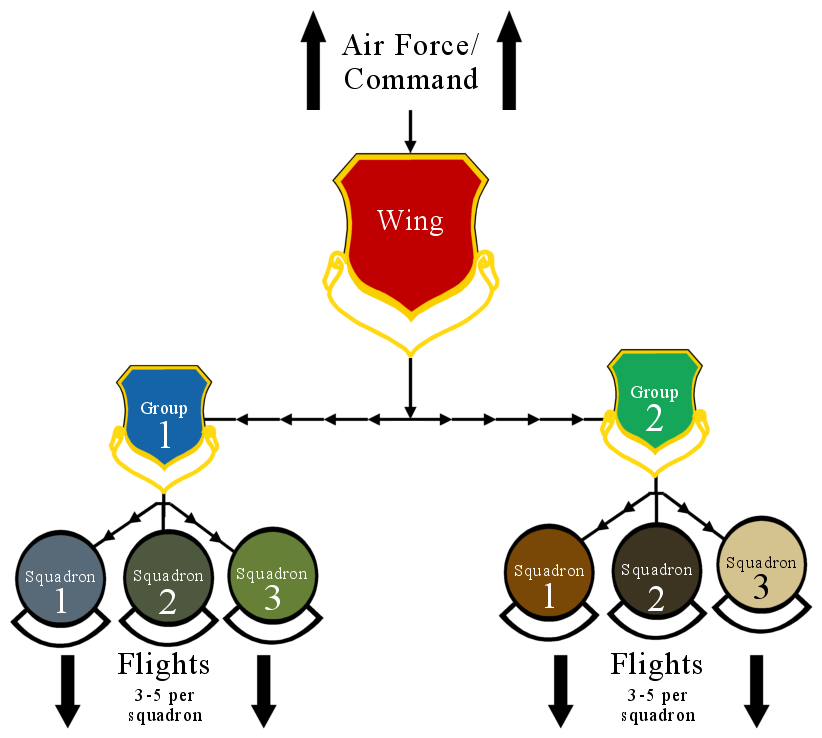
Fighter Wing
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadron" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Days Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allies of World War I, Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (1918), Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, the Allies pushed the Central Powers back, undoing their gains from the German spring offensive. The Germans retreated to the Hindenburg Line, but the Allies broke through the line with a series of victories, starting with the Battle of St Quentin Canal on 29 September. The offensive, together with a German Revolution of 1918–19, revolution breaking out in Germany, led to the Armistice of 11 November 1918 which ended the war with an Allied victory. The term "Hundred Days Offensive" does not refer to a battle or strategy, but rather the rapid series of Allied victories against which the German Army (German Empire), German Army had no reply. Background The German spring offensive of the German Army (Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberleutnant
() is the highest lieutenant officer rank in the German-speaking armed forces of Germany (Bundeswehr), the Austrian Armed Forces, and the Swiss Armed Forces. Austria Germany In the German Army, it dates from the early 19th century. Translated as "senior lieutenant", the rank is typically bestowed upon commissioned officers after five to six years of active-duty service. is used by both the German Army and the German Air Force. In the NATO military comparison system, a German is the equivalent of a First lieutenant in the Army/Air Forces of Allied nations. ;Other uses The equivalent naval rank is ''Oberleutnant zur See''. In Nazi Germany, within the SS, SA and Waffen-SS, the rank of Obersturmführer was considered the equivalent of an in the German Army. National People's Army In the GDR National People's Army (NPA) the rank was the highest lieutenant rank, until 1990. This was in reference to Soviet military doctrine and in line with other armed forces of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviator credited with shooting down five or more enemy aircraft during aerial combat. The exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ace is varied, but is usually considered to be five or more. The concept of the "ace" emerged in 1915 during World War I, at the same time as aerial dogfighting. It was a propaganda term intended to provide the home front with a cult of the hero in what was otherwise a war of attrition. The individual actions of aces were widely reported and the image was disseminated of the ace as a chivalrous knight reminiscent of a bygone era. For a brief early period when air-to-air combat was just being invented, the exceptionally skilled pilot could shape the battle in the skies. For most of the war, however, the image of the ace had little to do with the reality of air warfare, in which fighters fought in formation and air superiority depended heavily on the relative availability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdgeschwader II
''Jagdgeschwader II (Fighter Wing II, or JG II)'' was the Imperial German Air Service's second fighter wing. Established because of the great success of Manfred von Richthofen's preceding '' Jagdgeschwader I'' wing, ''Jagdgeschwader II'' and ''Jagdgeschwader III'' were founded on 2 February 1918. JG II was assigned four squadrons nominally equipped with 14 aircraft each. The new wing was supposed to be fully operational in time for an offensive slated for 21 March 1918. Named to raise and lead it was 23-victory flying ace ''Hauptmann'' Adolf von Tutschek. However, he was killed in action on 15 March 1918. His hasty replacement was 28-victory ace ''Hauptmann'' Rudolf Berthold. Grounded by wounds that rendered him narcotic-dependent, the ''Pour le Merite'' winner nevertheless firmly took charge. Under his leadership, JG II advanced 40 miles (64 kilometers) behind the German offensive. As the ground fighting stalled in early April, air fighting above it intensified. Then, on the nig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdgeschwader 1 (World War I)
''Jagdgeschwader'' I (JG I) of World War I, was a fighter wing of the German ''Luftstreitkräfte'', comprising four ''Jastas'' (fighter squadrons). The first unit of its type formed under that classification, JG I was formed on 24 June 1917, with Manfred von Richthofen as commanding officer, by combining ''Jastas'' 4, 6, 10 and 11. JG I became known as "The Flying Circus" (german: Der Fliegende Zirkus) or "Richthofen's Circus" because of the bright colours of its aircraft, and perhaps also because of the way the unit was transferred from one area of Allied air activity to another – moving like a travelling circus in trains, and frequently setting up in tents on improvised airfields. Formation During early 1917, it became apparent to the German High Command that they would always be outnumbered in air operations over the Western Front. The average Jasta could only muster some six or eight aircraft in total for a patrol, and would often face one Allied formation after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred Von Richthofen
Manfred Albrecht Freiherr von Richthofen (; 2 May 1892 – 21 April 1918), known in English as Baron von Richthofen or the Red Baron, was a fighter pilot with the German Air Force during World War I. He is considered the ace-of-aces of the war, being officially credited with 80 air combat victories. Originally a cavalryman, Richthofen transferred to the Air Service in 1915, becoming one of the first members of fighter squadron ''Jagdstaffel 2'' in 1916. He quickly distinguished himself as a fighter pilot, and during 1917 became the leader of ''Jasta 11''. Later he led the larger fighter wing '' Jagdgeschwader I'', better known as "The Flying Circus" or "Richthofen's Circus" because of the bright colours of its aircraft, and perhaps also because of the way the unit was transferred from one area of Allied air activity to another – moving like a travelling circus, and frequently setting up in tents on improvised airfields. By 1918, Richthofen was regarded as a nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasta 36
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 36, commonly abbreviated to Jasta 36, was a "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. The unit would score 123 confirmed aerial victories during the war, including 11 enemy observation balloons. In turn, they would suffer 13 killed in action, 15 wounded in action, two injured in flying accidents, and two taken prisoner of war. Operational history Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 36 was founded on 11 January 1917; however, it did not organize until 21 February. It began at FEA 13, Breslau, with its first commanding officer, Albert Dossenbach, assigned the following day. The new squadron began its operational history supporting 1 Armee from Le Châtelet. Le Chatelet took two weeks hectic construction to equip it as an airfield. It scored its first victory on 5 April 1917; coincidentally, it was Dossenbach's tenth. Spurred by his example, Jasta 36 pilots began to score; b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasta 27
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 27 (german: Königliche Preussische Jagdstaffel Nr. 27), commonly abbreviated to ''Jasta'' 27, was a "hunting group" (fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. Operational history As an independent squadron Jasta 27 was formed on 5 February 1917 at Ghent with eight aircraft and pilots. ''Armee-Flug-Park 4'' (Army Flight Park 4) at Ghent contributed three aircraft and pilots to the foundation. Two aircraft and pilots were transferred in from both ''Jagdstaffel 8'' and ''Jagdstaffel 18''. The newly appointed '' Staffelfuhrer'' (Squadron commander), Hans von Keudell, brought his own plane to the new unit, for the eighth aircraft. The newly formed unit moved forward to Gistel.VanWyngarden, p. 15. On 15 February 1917, Keudell led two of his pilots into combat in a three plane element of Albatros D.IIIs. He scored the first victory for the new squadron—his 12th overall—when he shot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdstaffel 26
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 26 was a "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. As one of the original German fighter squadrons, the unit would score 177 verified aerial victories, including four observation balloons destroyed. The Jasta would pay a bloody price for its success: five pilots killed in action, nine wounded in action, and one prisoner of war. Operational history As an independent squadron Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 26 (Jasta 26) was founded on 14 December 1916 at the FEA 9 training center in Darmstadt. On 18 January 1917, it entrained for Colmar Nord. It was detailed to support of ''Armee-Abteilung B''. Its first '' Staffelfuhrer'' (Commanding Officer) was Bruno Loerzer, assigned 21 January 1917. Its first war patrols followed a week later. On 25 February, his old friend Hermann Göring joined Jasta 26. Also, the squadron's first victory was scored on 25 February 1917. From there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |