|
Jack Northrop
John Knudsen Northrop (November 10, 1895 – February 18, 1981) was an American aircraft industrialist and designer who founded the Northrop Corporation in 1939. His career began in 1916 as a draftsman for Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company (founded 1912). He joined the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1923, where in time he became a project engineer. In 1927 he joined the Lockheed Corporation, where he was a chief engineer on the Lockheed Vega transport. He left in 1929 to found Avion Corporation, which he sold in 1930. Two years later, he founded the Northrop Corporation. This firm became a subsidiary of Douglas Aircraft in 1939, so he co-founded a second company named Northrop. Early life and entering aviation Born in Newark, New Jersey in 1895, Northrop grew up in Santa Barbara, California. In 1916 Northrop's first job in aviation was in working as a draftsman for the Santa Barbara-based Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company. After the outbreak of the First World War, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop YB-35
The Northrop YB-35, Northrop designation N-9 or NS-9, were experimental heavy bomber aircraft developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Army Air Forces during and shortly after World War II. The airplane used the radical and potentially very efficient flying wing design, in which the tail section and fuselage are eliminated and all payload is carried in a thick wing. Only prototypes and pre-production aircraft were built, although interest remained strong enough to warrant further development of the design as a jet bomber, under the designation Northrop YB-49, YB-49.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 93, 95, 103–6, Cypress, CA, 2013. . Design and development The B-35 was the brainchild of John Knudsen Northrop, Jack Northrop, who made the flying wing the focus of his work during the 1930s. In 1941 before the USA entered World War II, Northrop and Consolidated Vultee Corporation had been c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Wills Douglas, Sr
Donald is a masculine given name derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers, and partly associated with the spelling of similar-sounding Germanic names, such as '' Ronald''. A short form of ''Donald'' is ''Don''. Pet forms of ''Donald'' include ''Donnie'' and ''Donny''. The feminine given name ''Donella'' is derived from ''Donald''. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop N-9M
The Northrop N-9M was an approximately one-third scale, span all-wing aircraft used for the development of the full size, wingspan Northrop XB-35 and YB-35 flying wing long-range, heavy bomber. First flown in 1942, the N-9M (M for Model) was the third in a lineage of all-wing Northrop aircraft designs that began in 1929 when Jack Northrop succeeded in early experiments with his single pusher propeller, twin-tailed, twin-boom, all stressed metal skin Northrop X-216H monoplane, and a decade later, the dual-propeller N-1M of 1939–1941.O'Leary 2007, p. 62. Northrop's pioneering all-wing aircraft would lead Northrop Grumman many years later to eventually develop the advanced B-2 Spirit stealth bomber, which debuted in 1989 in US Air Force inventory. Design and development On 30 October 1941, the preliminary order for development of the B-35 Flying Wing bomber was confirmed, including engineering, testing, and most importantly a 60 ft (18 m) wingspan, one-third scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop N-1M
The Northrop N-1M (''Northrop Model 1 Mockup''), also known by the nickname "Jeep", is a retired American experimental aircraft used in the development of the flying wing concept by Northrop Aircraft during the 1940s. Design and development Jack Northrop became involved with all-wing aircraft designs in the late-1920s, with his first flying wing research prototype being built in the 1928–1930 time period. That first prototype, registered X-216H, had evolved from earlier design studies but was not yet a true flying wing as it retained a tail unit comprising twin rudders with a single horizontal stabilizer running between them; both rudders were connected by twin booms to the thick, all-wing blended fuselage. The aircraft had an open cockpit in the center wing section and single, rear-facing, pusher propeller connected to a Menasco Cirrus inverted-four piston engine blended into the all-wing shape. X-216H was first flown in 1929 with Edward Bellande at the controls; the aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop Snark
The Northrop SM-62 Snark is an early-model intercontinental range ground-launched cruise missile that could carry a W39 thermonuclear warhead. The Snark was deployed by the United States Air Force's Strategic Air Command from 1958 through 1961. It represented an important step in weapons technology during the Cold War. The Snark was named by Jack Northrop and took its name from the author Lewis Carroll's character the "snark". ‘’From Snark to Peacekeeper. Office of the Historian, Strategic Air Command, Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska (1990). The Snark was the only surface-to-surface cruise missile with such a long range that was ever deployed by the U.S. Air Force. Following the deployment of ICBMs, the Snark was rendered obsolete, and it was removed from deployment in 1961. Design and Development Project Mastiff, to create a missile for delivery for an atom bomb began immediately after the existence of the atomic bomb was revealed. Due to protracted security concerns of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop YB-49
The Northrop YB-49 was an American prototype jet-powered heavy bomber developed by Northrop Corporation shortly after World War II for service with the United States Air Force. The YB-49 featured a flying wing design and was a turbojet-powered development of the earlier, piston-engined Northrop XB-35 and YB-35. The two YB-49s actually built were both converted YB-35 test aircraft. The YB-49 never entered production, being passed over in favor of the more conventional Convair B-36 piston-driven design. Design work performed in the development of the YB-35 and YB-49 nonetheless proved to be valuable to Northrop decades later in the eventual development of the B-2 stealth bomber, which entered service in the early 1990s. Design and development With the XB-35 program seriously behind schedule by 1944, and the end of piston-engined combat aircraft in sight, the production contract for this propeller-driven type was cancelled in May of that year. Nevertheless, the Flying Wing des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop F-89 Scorpion
The Northrop F-89 Scorpion was an American all-weather, twin-engined interceptor aircraft built during the 1950s, the first jet-powered aircraft designed for that role from the outset to enter service. Though its straight wings limited its performance, it was among the first United States Air Force (USAF) jet fighters equipped with guided missiles and notably the first combat aircraft armed with air-to-air nuclear weapons (the unguided Genie rocket). Design and development The Scorpion stemmed from a United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) Air Technical Service Command specification ("Military Characteristics for All-Weather Fighting Aircraft") for a night fighter to replace the P-61 Black Widow. The preliminary specification, sent to aircraft manufacturers on 28 August 1945, required two engines and an armament of six guns, either machine guns or autocannon. The revised specification was issued on 23 November; it did not specify jet propulsion, but the desired maximum speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
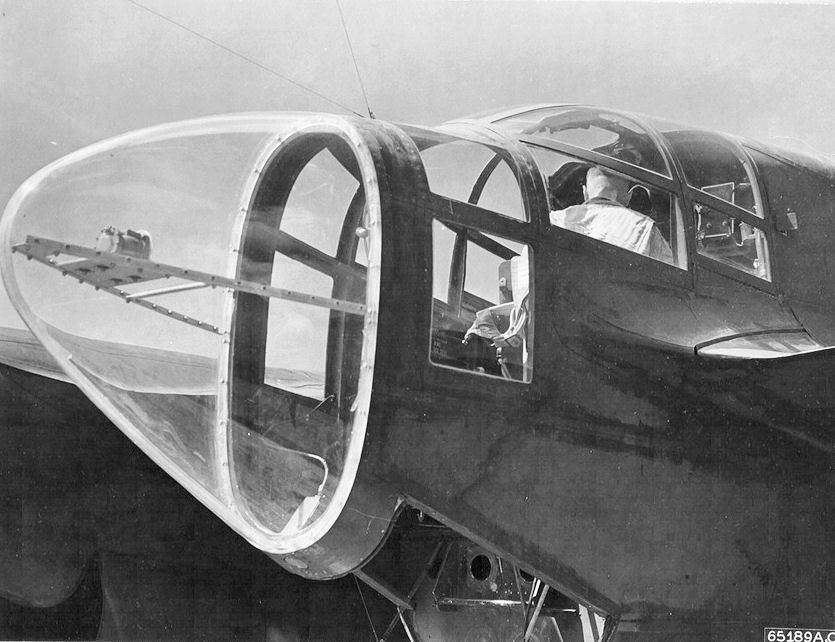
Northrop P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider ''Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on May 26, 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet
The Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet was a unique prototype fighter interceptor built by the Northrop Corporation. It was one of the most radical of the experimental aircraft built during World War II. Ultimately, it was unsuccessful and did not enter production. Design and development The initial idea for the XP-56 was quite radical for 1939. It was to have no horizontal tail, only a small vertical tail, used an experimental engine, and be produced using a novel metal, magnesium. The aircraft was to be a wing with a small central fuselage added to house the engine and pilot. It was hoped that this configuration would have less aerodynamic drag than a conventional airplane. The idea for this single-seat aircraft originated in 1939 as the Northrop N2B model. It was designed around the Pratt & Whitney liquid-cooled X-1800 engine in a pusher configuration driving contra-rotating propellers. The U.S. Army ordered Northrop to begin design work on 22 June 1940, and after reviewing the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Wing
A flying wing is a tailless fixed-wing aircraft that has no definite fuselage, with its crew, payload, fuel, and equipment housed inside the main wing structure. A flying wing may have various small protuberances such as pods, nacelles, blisters, booms, or vertical stabilizers. Similar aircraft designs, that are not technically flying wings, are sometimes casually referred to as such. These types include blended wing body aircraft and lifting body aircraft, which have a fuselage and no definite wings. A pure flying wing is theoretically the lowest drag design configuration for a fixed wing aircraft. However, because it lacks conventional stabilizing surfaces and the associated control surfaces, in its purest form the flying wing suffers from being unstable and difficult to control. The basic flying wing configuration became an object of significant study during the 1920s, often in conjunction with other tailless designs. In the Second World War, both Nazi Germany and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moye Stephens
Moye Wicks Stephens (February 21, 1906 – 1995) was an American aviator and businessman. He was a pioneer in aviation, circumnavigating the globe with adventure writer Richard Halliburton in 1931, and co-founding Northrop Aircraft, Inc. Family His father was also named Moye Wicks Stephens; his mother was Mary Hendrick Stephens. His grandparents, Judge and Mrs. Albert Moye Stephens, had a ranch in the mountains near Pomona, California. He married Contessa Gadina de Turiani, an aviator from Trieste, Italy, who had divorced millionaire aviator Ross Hadley. In later years Stephens lived in Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico; he died in Calistoga, California in 1995. Friends and acquaintances Stephens knew barnstormers and World War I flying aces, pioneers of early aviation. These were people such as Frank Clarke, Pancho Barnes, Sandy Sandblom, Leo Nomis, Bud Creeth, Eddie Bellande, Ross Hadley, and Stephens's lifelong best friend, Dick Rinaldi. He knew movie stars such as Richar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawthorne, California
Hawthorne is a city in the Los Angeles metropolitan area, located in southwestern Los Angeles County, California. It is part of a seventeen-city region commonly called the South Bay. As of the 2020 US census, Hawthorne had a population of 88,083. History Hawthorne was founded in 1905 as the "Hawthorne Improvement Company" by B.L. Harding and H.D. Lombard. Harding's daughter shared her birthday—the 4th of July, American Independence Day—with New England author Nathaniel Hawthorne, and a decision was made to name the city after him. Hawthorne was once a "whites only" settlement, commonly called a sundown town. During the 1930s, signs warned African-Americans to be out of Hawthorne by sundown. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of , over 99% of it land. To the north of Hawthorne is the unincorporated community of Lennox and the city of Inglewood. To the east is the unincorporated community of Athens and the city of Gardena. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
_(cropped).jpg)