|
Ja'far Ibn Abi Talib
Jaʿfar ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, جعفر بن أبي طالب September 629), also known as Jaʿfar al-Ṭayyār ( ar, جعفر الطيّار, lit=Ja'far the Flyer) was a companion and cousin of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, and an older brother of Ali. Early life Ja'far was the third son of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Fatimah bint Asad, hence a cousin of Muhammad. His older brothers were Talib and Aqil, and his younger brothers were Ali and Tulayq, and his sisters were Fakhita, Jumana and Raytah. When there was a drought in his birthplace of Mecca, Abu Talib could not afford to support his family. His brother 'Abbas therefore took charge of the young Ja'far.Muhammad ibn Ishaq, ''Sirat Rasul Allah''. Translated by Guillaume, A. (1955). ''The Life of Muhammad' Ja'far was an early convert to Islam. He married Asma bint Umais, who converted to Islam in 614–615.Ibn Saad/Bewley vol. 8 p. 196. London: Ta-Ha Publishers. Migration to Abyssinia When the Muslims we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is the artistic practice of handwriting and calligraphy, in the languages which use Arabic alphabet or the alphabets derived from it. It includes Arabic, Persian, Ottoman, and Urdu calligraphy.Chapman, Caroline (2012). ''Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture'', It is known in Arabic as ''khatt Arabi'' (), which translates into Arabic line, design, or construction. The development of Islamic calligraphy is strongly tied to the Qur'an; chapters and excerpts from the Qur'an are a common and almost universal text upon which Islamic calligraphy is based. Although artistic depictions of people and animals are not explicitly forbidden by the Qur'an, pictures have traditionally been limited in Islamic books in order to avoid idolatry. Although some scholars dispute this, Kufic script was supposedly developed around the end of the 7th century in Kufa, Iraq, from which it takes its name. The style later developed into several varieties, including floral, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awn Ibn Ja'far
ʿAwn ibn Jaʿfar () was a companion and relative of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was born in Abyssinia, the third son of Ja'far ibn Abi Talib and Asma bint Umais. The family returned to Medina in 628. He married his cousin, Umm Kulthum bint Ali Zaynab al-Ṣughrā ( ar, زَيْنَب ٱلصُّغْرَىٰ, lit=Zaynab the Younger), also known by her kunya Umm Kulthūm bint ʿAlī ( ar, أُمّ كُلْثُوم بِنْت عَلِيّ, link=no), was the granddaughter of the Islamic p ..., who was a granddaughter of Muhammad. They had no children.Ibn Saad/Bewley p. 299. References Companions of the Prophet {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historically spanned the geographical area of present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak approximately in 1270 until the 1974 coup d'etat of Emperor Haile Selassie by the Derg. By 1896, the Empire incorporated other regions such as Hararghe, Gurage and Wolayita, and saw its largest expansion with the federation of Eritrea in 1952. Throughout much of its existence, it was surrounded by hostile forces in the African Horn; however, it managed to develop and preserve a kingdom based on its ancient form of Christianity. Founded in 1270 by the Solomonic Dynasty nobleman Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Aksumite king and ultimately the Biblical Menelik I and the Queen of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) " e Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, with its followers ranging between 1-1.8 billion globally, or around a quarter of the world' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas Ibn Abd Al-Muttalib
Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib ( ar, ٱلْعَبَّاسُبْنُ عَبْدِ ٱلْمُطَّلِبِ, al-ʿAbbās ibn ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib; CE) was a paternal uncle and Sahabi (companion) of Muhammad, just three years older than his nephew. A wealthy merchant, during the early years of Islam he protected Muhammad while he was in Mecca, but only became a convert after the Battle of Badr in 624 CE (2 AH). His descendants founded the Abbasid dynasty in 750. Early years Abbas, born around 565 CE, was one of the younger sons of Abd al-Muttalib. His mother was Nutayla bint Janab of the Namir tribe. After his father's death, he took over the Zamzam Well and the distribution of water to the pilgrims. He became a spice-merchant in Mecca, a trade that made him wealthy. Conversion to Islam During the years when the Muslim religion was gaining adherents (610–622), Abbas provided protection to his kinsman but did not adopt the faith. He acted as a spokesman at the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahlul Bayt Digital Islamic Library Project
The Ahlul Bayt Digital Library Project (Ahlul Bayt DILP), established in 1996, is a non-profit Islamic organization that features work from a group of volunteers operating throughout the world. It operates the website Al-Islam.org – whose primary objective is to digitize and present quality resources related to the history, law, and society of the Islamic religion and its personalities – with particular emphasis on the Twelver Shi'ah Islamic school of thought. Al-Islam.org is a site that also serves as a means of introducing Islam to non-Muslims. Aims The Ahlul Bayt DILP aims to encourage the research of Islam and to facilitate the propagation of knowledge to locations where such resources are not commonly or easily accessible. To cater to this objective, the Ahlul Bayt DILP is constantly expanding its digital library, which consists of over 4000 resources accessible for free. The Ahlul Bayt DILP states that it also aims: History Since its launch, Al-islam.org has proven to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophets And Messengers In Islam
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers ( ar, رسل, rusul, sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, most of them through the interaction of an angel. Muslims believe that many prophets existed, including many not mentioned in the Quran. The Quran states: "And for every community there is a messenger." Belief in the Islamic prophets is one of the six articles of the Islamic faith. Muslims believe that the first prophet was also the first human being, Adam, created by God. Many of the revelations delivered by the 48 prophets in Judaism and many prophets of Christianity are mentioned as such in the Quran but usually with Arabic versions of their names; for example, the Jewish Elisha is called Alyasa', Job is Ayyub, Jesus is 'Isa, et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
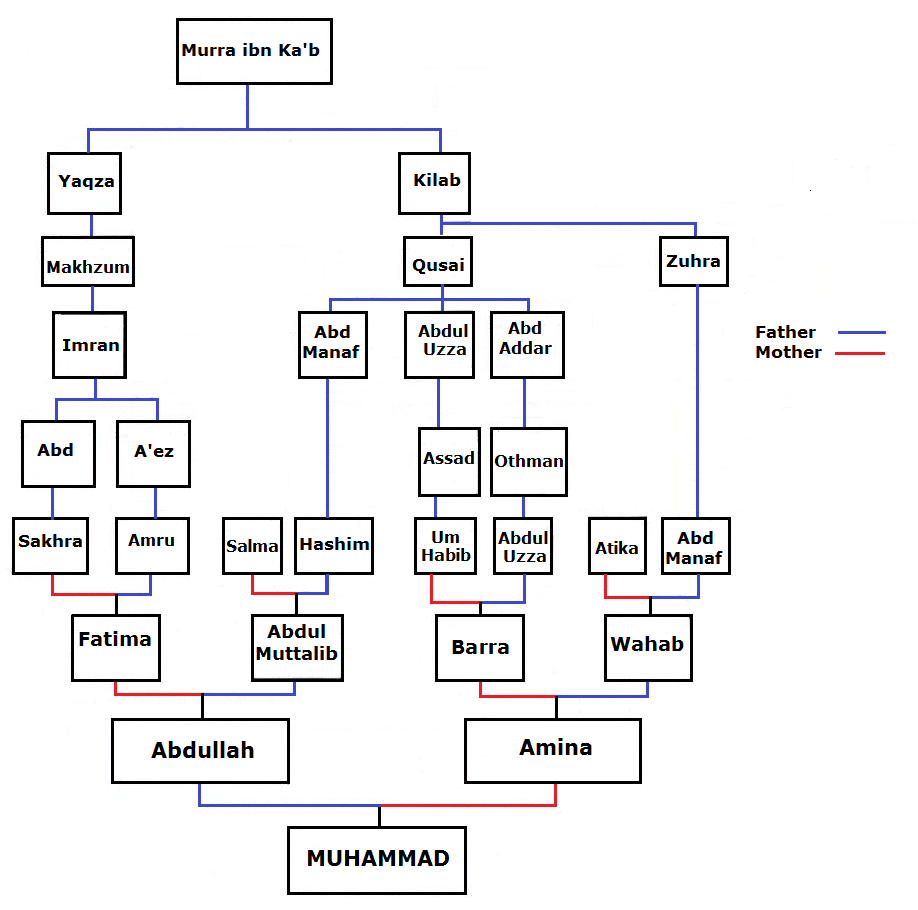
Family Tree Of Muhammad
This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad known as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Qurayshs tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label ‘arabicised’ is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayta Bint Abi Talib
Rayṭa bint Abī Ṭālib ( ar, رَيْطَة بِنْت أَبِي طَالِب), was a companion and first cousin of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Translated by A. Guillaume Translated by Haq, S. M.; Parts I & II Translated by Bewley, A. Family She was the youngest daughter of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Fatimah bint Asad. She was also known as "Asmā’", and she was probably the same daughter known as "Umm Ṭālib" ( ar, أُمّ طَالِب), indicating that she had a son named Talib. History In 628 CE, Muhammad assigned Umm Talib an income of 40 ' from Khaybar KhaybarOther standardized Arabic transliterations: / . Anglicized pronunciation: , . ( ar, خَيْبَر, ) is an oasis situated some north of the city of Medina in the Medina Province of Saudi Arabia. Prior to the rise of Islam in the 7th .... References Women companions of the Prophet {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumanah Bint Abi Talib
Jumānah bint Abī Ṭālib ( ar, جمانة بنت أبي طالب) was a companion and first cousin of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. She was a daughter of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Fatimah bint Asad. She married her cousin, Abu Sufyan ibn al-Harith, and they had a son, Ja'far. Abu Sufyan was hostile to Islam for a long time. In 630 he told Jumanah that he intended to convert. She responded: "Finally, you see that Bedouins and foreigners have followed Muhammad, while you have been his confirmed foe! You should have been the first person to assist him!" She accompanied him on his journey to meet Muhammad at Al-Abwa; but Muhammad refused to see him. They followed Muhammad all the way back to Mecca. After the conquest, Jumanah accompanied some women from the Muttalib clan on a visit to Muhammad. She "softened" him about her husband; but it was only after the Battle of Hunayn that he accepted Abu Sufyan's conversion as genuine. Muhammad gave Jumanah 30 of dates (i.e. about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakhitah Bint Abi Talib
Fākhitah bint Abī Ṭālib ( ar, فاختة بنت أبي طالب), also known as Hind and better known by her kunya Umm Hānī, was a cousin and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Early life She was the eldest daughter of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Fatima bint Asad,Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir'', vol. 8. Translated by Bewley, A. (1995). ''The Women of Madina''. London: Ta-Ha Publishers.Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari. ''Tarikh al-Rasul wa'l-Muluk''. Translated by Landau Tasseron, E. (1998). ''Volume 39: Biographies of the Prophet's Companions and Their Successors''. Albany: State University of New York University Press. hence a sister of Ali. Marriage Before 595 the young Muhammad asked Abu Talib's permission to marry Fakhitah, but Abu Talib accepted an alternative proposal from Hubayra ibn Abi Wahb, a member of the wealthy Makhzum clan. Muhammad asked: "Uncle, why have you married her off to Hubayra and ignored me?" Abu Talib replied: "N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talib Ibn Abi Talib
Ṭālib ibn Abī Ṭālib () was a first cousin of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a brother of Ali. Family He was born in Mecca, the eldest son of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and of Fatimah bint Asad.Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir''. Translated by Haq, S. M. (1967). ''Ibn Sa'd's Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir, Volume I Parts I & II'', 135. Delhi: Kitab Bhavan. The young Muhammad lived in their house from the time he and Talib were both eight years old.Muhammad ibn Ishaq. ''Sirat Rasul Allah''. Translated by Guillaume, A. (1955). ''The Life of Muhammad''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. He had no offspring.. Inheritance Law When his father Abu Talib died in 620, his inheritance was divided between Talib and his brother Aqil. Their two younger brothers, Ja'far and Ali, did not inherit anything. Battle of Badr In 624 Talib set out with the Meccan army to rescue the merchant-caravan that was threatened with a Muslim attack. When word came from Abu Sufyan that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)