|
JT3D
The Pratt & Whitney JT3D is an early turbofan aircraft engine derived from the Pratt & Whitney JT3C. It was first run in 1958 and was first flown in 1959 under a B-45 Tornado test aircraft. Over 8,000 JT3Ds were produced between 1959 and 1985. Most JT3D engines still in service today are used on military aircraft, where the engine is referred to by its US military designation of TF33. Design and development Aware of the competition from the Rolls-Royce Conway turbofan, Pratt & Whitney decided to develop the JT3D turbofan from the JT3C turbojet for later deliveries of the Boeing 707 and the Douglas DC-8, then nearing entry into service. A 2-stage fan replaced the first 3 stages of the 9-stage JT3C LP compressor. On the LP turbine, the second stage was enlarged and a third stage added. Unlike GE with the CJ805-23, Pratt & Whitney had not undertaken any transonic fan research prior to designing the JT3D, so they were unable to incorporate a single stage unit into the specification. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TF33 Engine At Davis-Monthan AFB 1984
The Pratt & Whitney JT3D is an early turbofan aircraft engine derived from the Pratt & Whitney J57, Pratt & Whitney JT3C. It was first run in 1958 and was first flown in 1959 under a B-45 Tornado test aircraft. Over 8,000 JT3Ds were produced between 1959 and 1985. Most JT3D engines still in service today are used on military aircraft, where the engine is referred to by its US military designation of TF33. Design and development Aware of the competition from the Rolls-Royce Conway turbofan, Pratt & Whitney decided to develop the JT3D turbofan from the JT3C turbojet for later deliveries of the Boeing 707 and the Douglas DC-8, then nearing entry into service. A 2-stage fan replaced the first 3 stages of the 9-stage JT3C LP compressor. On the LP turbine, the second stage was enlarged and a third stage added. Unlike GE with the CJ805-23, Pratt & Whitney had not undertaken any transonic fan research prior to designing the JT3D, so they were unable to incorporate a single stage unit in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-8
The Douglas DC-8 (sometimes McDonnell Douglas DC-8) is a long-range narrow-body airliner built by the American Douglas Aircraft Company. After losing the May 1954 US Air Force tanker competition to the Boeing KC-135, Douglas announced in July 1955 its derived jetliner project. In October 1955, Pan Am made the first order along with the competing Boeing 707, and many other airlines followed. The first DC-8 was rolled out in Long Beach Airport on April 9, 1958, and flew for the first time on May 30. FAA certification was achieved in August 1959 and the DC-8 entered service with Delta Air Lines on September 18. The six-abreast, low wing airliner was a four-engined jet aircraft with initial variants being long. The DC-8-10 was powered by Pratt & Whitney JT3C turbojets and had a MTOW, the DC-8-20 had more powerful JT4A turbojets for a MTOW. The intercontinental models had more fuel capacity and up to MTOW, powered by JT4As for the Series 30 and by Rolls-Royce Conway turbofa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first flew on December 20, 1957. Pan American World Airways began regular 707 service on October 26, 1958. With versions produced until 1979, the 707 was a swept wing, quadjet with podded engines. Its larger fuselage cross-section allowed six-abreast economy seating, retained in the later 720, 727, 737, and 757 models. Although it was not the first commercial jetliner in service, the 707 was the first to be widespread and is often credited with beginning the Jet Age. It dominated passenger air transport in the 1960s, and remained common through the 1970s, on domestic, transcontinental, and transatlantic flights, as well as cargo and military applications. It established Boeing as a dominant airliner manufacturer with its 7x7 series. The initial, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney J57
The Pratt & Whitney J57 (company designation: JT3C) is an axial-flow turbojet engine developed by Pratt & Whitney in the early 1950s. The J57 (first run January 1950) was the first 10,000 lbf (45 kN) thrust class engine in the United States. The J57/JT3C was developed into the J52 turbojet, the J75/JT4A turbojet, the JT3D/TF33 turbofan, and the XT57 turboprop (of which only one was built). The J57 and JT3C saw extensive use on fighter jets, jetliners, and bombers for many decades. Design and development The J57 was a development of the Pratt & Whitney XT45 (PT4) turboprop engine that was originally intended for the Boeing XB-52. As the B-52 power requirements grew, the design evolved into a turbojet, the JT3. Pratt & Whitney designed the J57 to have a relatively high overall pressure ratio to help improve both Thrust-specific fuel consumption and specific thrust, but it was known that throttling a single high pressure ratio compressor would cause stability prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
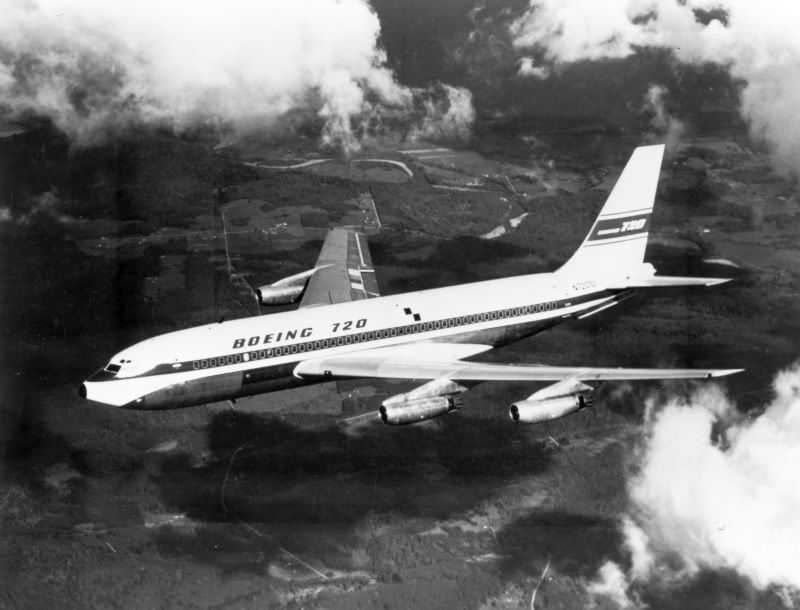
Boeing 720
The Boeing 720 is an American narrow-body airliner produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Announced in July 1957 as a 707 derivative for shorter flights from shorter runways, the 720 first flew on November 23, 1959. Its type certificate was issued on June 30, 1960, and it entered service with United Airlines on July 5, 1960. A total of 154 Boeing 720s and 720Bs were built until 1967. As a derivative, the 720 had low development costs, allowing profitability despite few sales. Compared to the 707-120, it has a length reduced by 8.33 feet (2.54 m), a modified wing and a lightened airframe for a lower maximum takeoff weight. Originally designed to be powered by four Pratt & Whitney JT3C turbojets, the initial 720 would cover a range with 131 passengers in two classes. The reconfigured 720B, powered by JT3D turbofans, first flew on October 6, 1960, and entered service in March 1961. It could seat 156 passengers in one class over a range. Some 720s were later converted to 720 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed C-141 Starlifter
The Lockheed C-141 Starlifter is a retired military strategic airlifter that served with the Military Air Transport Service (MATS), its successor organization the Military Airlift Command (MAC), and finally the Air Mobility Command (AMC) of the United States Air Force (USAF). The aircraft also served with airlift and air mobility wings of the Air Force Reserve (AFRES), later renamed Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC), the Air National Guard (ANG) and, later, one air mobility wing of the Air Education and Training Command (AETC) dedicated to C-141, C-5, C-17 and KC-135 training. Introduced to replace slower propeller driven cargo planes such as the Douglas C-124 Globemaster II and Douglas C-133 Cargomaster, the C-141 was designed to requirements set in 1960 and first flew in 1963. Production deliveries of an eventual 285 planes began in 1965: 284 for the USAF, and a company demonstrator later delivered to National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for use as an airborne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney J75
The Pratt & Whitney J75 (civilian designation: JT4A) is an axial-flow turbojet engine first flown in 1955. A two-spool design in the 17,000 lbf (76 kN) thrust class, the J75 was essentially the bigger brother of the Pratt & Whitney J57 (JT3C). It was known in civilian service as the JT4A, and in a variety of stationary roles as the GG4 and FT4. Design and development In military use, the J75 was used on the Convair F-106 Delta Dart, Lockheed U-2, and Republic F-105 Thunderchief. It was also utilized in the prototype and experimental Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow, Lockheed A-12, Martin P6M SeaMaster, North American YF-107, and Vought XF8U-3 Crusader III. Before the arrival of the Pratt & Whitney JT3D turbofan engine, the JT4A was used to power certain Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 models, bringing improved field performance in the medium-range Boeing 707-220 and Douglas DC-8-20, and intercontinental range in the Boeing 707-320 and the Douglas DC-8-30. By late 1959, P&W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing E-3 Sentry
The Boeing E-3 Sentry is an American airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) aircraft developed by Boeing. E-3s are commonly known as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System). Derived from the Boeing 707 airliner, it provides all-weather surveillance, command, control, and communications, and is used by the United States Air Force, NATO, French Air and Space Force, Royal Saudi Air Force and Chilean Air Force. The E-3 is distinguished by the distinctive rotating radar dome (rotodome) above the fuselage. Production ended in 1992 after 68 aircraft had been built. In the mid-1960s, the U.S. Air Force (USAF) was seeking an aircraft to replace its piston-engined Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star, which had been in service for over a decade. After issuing preliminary development contracts to three companies, the USAF picked Boeing to construct two airframes to test Westinghouse Electric and Hughes's competing radars. Both radars used pulse-Doppler technology, with Westinghou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) since the 1950s. The bomber is capable of carrying up to 70,000 pounds (32,000 kg) of weapons,"Fact Sheet: B-52 Superfortress." ''Minot Air Force Base'', United States Air Force, October 2005. Retrieved: 12 January 2009. and has a typical combat range of around 8,800 miles (14,080 km) without aerial refueling. Beginning with the successful contract bid in June 1946, the B-52 design evolved from a < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut.Contact Us ." Pratt & Whitney. Retrieved on January 7, 2011. "Corporate Headquarters Pratt & Whitney 400 Main Street East Hartford, CT 06108." As one of the "big three" aero-engine manufacturers, it competes with and Rolls-Royce, although it has also formed joint ventures with both of these companies. In additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-52H Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) since the 1950s. The bomber is capable of carrying up to 70,000 pounds (32,000 kg) of weapons,"Fact Sheet: B-52 Superfortress." ''Minot Air Force Base'', United States Air Force, October 2005. Retrieved: 12 January 2009. and has a typical combat range of around 8,800 miles (14,080 km) without aerial refueling. Beginning with the successful contract bid in June 1946, the B-52 design evolved from a < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Conway
The Rolls-Royce RB.80 Conway was the first turbofan engine to enter service. Development started at Rolls-Royce in the 1940s, but the design was used only briefly, in the late 1950s and early 1960s, before other turbofan designs replaced it. However, the Conway engine was used in versions of the Handley Page Victor, Vickers VC10, Boeing 707-420 and Douglas DC-8-40. The name "Conway" is the English spelling of the River Conwy, in Wales, in keeping with Rolls' use of river names for gas turbine engines. Development Background Alan Arnold Griffith had proposed a number of different bypass or turbofan engine designs as early as the 1930s while he and Hayne Constant were trying to get their axial-flow jet engines working at the Royal Aircraft Establishment. However, simpler turbojet designs were prioritized during World War II for their use in military applications. Priorities changed dramatically at the end of the war and in 1946 Rolls-Royce agreed that existing engines lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |