|
JT-60U
JT-60 (short for Japan Torus-60) is a large research tokamak, the flagship of Japan's magnetic fusion program, previously run by the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and currently run by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency's (JAEA) Naka Fusion Institute in Ibaraki Prefecture. It is properly an advanced tokamak, including a D-shaped plasma cross-section and active feedback control. First designed in the 1970s as the "Breakeven Plasma Test Facility" (BPTF), the goal of the system was to reach the deuterium equivalent of breakeven, breakeven fusion power, a goal set for the US's Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor, TFTR, the UK's Joint European Torus, JET and the Soviet T-15. JT-60 began operations in 1985, and like the TFTR and JET that began operations only shortly before it, JT-60 demonstrated performance far below predictions. Over the next two decades, JET and JT-60 led the effort to regain the performance originally expected of these machines. JT-60 underwent two major modific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint European Torus
The Joint European Torus, or JET, is an operational Magnetic confinement fusion, magnetically confined Plasma (physics), plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility is a joint European project with a main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. At the time of its design JET was larger than any comparable machine. JET was built with the hope of reaching fusion energy gain factor, ''scientific breakeven'' where the fusion energy gain factor ''Q'' =1.0. It began operation in 1983 and spent most of the next decade increasing its performance in a lengthy series of experiments and upgrades. In 1991 the first experiments including tritium were made, making JET the first reactor in the world to run on the production fuel of a 50–50 mix of tritium and deuterium. It was also decided to add a divertor, divertor design to JET, which occurred between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Energy Gain Factor
A fusion energy gain factor, usually expressed with the symbol ''Q'', is the ratio of fusion power produced in a nuclear fusion reactor to the power required to maintain the plasma in steady state. The condition of ''Q'' = 1, when the power being released by the fusion reactions is equal to the required heating power, is referred to as breakeven, or in some sources, scientific breakeven. The energy given off by the fusion reactions may be captured within the fuel, leading to ''self-heating''. Most fusion reactions release at least some of their energy in a form that cannot be captured within the plasma, so a system at ''Q'' = 1 will cool without external heating. With typical fuels, self-heating in fusion reactors is not expected to match the external sources until at least ''Q'' ≈ 5. If ''Q'' increases past this point, increasing self-heating eventually removes the need for external heating. At this point the reaction becomes self-sustaining, a condition called combustion, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. , it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. Tokamaks were initially conceptualized in the 1950s by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov, inspired by a letter by Oleg Lavrentiev. The first working tokamak was attributed to the work of Natan Yavlinsky on the T-1 in 1958. It had been demonstrated that a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helix. Devices like the z-pinch and stellarator had attempted this, but demonstrated serious instabilities. It was the development of the concept now known as the safety factor (labelled ''q'' in mathematical notation) that guided tokamak development; by arrang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). ( Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITER
ITER (initially the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, ''iter'' meaning "the way" or "the path" in Latin) is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy by replicating, on Earth, the fusion processes of the Sun. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for late 2025, it will be the world's largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment and the largest experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with ten times the plasma volume of any other tokamak operating today. The long-term goal of fusion research is to generate electricity. ITER's stated purpose is scientific research, and technological demonstration of a large fusion reactor, without electricity generation. ITER's goals are to achieve enough fusion to produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
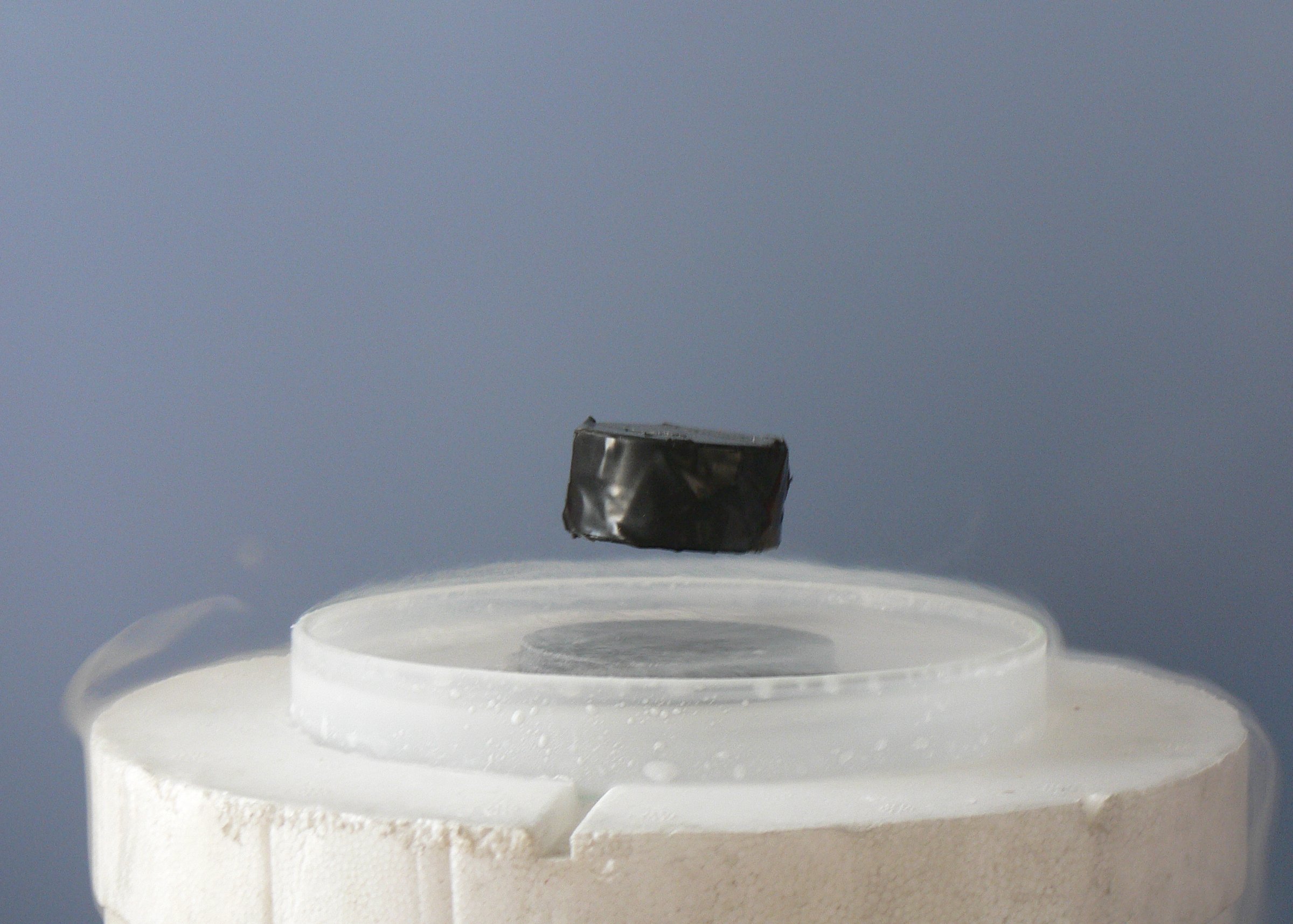
Superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotropes Of Iron
At atmospheric pressure, three allotropic forms of iron exist, depending on temperature: alpha iron (α-Fe), gamma iron (γ-Fe), and delta iron (δ-Fe). At very high pressure, a fourth form exists, called epsilon iron (ε-Fe). Some controversial experimental evidence suggests the existence of a fifth high-pressure form that is stable at very high pressures and temperatures. The phases of iron at atmospheric pressure are important because of the differences in solubility of carbon, forming different types of steel. The high-pressure phases of iron are important as models for the solid parts of planetary cores. The inner core of the Earth is generally assumed to consist essentially of a crystalline iron-nickel alloy with ε structure. The outer core surrounding the solid inner core is believed to be composed of liquid iron mixed with nickel and trace amounts of lighter elements. Standard pressure allotropes Alpha iron (α-Fe) Below 912 °C (1,674 °F), iron has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Beta
In statistical thermodynamics, thermodynamic beta, also known as coldness, is the reciprocal of the thermodynamic temperature of a system:\beta = \frac (where is the temperature and is Boltzmann constant).J. Meixner (1975) "Coldness and Temperature", ''Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis'' 57:3, 281-29abstract It was originally introduced in 1971 (as "coldness function") by , one of the proponents of the rational thermodynamics school of thought, based on earlier proposals for a "reciprocal temperature" function.Day, W.A. and Gurtin, Morton E. (1969) "On the symmetry of the conductivity tensor and other restrictions in the nonlinear theory of heat conduction", ''Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis'' 33:1, 26-32 (Springer-Verlag)abstractJ. Castle, W. Emmenish, R. Henkes, R. Miller, and J. Rayne (1965) Science by Degrees: ''Temperature from Zero to Zero'' (Westinghouse Search Book Series, Walker and Company, New York). Thermodynamic beta has units reciprocal to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EUROfusion
EUROfusion is a consortium of national fusion research institutes located in the European Union, the UK, Switzerland and Ukraine. It was established in 2014 to succeed the European Fusion Development Agreement ( EFDA) as the umbrella organisation of Europe's fusion research laboratories. The consortium is currently funded by the Euratom Horizon 2020 programme. Organisation The EUROfusion consortium agreement has been signed by 30 research organisations and universities from 25 European Union countries plus Switzerland, Ukraine and the United Kingdom. The EUROfusion's Programme Management Unit offices located in Garching, near Munich (Germany), are hosted by the Max Planck Institute of Plasma Physics (IPP). The IPP is also the seat for the co-ordinator of EUROfusion. Activities EUROfusion funds fusion research activities in accordance with thRoadmap to the realisation of fusion energy The Roadmap outlines the most efficient way to realise fusion electricity by 2050. Research carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Spherical Torus Experiment
The National Spherical Torus Experiment (NSTX) is a magnetic fusion device based on the '' spherical tokamak'' concept. It was constructed by the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) in collaboration with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Columbia University, and the University of Washington at Seattle. It entered service in 1999. In 2012 it was shut down as part of an upgrade program and became NSTX-U, for Upgrade. The spherical tokamak (ST) is an offshoot of the conventional tokamak design. Proponents claim that it has a number of practical advantages over these devices, some of them dramatic. For this reason the ST has seen considerable interest since it was proposed in the late 1980s. However, development remains effectively one generation behind mainline efforts such as JET. Other major experiments in the field include the pioneering START and MAST at Culham in the UK. NSTX studies the physics principles of spherically shaped plasmas—hot ionized gases in which nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |