|
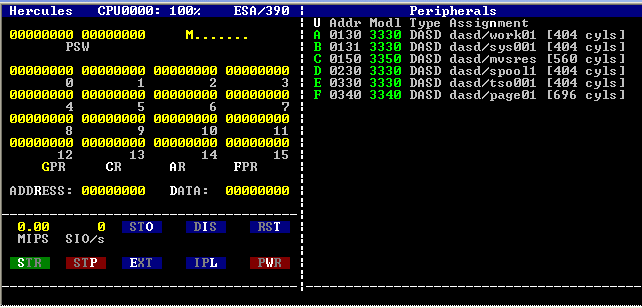
JES2
The Job Entry Subsystem (JES) is a component of IBM's MVS ( MVS/370 through z/OS) mainframe operating systems that is responsible for managing batch workloads. In modern times, there are two distinct implementations of the Job Entry System called JES2 and JES3. They are designed to provide efficient execution of batch jobs. Starting with z/OS 3.1, released in September 2023, IBM z/OS no longer includes JES3, and comes with JES2 only – JES3 sites must either migrate to JES2, or license JES3plus from Phoenix Software International, who has taken over future support and development of JES3 from IBM. Job processing is divided into several phases to provide parallelism through pipelining. These phases include input processing where jobs are read and interpreted, the execution phase where jobs run, and output processing where job output is printed or stored on DASD. Jobs that are in the same phase of execution are usually said to reside on a particular queue; for example, jobs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OS/360
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB and Input/Output Control System (IOCS) packages for the IBM 7090/7094 and even more so by the PR155 Operating System for the IBM 1410/ 7010 processors. It was one of the earliestJust a few years after Atlas Supervisor, Burroughs MCP and GECOS operating systems to require the computer hardware to include at least one direct access storage device. Although OS/360 itself was discontinued, successor operating systems, including the virtual storage MVS and the 64-bit z/OS, are still run and maintain application-level compatibility with OS/360. Overview IBM announced three different levels of OS/360, generated from the same tapes and sharing most of their code. IBM eventually renamed these options and made some significant design changes: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MVS/370
Multiple Virtual Storage, more commonly called MVS, is the most commonly used operating system on the System/370, System/390 and IBM Z IBM mainframe computers. IBM developed MVS, along with OS/VS1 and SVS, as a successor to OS/360. It is unrelated to IBM's other mainframe operating system lines, e.g., VSE, VM, TPF. Overview First released in 1974, MVS was extended by program products with new names multiple times, retaining the term MVS in the nomenclature: * first to MVS/SE (MVS/System Extensions),some print media used the singular, MVS/System Extension: Computerworld, 15 Dec 1980 - Page 5; 26 June 1978 - Page 8 * next to MVS/SP (MVS/System Product) Version 1, * next to MVS/XA (MVS/eXtended Architecture), * next to MVS/ESA (MVS/Enterprise Systems Architecture), and then extended * to OS/390 for the System/390 systems, and * finally to z/OS (when 64-bit support was added with the zSeries models). IBM added UNIX support (originally called OpenEdition MVS) in MVS/SP V4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Job Control Language
Job Control Language (JCL) is a scripting language used on IBM mainframe operating systems to instruct the system on how to run a batch processing, batch job or start a subsystem. The purpose of JCL is to say which programs to run, using which files or devices for input or output, and at times to also indicate under what conditions to skip a step. Parameters in the JCL can also provide accounting information for tracking the resources used by a job as well as which machine the job should run on. There are two distinct IBM Job Control Languages: * one for the operating system lineage that begins with DOS/360 and whose latest member is z/VSE; and * the other for the lineage from OS/360 to z/OS, the latter now including Job Entry Subsystem 2/3, JES extensions, #Job Entry Control Language, Job ''Entry'' Control Language (JECL). They share some basic syntax rules and a few basic concepts, but are otherwise very different. The VM (operating system), VM operating system does not have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Remote Job Entry
Remote job entry, or Remote Batch, is the procedure for sending requests for non-interactive data processing tasks ( jobs) to mainframe computers from remote workstations, and by extension the process of receiving the output from such jobs at a remote workstation. The RJE workstation is called a remote because it usually is located some distance from the host computer. The workstation connects to the host through a modem, digital link, packet-switching network or local area network (LAN). RJE is similar to uux and SSH, except that the workstation sends a complete job stream rather than a single command and that the user does not receive any output until the completion of the job.. The terms Remote Batch, Remote Job System and Remote Job Processing are also used for RJE facilities. Examples Remote Job Entry (RJE) is also the name of an OS/360 component that provided RJE services. An RJE workstation operator may have complete console control of the job flow between the workstat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a range of IBM mainframe computers announced as the successors to the IBM System/360, System/360 family on June 30, 1970. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migration path for customers; this, plus improved performance, were the dominant themes of the product announcement. Early 370 systems differed from the 360 largely in their internal circuitry, moving from the Solid Logic Technology hybrid integrated circuits containing separate transistors to more modern monolithic integrated circuits containing multiple transistors per integrated circuit, which IBM referred to as Monolithic System Technology, or MST. The higher density packaging allowed several formerly optional features from the 360 line to be included as standard features of the machines, floating-point support for instance. The 370 also added a small number of new instructions. At the time of its introduction, the development of virtual mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Job Entry Subsystem 1
Job Entry Subsystem (JES), aka Job Entry Subsystem 1 (JES1), was released by IBM as an integral part of OS/VS1 as an enhancement to the basic functions that users of VS1's predecessor, MFT, had. History IBM proclaimed JES1 to be "the single most important addition" to the job scheduling provided by VS1. IBM Systems Journal defined JES1's services as Spooling and scheduling, adding "Its three major components are peripheral services, central services, and queue management." JES1 was not popular, because HASP and ASP users often had made local modifications (edits), and wanted to retain their investment. Features JES1 permitted operators to submit batch jobs from local unit record equipment. In addition, Remote Entry Service (RES) permitted remote operators to submit jobs from remote sites to JES. The printed and punched output of jobs running on OS/VS1, whether submitted locally or remotely, is handled by JES and may be routed to local devices, to the originating site or to anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
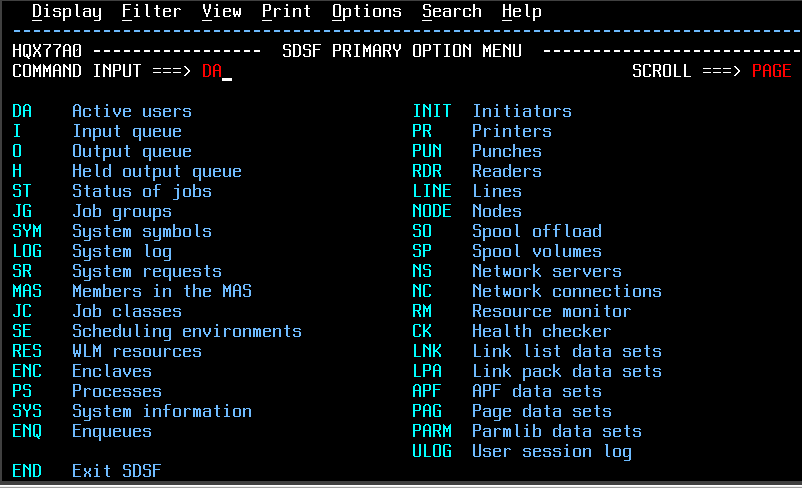
SDSF
The System Display and Search Facility (SDSF) is a component of IBM's mainframe operating system, z/OS, which allows users and administrators to view and control various aspects of the mainframe's operation and system resources using an interactive user interface. Some of the information displayed in SDSF includes Batch job output, Unix processes, scheduling environments, and the status of external devices such as printers and network lines, batch and system log files and dumps. History When it was a field-developed program offering, SDSF was known as the SPOOL Display and Search Facility The word ''SPOOL'' was changed to ''System'' when it became a program product in the late 1980s. With z/OS Release 1.9, SDSF supports a REXX interface, allowing batch programs to use SDSF facilities. This support includes stem variables containing SDSF-originated information. Prior to z/OS Release 1.10, SDSF was only supported for use with JES2 and not JES3, although ISV products from Pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spooling
In computing, spooling is a specialized form of multi-programming for the purpose of copying data between different devices. In contemporary systems, it is usually used for mediating between a computer application and a slow peripheral, such as a printer. Spooling allows programs to "hand off" work to be done by the peripheral and then proceed to other tasks, or to not begin until input has been transcribed. A dedicated program, the spooler, maintains an orderly sequence of jobs for the peripheral and feeds it data at its own rate. Conversely, for slow ''input'' peripherals, such as a card reader, a spooler can maintain a sequence of computational jobs waiting for data, starting each job when all of the relevant input is available; see batch processing. The spool itself refers to the sequence of jobs, or the storage area where they are held. In many cases, the spooler is able to drive devices at their full rated speed with minimal impact on other processing. Spooling is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Batch Job
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically be run at scheduled times as well as being run contingent on the availability of computer resources. History The term "batch processing" originates in the traditional classification of methods of production as job production (one-off production), batch production (production of a "batch" of multiple items at once, one stage at a time), and flow production (mass production, all stages in process at once). Early history Early computers were capable of running only one program at a time. Each user had sole control of the machine for a scheduled period of time. They would arrive at the computer with program and data, often on punched paper cards and magnetic or paper tape, and would load their program, run and debug it, and carry off thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OS/VS2 (SVS)
Single Virtual Storage (SVS) refers to Release 1 of Operating System/Virtual Storage 2 (OS/VS2); it is the successor system to the MVT option of Operating System/360. OS/VS2 (SVS) was a stopgap measure pending the availability of MVS, although IBM provided support and enhancements to SVS long after shipping MVS. SVS provides a ''single'' 16MiB address space which is shared by all tasks in the system, regardless of the size of physical memory. Differences from MVT OS/360 used the Interval Timer feature for providing time of day and for triggering time-dependent events. The support for S/370 made limited use of new timing facilities, but retained a dependency on the Interval Timer. SVS uses the TOD Clock, Clock Comparator and CPU Timer exclusively. OS/360 loads error recovery and transient SVC routines from SYS1.SVCLIB into small transient areas. SVS loads these routine from SYS1.LPALIB into the Pageable Link Pack Area (PLPA) during an IPL with the Create LPA (CLPA) option; there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pipeline (computing)
In computing, a pipeline, also known as a data pipeline, is a set of data processing elements connected in series, where the output of one element is the input of the next one. The elements of a pipeline are often executed in parallel or in time-sliced fashion. Some amount of buffer storage is often inserted between elements. Concept and motivation Pipelining is a commonly used concept in everyday life. For example, in the assembly line of a car factory, each specific task—such as installing the engine, installing the hood, and installing the wheels—is often done by a separate work station. The stations carry out their tasks in parallel, each on a different car. Once a car has had one task performed, it moves to the next station. Variations in the time needed to complete the tasks can be accommodated by "buffering" (holding one or more cars in a space between the stations) and/or by "stalling" (temporarily halting the upstream stations), until the next station becomes avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IBM System/360 Model 50
The IBM System/360 Model 50 is a member of the IBM System/360 family of computers. The Model 50 was announced in April 1964 with the other initial models of the family, and first shipped in August 1965 to the Bank of America. Models There are four models of the 360/50. They vary by the amount of core memory with which the system is offered. The F50, or 2050F is equipped with 65,536 bytes, the G50 has 131,072 bytes, the H50 262,144 bytes, and the I50 524,288 bytes. The system can also attach IBM 2361 Large Capacity Storage (LCS) modules which provide up to 8,388,608 bytes of additional storage, however with a considerably slower memory cycle time of 8 microseconds compared to the 2 microseconds of processor storage. Relative performance The system has a CPU cycle time of 500 nanoseconds, 25% faster than the Model 40 and 40% of the speed of the Model 65 which has a 200 nanosecond cycle time. Processor storage is magnetic core memory that transfers four bytes per 2 microsecond c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |