|
Jumpin' At The Woodside
"Jumpin' at the Woodside" is a song first recorded in 1938 by the Count Basie Orchestra, and considered one of the band's signature tunes. When first released it reached number 11 on the ''Billboard'' charts and remained on them for four weeks. Since then, it has become a frequently recorded jazz standard. Song details The song was recorded on August 22, 1938 for Decca and was released on December 17 of that year. It charted as high as #11 and was on the charts for four weeks. That original 1938 recording features solos by Earle Warren (alto sax), Buck Clayton (trumpet), Lester Young (tenor sax), and Herschel Evans (clarinet). The song is considered one of the Basie band's "signature" tunes, a "favorite", and even "a definition of swing." While many liner notes credit the tune only to Basie, historians and others also credit band member Eddie Durham. Like many Basie numbers of that era, it was a " head arrangement" collaboratively created by the band. Sullivan indicates Durh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
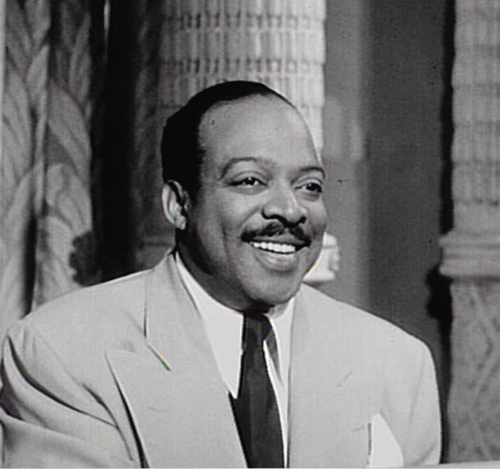
Count Basie
William James "Count" Basie (; August 21, 1904 – April 26, 1984) was an American jazz pianist, organist, bandleader, and composer. In 1935, he formed the Count Basie Orchestra, and in 1936 took them to Chicago for a long engagement and their first recording. He led the group for almost 50 years, creating innovations like the use of two "split" tenor saxophones, emphasizing the rhythm section, riffing with a big band, using arrangers to broaden their sound, and others. Many musicians came to prominence under his direction, including the tenor saxophonists Lester Young and Herschel Evans, the guitarist Freddie Green, trumpeters Buck Clayton and Harry "Sweets" Edison, plunger trombonist Al Grey, and singers Jimmy Rushing, Helen Humes, Thelma Carpenter, and Joe Williams. Biography Early life and education William Basie was born to Lillian and Harvey Lee Basie in Red Bank, New Jersey. His father worked as a coachman and caretaker for a wealthy judge. After automobile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Avenue (Manhattan)
Seventh Avenue – co-named Fashion Avenue in the Garment District and known as Adam Clayton Powell Jr. Boulevard north of Central Park – is a thoroughfare on the West Side of the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It is southbound below Central Park and a two-way street north of the park. Seventh Avenue originates in the West Village at Clarkson Street, where Varick Street becomes Seventh Avenue South (which becomes Seventh Avenue proper after the road crosses Greenwich Avenue and West 11th Street). It is interrupted by Central Park from 59th to 110th Street. Artisans' Gate is the 59th Street exit from Central Park to Seventh Avenue. North of Warriors' Gate at the north end of the Park, the avenue carries traffic in both directions through Harlem, where it is called Adam Clayton Powell Jr. Boulevard. Addresses continue as if the street was continuous through Central Park, with the first block north of the park being the 1800 block. The United States Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitey's Lindy Hoppers
Whitey's Lindy Hoppers was a professional performing group of exceptional swing dancers that was first organized in the late 1920s by Herbert "Whitey" White in the Savoy Ballroom and disbanded in 1942 after its male members were drafted into World War II. The group took on many different forms and had several different names and sub-groups, including Whitey's Hopping Maniacs, Harlem Congeroo Dancers, and The Hot Chocolates. In addition to touring nationally and internationally, the group appeared in several films and Broadway theatre productions. Dorothy Dandridge and Sammy Davis Jr. were among the group's celebrity regulars. History Beginning in the late 1920s, White, a bouncer at the Savoy Ballroom and former dancing waiter, began organizing exceptional dancers, first under the aegis of George Snowden and then under White himself. Although many members felt mistreated by White, many admired his promotion of the dance. In 1934, at the age of 14, Norma Miller became the youngest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindy Hop
The Lindy Hop is an American dance which was born in the Black communities of Harlem, New York City, in 1928 and has evolved since then. It was very popular during the swing era of the late 1930s and early 1940s. Lindy is a fusion of many dances that preceded it or were popular during its development but is mainly based on jazz, tap, breakaway, and Charleston. It is frequently described as a jazz dance and is a member of the swing dance family. In its development, the Lindy Hop combined elements of both partnered and solo dancing by using the movements and improvisation of African-American dances along with the formal eight-count structure of European partner dances – most clearly illustrated in the Lindy's basic step, the swingout. In this step's open position, each dancer is generally connected hand-to-hand; in its closed position, leads and follows are connected as though in an embrace on one side and holding hands on the other. There was renewed interest in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roseland Ballroom
The Roseland Ballroom was a multipurpose hall, in a converted ice skating rink, with a colorful ballroom dancing pedigree, in New York City's theater district, on West 52nd Street in Manhattan. The venue, according to its website, accommodated 3,200 standing (with an additional 300 upstairs), 2,500 for a dance party, between 1,300 and 1,500 in theatre style, 800–1,000 for a sit-down dinner, and 1,500 for a buffet and dancing. The venue hosted a wide range of events, from a Hillary Clinton birthday party, to annual gay circuit parties, to movie premieres, to musical performances of all genres, including Beyoncé's Elements of 4 show and internet stars Team StarKid's Apocalyptour National Concert Tour. It was also known as the place American singer Fiona Apple broke down during a concert in 2000. The rear of the venue faced West 53rd Street and the Ed Sullivan Theater. On October 18, 2013, it was announced that the venue would close on April 7, 2014. Lady Gaga complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ella Fitzgerald
Ella Jane Fitzgerald (April 25, 1917June 15, 1996) was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction, phrasing, timing, intonation, and a "horn-like" improvisational ability, particularly in her scat singing. After a tumultuous adolescence, Fitzgerald found stability in musical success with the Chick Webb Orchestra, performing across the country but most often associated with the Savoy Ballroom in Harlem. Her rendition of the nursery rhyme " A-Tisket, A-Tasket" helped boost both her and Webb to national fame. After taking over the band when Webb died, Fitzgerald left it behind in 1942 to start her solo career. Her manager was Moe Gale, co-founder of the Savoy, until she turned the rest of her career over to Norman Granz, who founded Verve Records to produce new records by Fitzgerald. With Verve she recorded some of her more widely noted works, particul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Da Capo Press
Da Capo Press is an American publishing company with headquarters in Boston, Massachusetts. It is now an imprint of Hachette Books. History Founded in 1964 as a publisher of music books, as a division of Plenum Publishers, it had additional offices in New York City, Philadelphia, Los Angeles, and Emeryville, California. The year prior, Da Capo Press had net sales of over $2.5 million. Da Capo Press became a general trade publisher in the mid-1970s. It was sold to the Perseus Books Group in 1999 after Plenum was sold to Wolters Kluwer. In the last decade, its production has consisted of mostly nonfiction titles, both hardcover and paperback, focusing on history, music, the performing arts, sports, and popular culture. In 2003, Lifelong Books was founded as a health and wellness imprint. When Marlowe & Company became part of the imprint in 2007, Lifelong's range was expanded to include the New Glucose Revolution series and numerous diabetes Diabetes, also known as diabete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
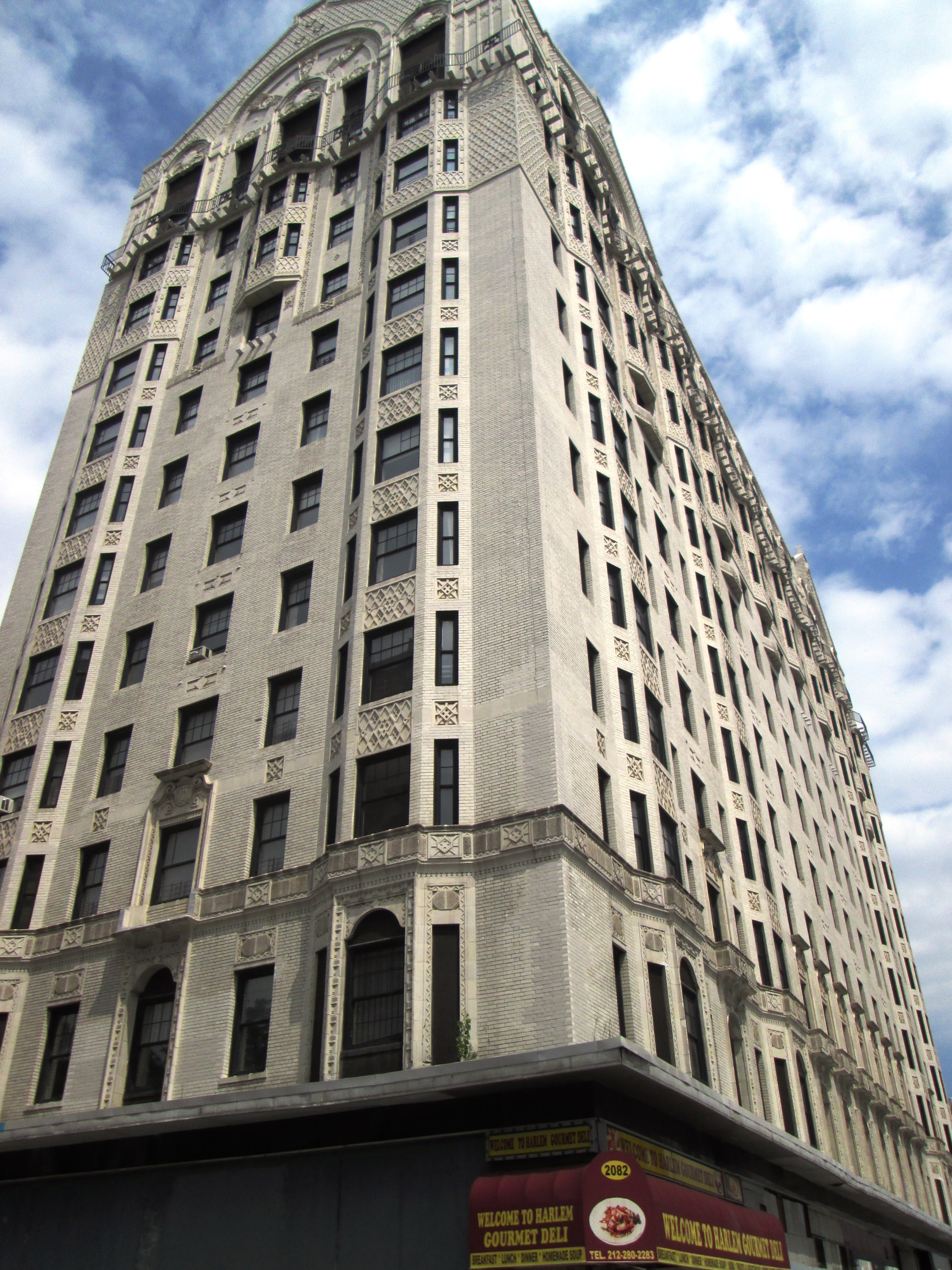
Hotel Theresa
The Hotel Theresa is located at 2082-96 Adam Clayton Powell Jr. Boulevard between West 124th and 125th Streets in the Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. In the mid-20th century, it was a vibrant center of African American life in the area and the city. The 13-story hotel was built in 1912–13 by German-born stockbroker Gustavus Sidenberg (1843–1915), whose wife the hotel is named after,Aberjhani. "Hotel Theresa" in Aberjhani and West, Sandra L. (eds.''Encyclopedia of the Harlem Renaissance'' Facts On File, 2003. p. 158 and was designed by the firm of George & Edward Blum, who specialized in designing apartment buildings. The hotel, which was known in its heyday as "the Waldorf of Harlem", exemplifies the Blums' inventive use of terracotta for ornamentation, and has been called "one of the most visually striking structures in northern Manhattan". The building, now an office building known as Theresa Towers, was designated a New York City landmark in 1993 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syracuse University Press
Syracuse University Press, founded in 1943, is a university press that is part of Syracuse University. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. History SUP was formed in August 1943 when president William P. Tolley promised Thomas J. Watson that the university will organize a press to print IBM's ''Precision Measurements in the Metal Workings Industry''. Matthew Lyle Spencer of the School of Journalism became the first chair of the board of directors and Lawrence Siegfried was the first editor. About The areas of focus for the Press include Middle East studies, Native American studies, peace and conflict resolution, Irish studies and Jewish studies, New York State, television and popular culture, sports and entertainment. The Press has an international reputation in Irish studies and Middle East studies. In March 2017, SU Press received HumanitieOpen Book Programaward from the National Endowment for the Humanities The National Endowment for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Segregation In The United States
In the United States, racial segregation is the systematic separation of facilities and services such as housing, healthcare, education, employment, and transportation on racial grounds. The term is mainly used in reference to the legally or socially enforced separation of African Americans from whites, but it is also used in reference to the separation of other ethnic minorities from majority and mainstream communities. While mainly referring to the physical separation and provision of separate facilities, it can also refer to other manifestations such as prohibitions against interracial marriage (enforced with anti-miscegenation laws), and the separation of roles within an institution. Notably, in the United States Armed Forces up until 1948, black units were typically separated from white units but were still led by white officers. Signs were used to indicate where African Americans could legally walk, talk, drink, rest, or eat. The U.S. Supreme Court upheld the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negro League Baseball
The Negro leagues were United States professional baseball leagues comprising teams of African Americans and, to a lesser extent, Latin Americans. The term may be used broadly to include professional black teams outside the leagues and it may be used narrowly for the seven relatively successful leagues beginning in 1920 that are sometimes termed "Negro Major Leagues". In the late 19th century, the baseball color line developed in professional baseball, excluding African Americans from league play. In 1885, the Cuban Giants formed the first black professional baseball team. The first league, the National Colored Base Ball League, was organized strictly as a minor league but failed in 1887 after only two weeks owing to low attendance. After several decades of mostly independent play by a variety of teams, in 1920 the first Negro National League was formed and ultimately seven major leagues existed at various times over the next thirty years. After integration, the quality o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


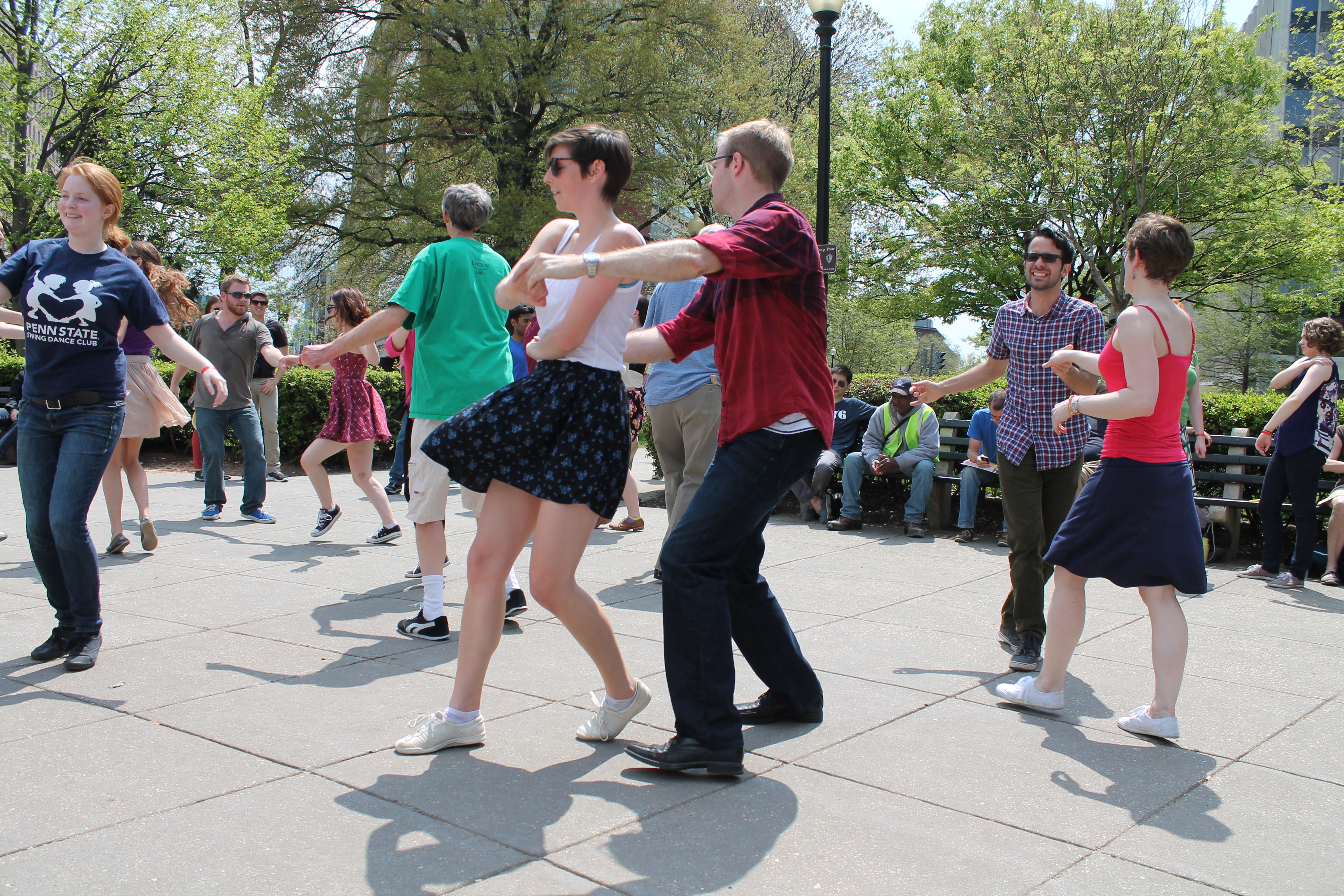
.jpg)


