|
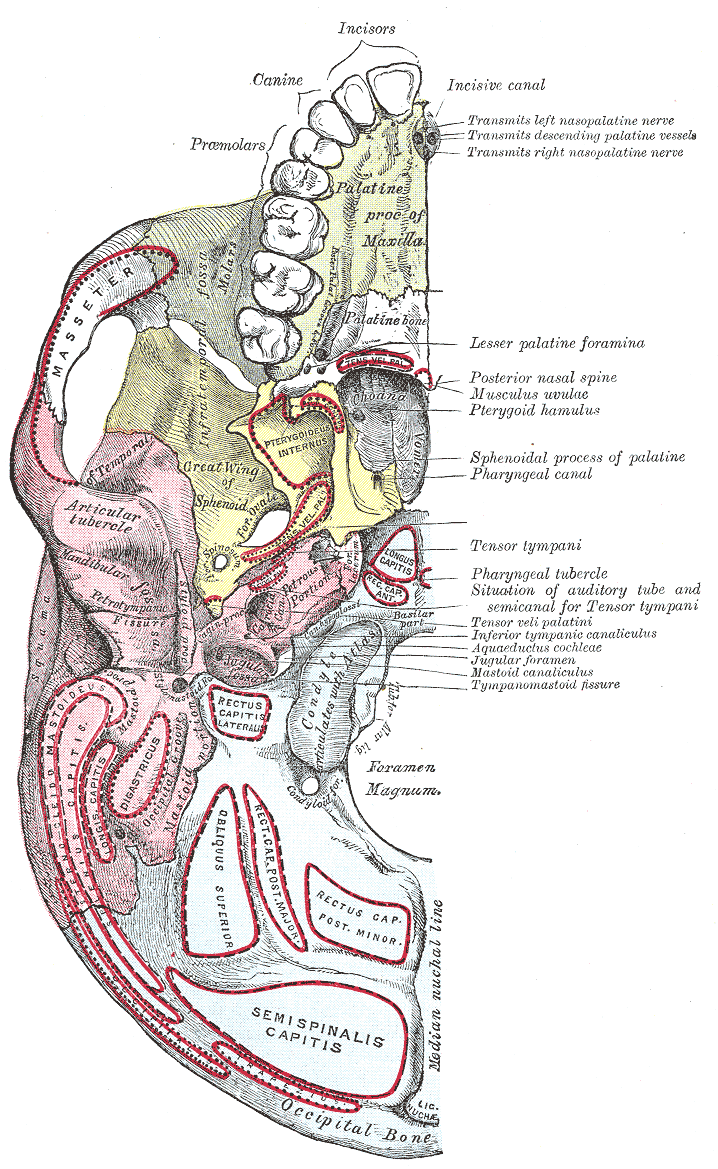
Jugular Tubercle
The jugular tubercle is an oval eminence on the superior surface of the lateral parts of occipital bone. It overlies the hypoglossal canal and is sometimes crossed by an oblique groove for the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. References External links * Diagram at wayne.edu Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the pharynx. The squamous part is the curved, expanded plate behind the foramen magnum and is the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglossal Canal
The hypoglossal canal is a foramen in the occipital bone of the skull. It is hidden medially and superiorly to each occipital condyle. It transmits the hypoglossal nerve. Structure The hypoglossal canal lies in the epiphyseal junction between the basiocciput and the jugular process of the occipital bone. Variation Embryonic variants sometimes lead to the presence of more than two canals as the occipital bone is formed. Development The hypoglossal canal is formed during the embryological stage of development in mammals. Function The hypoglossal canal transmits the hypoglossal nerve from its point of entry near the medulla oblongata to its exit from the base of the skull near the jugular foramen A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including th .... Clinical significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: * Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone * Frontal bone * Temporal bone Sinuses * Occipital sinus *Superior sagittal sinus * Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum * Optic foramen * Foramen lacerum * Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum *Foramen ovale * Jugular foramen * Internal auditory meatus * Mastoid foramen * Sphenoidal emissary foramen * Foramen spinosum Sutures * Frontoethmoidal suture * Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture * Sphenoethmoidal suture *Petrosquamous suture The petrosquamous suture is a cranial suture between the petrous portion and the squama of the temporal bone. It forms the Koerner's septum. The petr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the pharynx. The squamous part is the curved, expanded plate behind the foramen magnum and is the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum ( la, great hole) is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull. The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a biped's foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border of the cerebellar tentorium; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Parts Of Occipital Bone
The lateral parts of the occipital bone (also called the exoccipitals) are situated at the sides of the foramen magnum; on their under surfaces are the condyles for articulation with the superior facets of the atlas. Description The condyles are oval or reniform (kidney-shaped) in shape, and their anterior extremities, directed forward and medialward, are closer together than their posterior, and encroach on the basilar portion of the bone; the posterior extremities extend back to the level of the middle of the foramen magnum. The articular surfaces of the condyles are convex from before backward and from side to side, and look downward and lateralward. To their margins are attached the capsules of the atlantoöccipital articulations, and on the medial side of each is a rough impression or tubercle for the alar ligament. At the base of either condyle the bone is tunnelled by a short canal, the hypoglossal canal (anterior condyloid foramen). This begins on the cranial surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a triangular depression into which the aqueduct of cochlea opens. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves because part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, whereas the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder. Traditional descriptions of the accessory nerve divide it into a spinal part and a cranial part. The cranial component rapidly joins the vagus nerve, and there is ongoing debate about whether the cranial part should be considered part of the accessory nerve proper. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" usually refers only to nerve supplying the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, also called the spinal accessory nerve. Strength testing of these muscles can be measured during a neurological examination to assess funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |