|
Journal Of Theoretical Biology
The ''Journal of Theoretical Biology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical biology, as well as mathematical, computational, and statistical aspects of biology. Some research areas covered by the journal include cell biology, evolutionary biology, population genetics, morphogenesis, and immunology. The journal was established in 1961. Its founding editor-in-chief was English biologist James F. Danielli, who remained editor until his death in 1984. The journal is published by Elsevier and, , the editors-in-chief are Denise Kirschner (University of Michigan Medical School), Mark Chaplain (University of St. Andrews), and Akira Sawaki (Aichi Cancer Center, Nagoya). Lewis Wolpert served as editor-in-chief for more than 55 years. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'' the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.691. Notable articles The following are the most highly cited articles (more than 2000 citations at April 2021) that have been published in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of the living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development and behavior of the systems, as opposed to experimental biology which deals with the conduction of experiments to prove and validate the scientific theories. The field is sometimes called mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side, or theoretical biology to stress the biological side. Theoretical biology focuses more on the development of theoretical principles for biology while mathematical biology focuses on the use of mathematical tools to study biological systems, even though the two terms are sometimes interchanged. Mathematical biology aims at the mathematical representation and modeling of biological processes, using techniques and tools of applied mathematics. It can be useful in both theoretical and prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Danielli
James Frederic Danielli FRS (1911–1984) was an English biologist. He was famous for research on the structure and the permeability of cell membranes, developing a physical-chemical model in collaboration with the physiologist Hugh Davson Hugh Davson, Baron Davson (25 November 1909 – 2 July 1996) was an English physiologist who worked on membrane transport and ocular fluids. Davson was born in Paddington, London, the son of physician Wilfred Maynard Davson and Mary Louisa Scott. .... This became known as the Davson-Danielli or "protein sandwich" model. He also carried out studies on the chemistry of enzymes and proteins and tried to construct an artificial "cell". References English physiologists Fellows of the Royal Society 1911 births 1984 deaths {{England-med-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Flag Model
The French flag model is a conceptual definition of a morphogen, described by Lewis Wolpert in the 1960s. A morphogen is defined as a signaling molecule that acts directly on cells (not through serial induction) to produce specific cellular responses dependent on morphogen concentration. During early development, morphogen gradients generate different cell types in distinct spatial order. French flag patterning is often found in combination with others: vertebrate limb development is one of the many phenotypes exhibiting Turing overlapped with a complementary pattern (in this case Turing pattern). Overview In the French flag model, the French flag is used to represent the effect of a morphogen on cell differentiation: a morphogen affects cell states based on concentration, these states are represented by the different colors of the French flag: high concentrations activate a "blue" gene, lower concentrations activate a "white" gene, with "red" serving as the default state in cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregarious Behaviour
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies. Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother wasp stays near her larvae in the nest, parasites are less likely to eat the larvae. Biologists suspect that pressures from parasites and other predators selected this behavior in wasps of the family Vespidae. This wasp behaviour evidences the most fundamental characteristic of animal sociality: parental investment. Parental investment is any expenditure of resources (time, energy, social capital) to benefit one's offspring. Parental investment detracts from a parent's capacity to invest in future reproduction and aid to kin (including other offspring). An animal that cares for its young but shows no other sociality traits is said to be ''subsocial''. An animal that exhibits a high degree of sociality is called a ''social animal''. The highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocatalytic Sets
An autocatalytic set is a collection of entities, each of which can be created catalytically by other entities within the set, such that as a whole, the set is able to catalyze its own production. In this way the set ''as a whole'' is said to be autocatalytic. Autocatalytic sets were originally and most concretely defined in terms of molecular entities, but have more recently been metaphorically extended to the study of systems in sociology, ecology, and economics. Autocatalytic sets also have the ability to replicate themselves if they are split apart into two physically separated spaces. Computer models illustrate that split autocatalytic sets will reproduce all of the reactions of the original set in each half, much like cellular mitosis. In effect, using the principles of autocatalysis, a small metabolism can replicate itself with very little high level organization. This property is why autocatalysis is a contender as the foundational mechanism for complex evolution. Prio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handicap Principle
The handicap principle is a hypothesis proposed by the biologist Amotz Zahavi to explain how evolution may lead to "honest" or reliable signalling between animals which have an obvious motivation to bluff or deceive each other. It suggests that costly signals must be reliable signals, costing the signaller something that could not be afforded by an individual with less of a particular trait. For example, in sexual selection, the theory suggests that animals of greater biological fitness signal this status through handicapping behaviour, or morphology that effectively lowers this quality. The central idea is that sexually selected traits function like conspicuous consumption, signalling the ability to afford to squander a resource. Receivers then know that the signal indicates quality, because inferior-quality signallers are unable to produce such wastefully extravagant signals. History The handicap principle was proposed in 1975 by Israeli biologist Amotz Zahavi. The generali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclusive Fitness
In evolutionary biology, inclusive fitness is one of two metrics of evolutionary success as defined by W. D. Hamilton in 1964: * Personal fitness is the number of offspring that an individual begets (regardless of who rescues/rears/supports them) * Inclusive fitness is the number of offspring equivalents that an individual rears, rescues or otherwise supports through its behaviour (regardless of who begets them) An individual's own child, who carries one half of the individual's genes, is defined as one offspring equivalent. A sibling's child, who will carry one-quarter of the individual's genes, is 1/2 offspring equivalent. Similarly, a cousin's child, who has 1/16 of the individual's genes, is 1/8 offspring equivalent. From the gene's point of view, evolutionary success ultimately depends on leaving behind the maximum number of copies of itself in the population. Prior to Hamilton's work, it was generally assumed that genes only achieved this through the number of viable off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarivate Analytics
Clarivate Plc is a British-American publicly traded analytics company that operates a collection of subscription-based services, in the areas of bibliometrics and scientometrics; business / market intelligence, and competitive profiling for pharmacy and biotech, patents, and regulatory compliance; trademark protection, and domain and brand protection. In the academy and the scientific community, Clarivate is known for being the company which calculates the impact factor, using data from its Web of Science product family, that also includes services/applications such as Publons, EndNote, EndNote Click, and ScholarOne. Its other product families are Cortellis, DRG, CPA Global, Derwent, MarkMonitor, CompuMark, and Darts-ip, and also the various ProQuest products and services. Clarivate was formed in 2016, following the acquisition of Thomson Reuters' Intellectual Property and Science Business by Onex Corporation and Baring Private Equity Asia. Clarivate has been growing fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
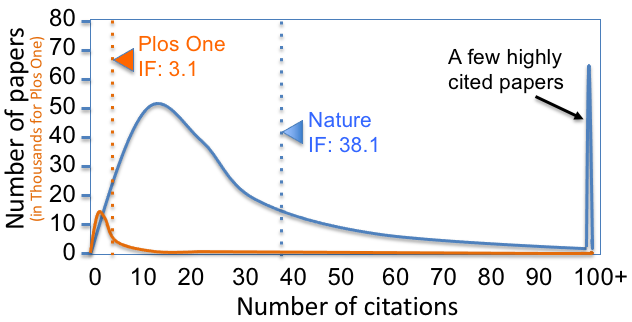
Impact Factor
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. As a journal-level metric, it is frequently used as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its field; journals with higher impact factor values are given the status of being more important, or carry more prestige in their respective fields, than those with lower values. While frequently used by universities and funding bodies to decide on promotion and research proposals, it has come under attack for distorting good scientific practices. History The impact factor was devised by Eugene Garfield, the founder of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) in Philadelphia. Impact factors began to be calculated yearly starting from 1975 for journals listed in the ''Journal Citation Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Citation Reports
''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publicationby Clarivate Analytics (previously the intellectual property of Thomson Reuters). It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science-Core Collections. It provides information about academic journals in the natural sciences and social sciences, including impact factors. The ''JCR'' was originally published as a part of ''Science Citation Index''. Currently, the ''JCR'', as a distinct service, is based on citations compiled from the '' Science Citation Index Expanded'' and the '' Social Sciences Citation Index''.- - - Basic journal information The information given for each journal includes: * the basic bibliographic information of publisher, title abbreviation, language, ISSN * the subject categories (there are 171 such categories in the sciences and 54 in the social sciences) Citation information * Basic citation data: ** the number of articles published during that year and ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |