|
Joint Monitoring Programme For Water Supply And Sanitation
The Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation by WHO and UNICEF is the official United Nations mechanism tasked with monitoring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goal Number 6 (SDG 6) since 2016. Previously, until 2015, JMP was tasked with monitoring the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) relating to drinking water and sanitation (MDG 7, Target 7c), which was to: "Halve, by 2015, the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking-water and basic sanitation". The JMP is housed within the World Health Organization and UNICEF, and supported by a Strategic Advisory Group of independent technical and policy experts as well as various Technical Task Forces convened around important specific topics. Activities The JMP's four priority areas of activity for 2010-2015 were: * maintaining the integrity of the JMP database and ensuring accurate global estimates; * disseminating data to stakeholders; * fulfilling the JMP's normative rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Development Goal 6
Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6 or Global Goal 6) is about "clean water and sanitation for all". It is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015, the official wording is: "Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all." The goal has eight targets to be achieved by 2030. Progress toward the targets will be measured by using eleven indicators. The six "outcome-oriented targets" include: Safe and affordable drinking water; end open defecation and provide access to sanitation, and hygiene, improve water quality, wastewater treatment and safe reuse, increase water-use efficiency and ensure freshwater supplies, implement IWRM, protect and restore water-related ecosystems. The two "means of achieving" targets are to expand water and sanitation support to developing countries, and to support local engagement in water and sanitation management. In 2017, 2.2 billion people lacked safely ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, coverin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
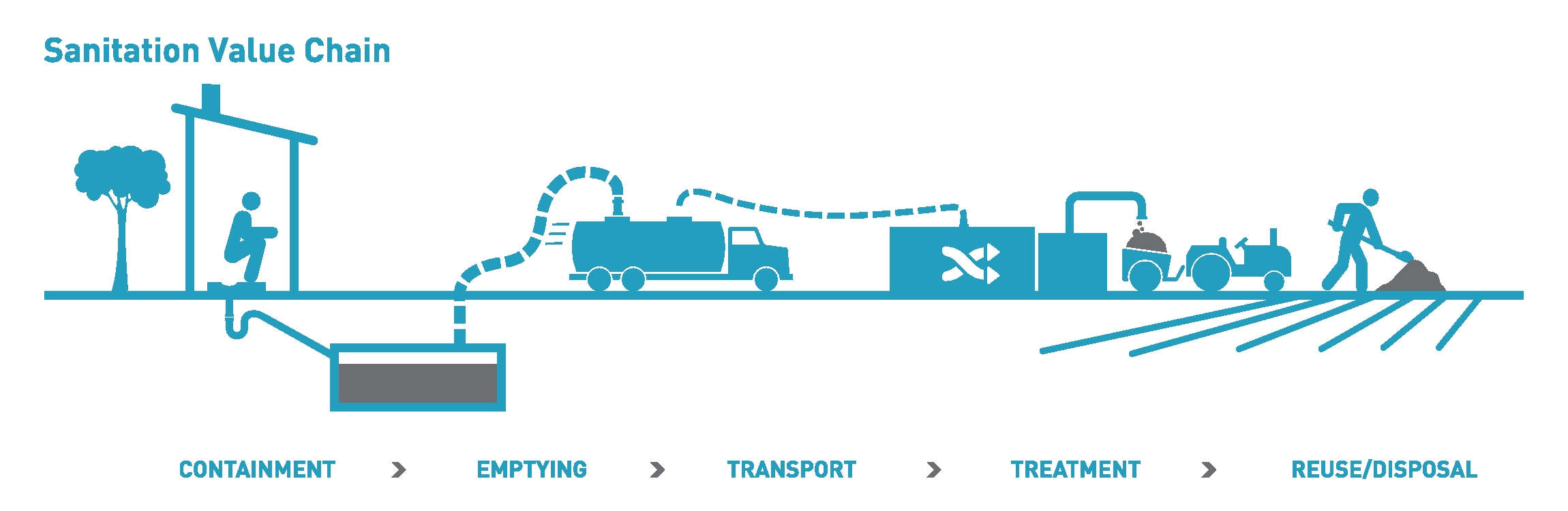
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Defecation
Open defecation is the human practice of defecating outdoors ("in the open") rather than into a toilet. People may choose fields, bushes, forests, ditches, streets, canals, or other open spaces for defecation. They do so either because they do not have a toilet readily accessible or due to traditional cultural practices. The practice is common where sanitation infrastructure and services are not available. Even if toilets are available, behavior change efforts may still be needed to promote the use of toilets. 'Open defecation free' (ODF) is a term used to describe communities that have shifted to using toilets instead of open defecation. This can happen, for example, after community-led total sanitation programs have been implemented. Open defecation can pollute the environment and cause health problems and diseases. High levels of open defecation are linked to high child mortality, poor nutrition, poverty, and large disparities between rich and poor. Ending open defecati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called '' simple linear regression''; for more than one, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improved Water Source
An improved water source (or improved drinking-water source or improved water supply) is a term used to categorize certain types or levels of water supply for monitoring purposes. It is defined as a type of water source that, by nature of its construction or through active intervention, is likely to be protected from outside contamination, in particular from contamination with fecal matter.WHO and UNICEdefinitions of improved drinking-water source on the JMP website, WHO, Geneva and UNICEF, New York, accessed on June 10, 2012 The term was coined by the Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation of UNICEF and WHO in 2002 to help monitor the progress towards Goal Number 7 of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The opposite of "improved water source" has been termed "unimproved water source" in the JMP definitions. The same terms are used to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Target 6.1, Indicator 6.1.1) from 2015 onwards.WHO and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographic And Health Surveys
The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program is responsible for collecting and disseminating accurate, nationally representative data on health and population in developing countries. The project is implemented by ICF International and is funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) with contributions from other donors such as UNICEF, UNFPA, WHO, and UNAIDS. The DHS is highly comparable to the Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys and the technical teams developing and supporting the surveys are in close collaboration. Since September 2013, ICF International has been partnering with seven internationally experienced organizations to expand access to and use of the DHS data: Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Center for Communication Programs; Program for Appropriate Technology in Health ( PATH); Avenir Health; Vysnova; Blue Raster; Kimetrica; and EnCompass. Overview Since 1984, The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program has provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys
The Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS) are household surveys implemented by countries under the programme developed by the United Nations Children's Fund to provide internationally comparable, statistically rigorous data on the situation of children and women. The first round of surveys (MICS1) was carried out in over 60 countries in mainly 1995 and 1996 in response to the World Summit for Children and measurement of the mid-decade progress. A second round (MICS2) in 2000 increased the depth of the survey, allowing monitoring of a larger number of globally agreed indicators. A third round (MICS3) started in 2006 and aimed at producing data measuring progress also toward the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), A World Fit for Children, and other major relevant international commitments. The fourth round, launched in 2009, aimed at most data collection conducted in 2010, but in reality most MICS4s were implemented in 2011 and even into 2012 and 2013. This represented a scale- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improved Sanitation
Improved sanitation (related to but distinct from a "safely managed sanitation service") is a term used to categorize types of sanitation for monitoring purposes. It refers to the management of human feces at the household level. The term was coined by the Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation of UNICEF and WHO in 2002 to help monitor the progress towards Goal Number 7 of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The opposite of " improved sanitation" has been termed "unimproved sanitation" in the JMP definitions. The same terms are used to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Target 6.2, Indicator 6.2.1) from 2015 onwards.WHO and UNICEF (2017Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), 2017 Here, they are a component of the definition for "safely managed sanitation service". The Joint Monitoring Program (J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millennium Development Goal
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These were based on the OECD DAC International Development Goals agreed by Development Ministers in the "Shaping the 21st Century Strategy". The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) succeeded the MDGs in 2016. All 191 United Nations member states, and at least 22 international organizations, committed to help achieve the following Millennium Development Goals by 2015: # To eradicate extreme poverty and hunger # To achieve universal primary education # To promote gender equality and empower women # To reduce child mortality # To improve maternal health # To combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases # To ensure environmental sustainability # To develop a global partnership for development Each goal had specific target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improved Water Source
An improved water source (or improved drinking-water source or improved water supply) is a term used to categorize certain types or levels of water supply for monitoring purposes. It is defined as a type of water source that, by nature of its construction or through active intervention, is likely to be protected from outside contamination, in particular from contamination with fecal matter.WHO and UNICEdefinitions of improved drinking-water source on the JMP website, WHO, Geneva and UNICEF, New York, accessed on June 10, 2012 The term was coined by the Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation of UNICEF and WHO in 2002 to help monitor the progress towards Goal Number 7 of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The opposite of "improved water source" has been termed "unimproved water source" in the JMP definitions. The same terms are used to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Target 6.1, Indicator 6.1.1) from 2015 onwards.WHO and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313) The goals are: No poverty, zero hunger, good health and well-being, quality education, gender equality, clean water and sanitation, affordable and clean energy, decent work and economic growth, industry, innovation and infrastructure, Reduced Inequality, Sustainable Cities and Communities, Responsible Consumption and Production, Climate Action, Life Below Water, Life On Land, Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions, Partnerships for the Goals. The SDGs emphasize the interconnected environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development by putting sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

