|
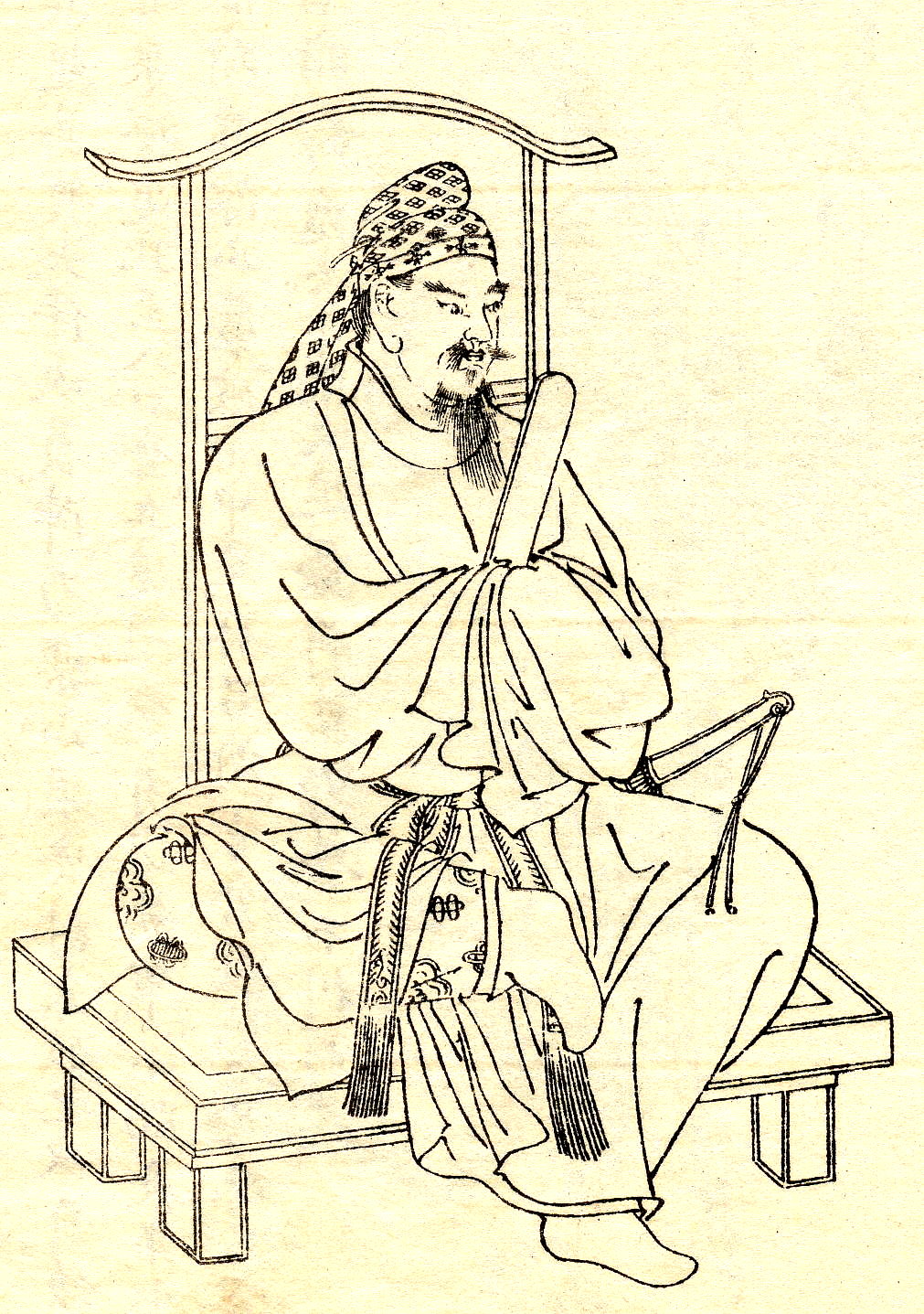
John The Good (bishop Of Milan)
John the Good ( la, Ioannes Bonus, it, Giovanni Bono or ''Buono'') was Archbishop of Milan from c. 641 to 669. He is honoured as a Saint in the Catholic Church and his feast day is on January 2. Life The reign of John ''the Good'' is remembered for the return of the bishop to the town of Milan after an exile of more than 70 years. Actually in 569, the Lombards invaded Northern Italy and conquered its center, Milan, which was recovering from the terrible Gothic War. The bishop of Milan, Honoratus escaped to Genoa and Honoratus' successors remained in Genoa. Genoa was then a suffragan diocese of Milan but still under the control of the Byzantine Empire. John ''the Good'' was born in the diocese of Genoa in the village of Recco (also the nearby town of Camogli claims the birth of John). It is not exactly known when he became bishop of Milan, but it is believed that his election was in consequence of the 641 conquest of Genoa by the Lombard's King Rothari. John as bishop returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recco
The RECCO is a rescue technology used by organised rescue teams as an additional tool to more quickly locate people buried by an avalanche or lost in the outdoors. The system is based on a harmonic radar system and composed by a detector and a passive reflector integrated into outdoor clothing and gears. History The RECCO rescue technology was developed by Magnus Granhed, in response to his personal experience with a fatal avalanche accident in Åre, Sweden, in 1973. Starting in the winter of 1978–1979, Granhed collaborated with Bengt Enander's team at the Department of Electromagnetic Theory, Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm to develop an avalanche rescue system, using the principle of harmonic radar. Granhed formed RECCO AB in 1983 and created the first functional prototype. In 1987, a woman was localised with the RECCO rescue technology from a helicopter in Lenzerheide, Switzerland, in the first live rescue found using the technology. In 2015, RECCO introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblioteca Ambrosiana
The Biblioteca Ambrosiana is a historic library in Milan, Italy, also housing the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana, the Ambrosian art gallery. Named after Ambrose, the patron saint of Milan, it was founded in 1609 by Cardinal Federico Borromeo, whose agents scoured Western Europe and even Greece and Syria for books and manuscripts. Some major acquisitions of complete libraries were the manuscripts of the Benedictine monastery of Bobbio (1606) and the library of the Paduan Vincenzo Pinelli, whose more than 800 manuscripts filled 70 cases when they were sent to Milan and included the famous ''Iliad'', the '' Ilias Picta''. History During Cardinal Borromeo's sojourns in Rome, 1585–95 and 1597–1601, he envisioned developing this library in Milan as one open to scholars and that would serve as a bulwark of Catholic scholarship in the service of the Counter-Reformation against the treatises issuing from Protestant presses. To house the cardinal's 15,000 manuscripts and twice that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Christian Saints
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
669 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 669 ( DCLXIX) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 669 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Arab forces that have taken Chalcedon, on the Asian shore of the Bosporus, threaten the Byzantine capital Constantinople. The Muslim-Arabs are decimated by famine and disease. Yazid, Arab commander, retreats to the island of Cyzicus (modern Turkey). Britain * King Ecgberht of Kent loses the overlordship of Surrey to King Wulfhere of Mercia. Ecgberht then grants the old Saxon Shore Fort at Reculver (south-east England) to a priest named Bassa, in order to establish a monastery dedicated to St. Mary (approximate date). Asia * November 14 – Kamatari, Japanese statesman and reformer, receives the surname Fujiwara f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishops Of Milan
The Archdiocese of Milan ( it, Arcidiocesi di Milano; la, Archidioecesis Mediolanensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Italy which covers the areas of Milan, Monza, Lecco and Varese. It has long maintained its own Latin liturgical rite usage, the Ambrosian rite, which is still used in the greater part of the diocesan territory. Among its past archbishops, the better known are Ambrose, Charles Borromeo, Pope Pius XI and Pope Paul VI. The Archdiocese of Milan is the metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical province of Milan, which includes the suffragan dioceses of Bergamo, Brescia, Como, Crema, Cremona, Lodi, Mantova, Pavia, and Vigevano."Archdiocese of Milano " '' |
Transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept. Description The transept of a church separates the nave from the sanctuary, apse, choir, chevet, presbytery, or chancel. The transepts cross the nave at the crossing, which belongs equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Upon its four piers, the crossing may support a spire (e.g., Salisbury Cathedral), a central tower (e.g., Gloucester Cathedral) or a crossing dome (e.g., St Paul's Cathedral). Since the altar is usually located at the east end of a church, a transept extends to the north and south. The north and south end walls often hold decorated windows of stained glass, such as rose windows, in sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
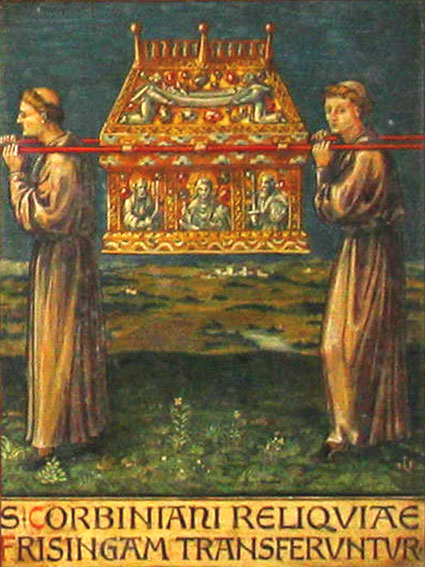
Translation (relic)
In Christianity, the translation of relics is the removal of holy objects from one locality to another (usually a higher-status location); usually only the movement of the remains of the saint's body would be treated so formally, with secondary relics such as items of clothing treated with less ceremony. Translations could be accompanied by many acts, including all-night vigils and processions, often involving entire communities. The solemn translation (in Latin, ''translatio'') of relics is not treated as the outward recognition of sanctity. Rather, miracles confirmed a saint's sanctity, as evinced by the fact that when, in the twelfth century, the Papacy attempted to make sanctification an official process; many collections of miracles were written in the hope of providing proof of the saint-in-question's status. In the early Middle Ages, however, solemn translation marked the moment at which, the saint's miracles having been recognized, the relic was moved by a bishop or abbot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Borromeo
Charles Borromeo ( it, Carlo Borromeo; la, Carolus Borromeus; 2 October 1538 – 3 November 1584) was the Archbishop of Milan from 1564 to 1584 and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. He was a leading figure of the Counter-Reformation combat against the Protestant Reformation together with Ignatius of Loyola and Philip Neri. In that role he was responsible for significant reforms in the Catholic Church, including the founding of seminaries for the education of priests. He is honoured as a saint by the Catholic Church, with a feast day on 4 November. Early life Borromeo was a descendant of nobility; the Borromeo family was one of the most ancient and wealthy in Lombardy, made famous by several notable men, both in the church and state. The family coat of arms included the Borromean rings, which are sometimes taken to symbolize the Holy Trinity. Borromeo's father Gilbert was Count of Arona. His mother Margaret was a member of the Milan branch of the House of Medici. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aribert, Archbishop Of Milan
Aribert (or Heribert) (Italian: ''Ariberto da Intimiano'', Lombard: ''Aribert de Intimian'') ( Intimiano, between 970 and 980 - Milan, 16 January 1045) was the archbishop of Milan from 1018, a quarrelsome warrior-bishop in an age in which such figures were not uncommon. Biography Aribert went to Konstanz in June 1025, with other bishops of Northern Italy, to pay homage to Conrad II of Germany, the beleaguered founder of the Salian dynasty. There, in exchange for privileges, he agreed to crown Conrad with the Iron Crown of Lombardy, which the magnates had offered to Odo of Blois. This he did, on 26 March 1026, at Milan, for the traditional seat of Lombard coronations, Pavia, was still in revolt against imperial authority. He journeyed to Rome a year later for the imperial coronation of Conrad by Pope John XIX on 26 March 1027; at a synod at the Lateran he negotiated a decision of the precedence of the archdiocese of Milan over that of Ravenna. He subsequently joined an imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Michael (Roman Catholic)
Michael (archangel), Saint Michael the Archangel is referenced in the Old Testament and has been part of Christian teachings since the earliest times. In Catholic Church, Catholic writings and traditions he acts as the defender of the Church and chief opponent of Satan, and assists people at the hour of death. A widely used "Prayer to Saint Michael" was brought into official use by Pope Leo XIII in 1886 and was recommended by Pope John Paul II in 1994. In scripture Michael is mentioned by name five times in the Bible. * , Gabriel says, "...but the prince of the kingdom of Persia stood in my way for twenty-one days, until finally Michael, one of the chief princes, came to help me." * , "No one supports me against all these except Michael, your prince, standing as a reinforcement and a bulwark for me." * , "At that time there shall arise Michael, the great prince, guardian of your people; It shall be a time unsurpassed in distress since nations began until that time." * , "Yet the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of Milan
Milan Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Milano ; lmo, Domm de Milan ), or Metropolitan Cathedral-Basilica of the Nativity of Saint Mary ( it, Basilica cattedrale metropolitana di Santa Maria Nascente, links=no), is the cathedral church of Milan, Lombardy, Italy. Dedicated to the Nativity of St Mary (''Santa Maria Nascente''), it is the seat of the Archbishop of Milan, currently Archbishop Mario Delpini. The cathedral took nearly six centuries to complete: construction began in 1386, and the final details were completed in 1965. It is the largest church in the Italian Republic—the larger St. Peter's Basilica is in the State of Vatican City, a sovereign state—and possibly the second largest in Europe and the third largest in the world (its size and position remain a matter of debate). History Milan's layout, with streets either radiating from the Duomo or circling it, reveals that the Duomo occupies what was the most central site in Roman Mediolanum, that of the public bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feast Day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does not mean "a large meal, typically a celebratory one", but instead "an annual religious celebration, a day dedicated to a particular saint". The system arose from the early Christian custom of commemorating each martyr annually on the date of their death, or birth into heaven, a date therefore referred to in Latin as the martyr's ''dies natalis'' ('day of birth'). In the Eastern Orthodox Church, a calendar of saints is called a ''Menologion''. "Menologion" may also mean a set of icons on which saints are depicted in the order of the dates of their feasts, often made in two panels. History As the number of recognized saints increased during Late Antiquity and the first half of the Middle Ages, eventually every day of the year had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |