|
John Hill (Royal Navy Officer)
Rear-Admiral Sir John Hill (c. 1774 – 20 January 1855) was an officer of the Royal Navy who served during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Hill entered the navy at a young age, probably after a period of being nominally on naval ships in order to gain seniority. He served on several ships during the years of peace between the end of the American War of Independence and the start of the French Revolutionary Wars, and was promoted to lieutenant shortly after the outbreak of the latter conflict. He served in the English Channel and the Mediterranean, and was one of the officers of at the Battle of the Nile in 1798. He was promoted to commander for his good service in the battle, but only commanded one ship, the troopship , before the Peace of Amiens. He distinguished himself in the service of the Transport Board during the Napoleonic Wars, overseeing the movement of troops to and from continental Europe and earning the thanks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deal, Kent
Deal is a coastal town in Kent, England, which lies where the North Sea and the English Channel meet, north-east of Dover and south of Ramsgate. It is a former fishing, mining and garrison town whose history is closely linked to the anchorage in the Downs. Close to Deal is Walmer, a possible location for Julius Caesar's first arrival in Britain. Deal became a 'limb port' of the Cinque Ports in 1278 and grew into the busiest port in England; today it is a seaside resort, its quaint streets and houses a reminder of its history along with many ancient buildings and monuments. In 1968, Middle Street was the first conservation area in Kent. The coast of France is approximately from the town and is visible on clear days. The Tudor-era Deal Castle, commissioned by then-King, Henry VIII, has a rose floor plan. History Deal is first mentioned as a village in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as ''Addelam''. It is referred to as ''Dela'' in 1158, and ''Dale'' in 1275 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb Vessel
A bomb vessel, bomb ship, bomb ketch, or simply bomb was a type of wooden sailing naval ship. Its primary armament was not cannons ( long guns or carronades) – although bomb vessels carried a few cannons for self-defence – but mortars mounted forward near the bow and elevated to a high angle, and projecting their fire in a ballistic arc. Explosive shells (also called ''bombs'' at the time) or carcasses were employed rather than solid shot. Bomb vessels were specialized ships designed for bombarding (hence the name) fixed positions on land. In the 20th century, this naval gunfire support role was carried out by the most similar purpose-built World War I- and II-era monitors, but also battleships, cruisers, and destroyers. Development The first recorded deployment of bomb vessels by the English was for the siege of Calais in 1347 when Edward III deployed single deck ships with bombardes and other artillery. The first specialised bomb vessels were built towards the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Pakenham (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Thomas Pakenham GCB (29 September 1757 – 2 February 1836), styled The Honourable from birth to 1820, was a British naval officer and politician. Biography Pakenham was born the fourth son of The 1st Baron Longford and his wife Elizabeth, Baroness Longford (she was later created, in June 1785, The 1st Countess of Longford). He entered the Royal Navy in 1771 on board the , with Captain John MacBride, with whom he moved to the in 1773. In 1774 he was on the coast of Guinea with William Cornwallis in the , and in 1775 was acting lieutenant of the on the coast of North America. In the following year he was promoted by Lord Shuldham to be lieutenant of the frigate , and while in her saw much boat service, in the course of which he was severely wounded. In 1778 he joined the , commanded by Lord Mulgrave, in the fleet under Keppel, and was present in the Battle of Ushant on 27 July. In the following spring he was moved into the ''Europe'', going to North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Fleet
The Channel Fleet and originally known as the Channel Squadron was the Royal Navy formation of warships that defended the waters of the English Channel from 1854 to 1909 and 1914 to 1915. History Throughout the course of Royal Navy's history there had been different squadrons stationed in home waters. One of the earliest known naval formations to be based at Plymouth was called the Western Squadron which was the forerunner of the Channel Squadron that was later known as the Channel Fleet. In 1650 Captain William Penn, Commander-in-Chief, was charged with guarding the Channel from Beachy Head to Lands End with six ships. This system continued following the Restoration. It was the start of what was to become a Western Squadron. From 1690 the squadron operated out of Plymouth Dockyard during wartime periods, which was for most of the 18th century and early 19th century. In 1854 The Channel Squadron, sometimes known as the Particular Service Squadron, was established. The Channel Squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Mann (Royal Navy Officer)
Robert Mann (c.1748 – 20 September 1813) was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served during the American War of Independence and the French Revolutionary Wars, eventually rising to the rank of admiral of the red. Early career Mann was born into a naval family. His father, the elder Robert Mann, was a captain in the navy. He was mortally wounded while commanding during the capture of the French privateer ''Gloire'' on 7 March 1762, during the Seven Years' War. His son, the younger Robert Mann, was born in 1745, being baptised at Wandsworth on 18 July 1745. (This date is confirmed by his grave at All Saints Milford-on-Sea which shows his age as 68 when he died in 1813.) He embarked on a naval career and was commissioned as lieutenant on 26 May 1768, having been wounded in the neck by a musket ball in the action when his father was killed. The grave shows his name as Man rather than Mann, and that all his correspondence, as well as that of his father, used the same spelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Dickson
Admiral Sir Archibald Dickson, 1st Baronet (c.1739–1803) was a Royal Navy officer. Naval career He was born around 1739 the son of Archibald Dickson. He initially entered the merchant navy in 1752. He moved to the Royal Navy in 1755 and passed the lieutenants exam in 1759. In 1765 he was given command of HMS Egmont and in 1771 took command of HMS Thunder. Promoted to captain on 31 January 1774, Dickson was given command of the fourth-rate HMS ''Antelope'' in January 1774 and the sixth-rate HMS ''Greyhound'' in October 1775. In Greyhound, he took part in the action against the Penobscot Expedition in July 1779 and fought at the Battle of Martinique in April 1780 during the American Revolutionary War. He was next given command of the third-rate HMS ''Dublin'' and saw action at the Battle of Cape Spartel in October 1782. After that he was given command of the third-rate HMS ''Goliath'' in 1786, of the third-rate HMS ''Captain'' in 1790 and the third-rate HMS ''Egmont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
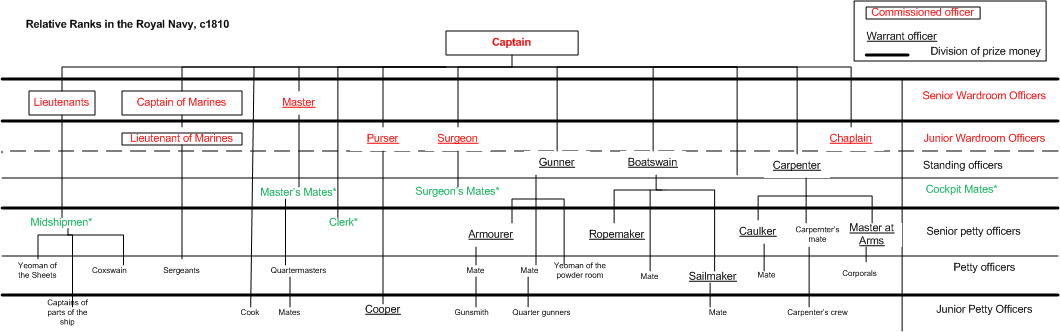
Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Kenya. In the 17th century, a midshipman was a rating for an experienced seaman, and the word derives from the area aboard a ship, amidships, either where he worked on the ship, or where he was berthed. Beginning in the 18th century, a commissioned officer candidate was rated as a midshipman, and the seaman rating began to slowly die out. By the Napoleonic era (1793–1815), a midshipman was an apprentice officer who had previously served at least three years as a volunteer, officer's servant or able seaman, and was roughly equivalent to a present-day petty officer in rank and responsibilities. After serving at least three years as a midshipman or master's mate, he was eligible to take the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master's Mate
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the Royal Navy, United States Navy and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer who assisted the master. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of Sub-Lieutenant in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers. Royal Navy Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted the master but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a superior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a first rate, three on a third rate, and two on most frigates. Duties Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected from the ranks of the quartermasters, who they supervised, or from the ranks of midshipmen who wanted more responsib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)