|
Johann Friedrich, Duke Of Pomerania
John Frederick (german: Johann Friedrich; 27 August 1542 – 9 February 1600) was Duke of Pomerania from 1560 to 1600, and Bishop of Cammin (Kamień) from 1556 to 1574. Elected bishop in 1556 and heir of the duchy in 1560, he remained under tutelage of his great-uncle Barnim XI until he took on his offices in 1567. Biography Johann Friedrich was the oldest of ten siblings born to Philipp I of Pomerania-Wolgast and Maria of Saxony. At the age of 14, he was elected bishop of Cammin on 29 August 1556, after his predecessor Martin von Weiher had died on 8 June. Starting with John Frederick, the House of Pomerania held this title until the last duke died in 1637, thus ending the considerable independence of the bishopric's territory from the rest of the Duchy of Pomerania. In 1560, the bishopric's administration was reformed accordingly. When his father died on 14 February 1560, John Frederick nominally became duke of Pomerania but was still under the tutelage of his great-uncle, Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Griffins
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been taken from the ducal coat of arms. Duke Wartislaw I (died 1135) was the first historical ruler of the Duchy of Pomerania and the founder of the Griffin dynasty. The most prominent Griffin was Eric of Pomerania, who became king of the Kalmar Union in 1397, thus ruling Denmark, Sweden and Norway. The last Griffin duke of Pomerania was Bogislaw XIV, who died during the Thirty Years' War, which led to the division of Pomerania between Brandenburg-Prussia and Sweden. Duchess Anna von Croy, daughter of Duke Bogislaw XIII and the last Griffin, died in 1660. Name of the Dynasty The dynasty is known by two names, ''Pomerania'', after their primary fief, and ''Griffin'', after their coat of arms, which had featured a griffin since the late 12th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of The Duchy Of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania was partitioned several times to satisfy the claims of the male members of the ruling House of Pomerania dynasty.Kyra T. Inachin, ''Die Geschichte Pommerns'', Hinstorff Rostock, 2008, p.30, The partitions were named after the ducal residences: Pomerania-Barth, -Demmin, -Rügenwalde, -Stettin, -Stolp, and -Wolgast. None of the partitions had a hereditary character,Norbert Buske, ''Pommern'', Helms Schwerin 1997, p.21, the members of the House of Pomerania inherited the duchy in common. The duchy thus continued to exist as a whole despite its division. The only exception was made during a war with the Margraviate of Brandenburg, when in 1338 Barnim III of Pomerania-Stettin was granted his partition as a fief directly from the Holy Roman Emperor, while Pomerania-Wolgast remained under formal Brandenburgian overlordship.Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, pp.107-109, However, already in 1348, German king and later emperor Charles IV again granted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Saxon Circle
The Upper Saxon Circle (german: Obersächsischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire, created in 1512. The circle was dominated by the electorate of Saxony (the circle's director) and the electorate of Brandenburg. It further comprised the Saxon Ernestine duchies and Pomerania. The Lusatias that fell to Saxony by the 1635 Peace of Prague were never encircled. Composition The circle was made up of the following states: Sources * The list of states making up the Upper Saxon Circle is based on that in the German German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) ** Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Ge ... Wikipedia article Obersächsischer Reichskreis. External links *Imperial Circles in the 16th Century– Historical Maps of Germany {{Authority control Circles of the Holy Roman Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coining (metalworking)
Coining is a form of precision stamping in which a workpiece is subjected to a sufficiently high stress to induce plastic flow on the surface of the material. A beneficial feature is that in some metals, the plastic flow reduces surface grain size, and work hardens the surface, while the material deeper in the part retains its toughness and ductility. The term comes from the initial use of the process: manufacturing of coins. Coining is used to manufacture parts for all industries and is commonly used when high relief or very fine features are required. For example, it is used to produce coins, badges, buttons, precision-energy springs and precision parts with small or polished surface features. Coining is a cold working process similar in other respects to forging, which takes place at elevated temperature; it uses a great deal of force to plastically deform a workpiece, so that it conforms to a die. Coining can be done using a gear driven press, a mechanical press, or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuenkamp
Franzburg () is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Rügen district of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated 20 km southwest of Stralsund. Before the Protestant Reformation, later Franzburg was the site of Neuenkamp Abbey. Neuenkamp Abbey In the course of the medieval conversion of Pomerania and German Ostsiedlung, prince Wizlaw I granted the central parts of the woods covering the mainland section of his Principality of Rügen, then Danish, to Cistercian monks from Camp Abbey in Lower Saxony who build Neuenkamp Abbey on 8 November 1231. The monks erected a church that, with a length of 80 meters, a width of 15 meters, and an arch height of 25 meters, was then the largest church in all Pomerania. The possessions of the abbey rapidly increased, 50 years after its foundation the abbey's territory reached the coast. The woods were cleared, and numerous villages of the '' Hagenhufendorf'' type were set up and populated with German settlers. In 1325, the last prince of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
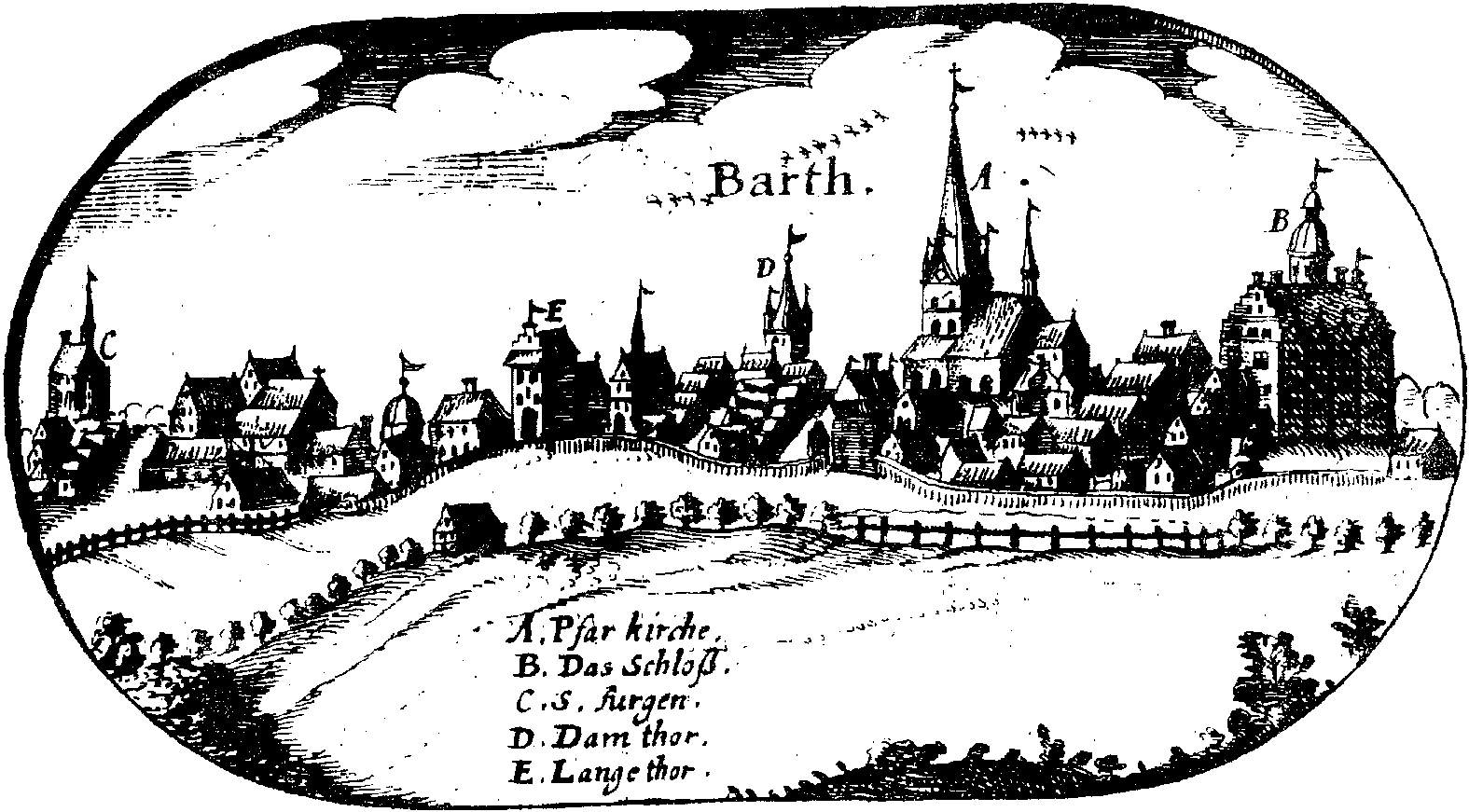
Barth, Germany
Barth is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated at a lagoon (Bodden) of the Baltic Sea facing the Fischland-Darss-Zingst peninsula. Barth belongs to the district of Vorpommern-Rügen. It is close to the Western Pomerania Lagoon Area National Park. In 2011, it held a population of 8,706. History Barth dates back to the medieval German Ostsiedlung, before which the area was settled by Wends of the Liuticians or Rani tribe. Jaromar II, Danish prince of Rügen, granted the town Lübeck law in 1255. In the same document, he agreed to remove his burgh, ''Borgwall'' or ''Neue Burg'', then on the northwestern edge of the town's projected limits. Another Wendish burgh, ''Alte Burg'' near today's train station, was not used anymore. The German town was set up on empty space between the burghs. Not a member of the Hanseatic League, the town never grew to the importance and size of neighboring Hanseatic towns like Stralsund. The last prince of Rügen, Witzlaw III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir VI, Duke Of Pomerania
Casimir VI (also known as Casimir IX; 22 March 1557 – 10 May 1605) was a member of the House of Pomerania who ruled as Lutheran Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Cammin. Life Casimir was born in Wolgast. He was the tenth child of Duke Philip I of Pomerania-Wolgast and his wife Maria of Saxony. Philip I died in 1560; he was survived by five of his sons. Apart from Casimir VI, they were John Frederick (born: 1542), Bogislaw XIII (born: 1544), Ernest Louis (born: 1545), Barnim X (born: 1549). Initially, the Lord High Stewart Ulrich von Schwerin, acted as regent. He was supported by an eleven-member regency council. On 25 July 1569, the elder brothers wrote the Treaty of Jasenitz, dividing Pomerania among themselves. For Casimir, it was planned that he would later become the Lutheran administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Cammin. In 1574, John Frederick renounced that position, and Casimir took over the diocese, aged just 17 years. In 1578, he undertook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Ludwig, Duke Of Pomerania
Ernst Ludwig (20 November 1545, in Wolgast – 17 June 1592, in Wolgast)Thümmel (2002), p.87 was duke of Pomerania from 1560 to 1592. From 1569 to 1592, he was duke in the ''Teilherzogtum'' Pomerania-Wolgast, sharing the rule over the Duchy of Pomerania with his older brother Johann Friedrich, duke in the other ''Teilherzogtum'' Pomerania-Stettin and bishop of Cammin.Nicklas (2002), p.135 Life Ernst Ludwig was one of ten siblings born to Philipp I of Pomerania-Wolgast and Maria of Saxony. After the death of his father on 14 February 1560, all siblings were under the guardianship of their great-uncle, Barnim XI. With one of his brothers, Barnim XII, Ernst Ludwig studied at the University of Wittenberg from 1563 to 1565, where they resided in the house of Martin Luther. With another brother, Bogislaw XIII, Duke of Pomerania, Bogislaw XIII, he temporarily lived at the court of Johann Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar. In 1569, Barnim XI retired, and the Partitions of the Duchy of Pom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teilherzogtum
The district duchy, also known as the district principality, was a type of the state under the patrimonial system, such as duchy or principality, formed in the feudal system, as a result of land partition between the members of a royal family. It occurred in the Middle Ages and early modern period, notably in Europe, in states such as the Holy Roman Empire, Duchy of Poland, and Kievan Rus'.Tadeusz Manteuffel: ''Historia powszechna. Średniowiecze.'' Warsaw: Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, 1990, p. 250. ISBN 83-01-08685-8. Holy Roman Empire Bavaria *Bavaria-Ingolstadt *Bavaria-Landshut *Bavaria-Munich *Bavaria-Straubing Mecklenburg *Mecklenburg-Güstrow *Mecklenburg-Schwerin *Mecklenburg-Stargard *Mecklenburg-Strelitz Palatinate *Palatinate-Birkenfeld *Palatinate-Birkenfeld-Bischweiler *Palatinate-Birkenfeld-Gelnhausen *Palatinate-Birkenfeld-Zweibrücken *Palatinate-Kleeburg *Palatinate-Landsberg *Palatinate-Lautern *Palatinate-Mosbach *Palatinate-Mosbach-Neumarkt *Palatinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnim X, Duke Of Pomerania
Barnim X, or according to another account Barnim XII (15 February 1549, in Wolgast – 1 September 1603, in Szczecin) was a duke of Pomerania and a member of the House of Griffins. He administered from 1569, the Rügenwalde district. From 1600 until his death, he ruled in Pomerania-Stettin. Life Barnim was the sixth child of Duke Philip I of Pomerania-Wolgast and his wife Maria of Saxony, Duchess of Pomerania. Philip died in 1560 and was survived by five of his sons; in addition to Barnim, they were his older brothers John Frederick (1542–1600), Bogislaw XIII (1544–1606) and Ernest Louis (1545–1592) and Barnim's younger brother Casimir VI (1557–1605). A guardianship government was set up for all the brothers. It consisted of the Lord Chamberlain Ulrich von Schwerin as a regent and a regency council of eleven people. Barnim and his brother Ernest Louis studied from 1563 at the University of Wittenberg, where they lived until 1565 at the home of a Martin Luther, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollin (town)
Wolin (Polish language, Polish pronouciation: ; formerly german: Wollin) is a town in northwestern Poland, situated on the southern tip of the Wolin island off the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of the historic region of Western Pomerania. The island lies at the edge of the strait of Dziwna in Kamień County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship. The town, now a fishing port and gateway to the island's bathing resorts, has a population of approximately 4,900. Dating from the 9th century, it has been associated with the semi-legendary settlements of Jomsburg, Jumne, Julin and Vineta.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, ''Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde Band 16'', 2nd edition, Walter de Gruyter, 2000, pp.120-121, It played an important role in the conversion of Pomerania and in 1140 became the first see of the Cammin bishopric, Pomeranian diocese. Several ruins from the Slavic peoples, Slavic period occupy the area. The early medieval town fell victim to the late 12th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |