|
Job Von Witzleben (Prussia)
Karl Ernst Job Wilhelm von Witzleben (20 July 1783 – 9 July 1837) was a Prussian lieutenant general, adjutant-general to the king, and minister of war. Career Born in Halberstadt, Witzleben was the first-born son of Lieutenant Heinrich Günther von Witzleben (1755–1825) and his wife Amalie Karoline Luise Wilhelmine, née von Wulffen (1766–1807). Of Thuringian ''Uradel'', he became a personal squire to the Hohenzollern king Frederick William II of Prussia in 1793, and then an ensign in the Royal Guard in 1799. His active career was promoted by King Frederick William III who became a close friend. Witzleben achieved the rank of Second Lieutenant in 1802. He was captured in the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt fought on 14 October 1806, but was exchanged in August 1807. His work ''Ideas on the Reorganisation of the Light Infantry'', caught the attention of Gerhard von Scharnhorst, so that he was transferred in December 1808 to the newly formed ''Garde-Jäger-Bataillon' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Wilhelm Von Dobschütz
Leopold Wilhelm von Dobschütz (1 January 1763 in Brzeg, Brieg, Niederschlesien – 3 February 1836 at Gut Zölling, Landkreis Freystadt i. Niederschles., Kreis Freystadt, prev. Landkreis Sagan, Kreis Sagan, Niederschlesien) was a Prussian "general of cavalry", the "hero of Dennewitz" and "liberator of Wittenberg", military governor of the Rhine province and of Breslau. He was Gutsherr of Zölling, which his wife had inherited, and the Gütern Ober- and Nieder-Briesnitz as well as Schönbrunn, all in the district Sagan. As to the year of his birth, there are different statements: The year 1763 is belied by his gravestone inscription and the "Seniority List of the royal Prussian army for the year 1801"; in his marriage certificate of 1787, his age is indicated as 28 years, according to which he would have been born in 1759. In other sources, one finds the years 1761 and 1764, though 1763 is more likely to be correct. Family Though nothing certain is known as to his parents, his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William II Of Prussia
Frederick William II (german: Friedrich Wilhelm II.; 25 September 1744 – 16 November 1797) was King of Prussia from 1786 until his death in 1797. He was in personal union the Prince-elector of Brandenburg and (via the Orange-Nassau inheritance of his grandfather) sovereign prince of the Canton of Neuchâtel. Pleasure-loving and indolent, he is seen as the antithesis to his predecessor, Frederick the Great. (Frederick II). Under his reign, Prussia was weakened internally and externally, and he failed to deal adequately with the challenges to the existing order posed by the French Revolution. His religious policies were directed against the Enlightenment and aimed at restoring a traditional Protestantism. However, he was a patron of the arts and responsible for the construction of some notable buildings, among them the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin. Haydn, Mozart and Beethoven all dedicated works to him. Early life Frederick William was born in Berlin, the son of Prince Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottenburg
Charlottenburg () is a Boroughs and localities of Berlin, locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a German town law, town in 1705 and named after Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums. Charlottenburg was an independent city to the west of Berlin until 1920 when it was incorporated into "Greater Berlin Act, Groß-Berlin" (Greater Berlin) and transformed into a borough. In the course of Berlin's 2001 administrative reform it was merged with the former borough of Wilmersdorf becoming a part of a new borough called Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Later, in 2004, the new borough's districts were rearranged, dividing the former borough of Charlottenburg into the localities of Charlottenburg proper, Westend (Berlin), Westend and Charlottenburg-Nord. Geography Charlottenburg is located in Berlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
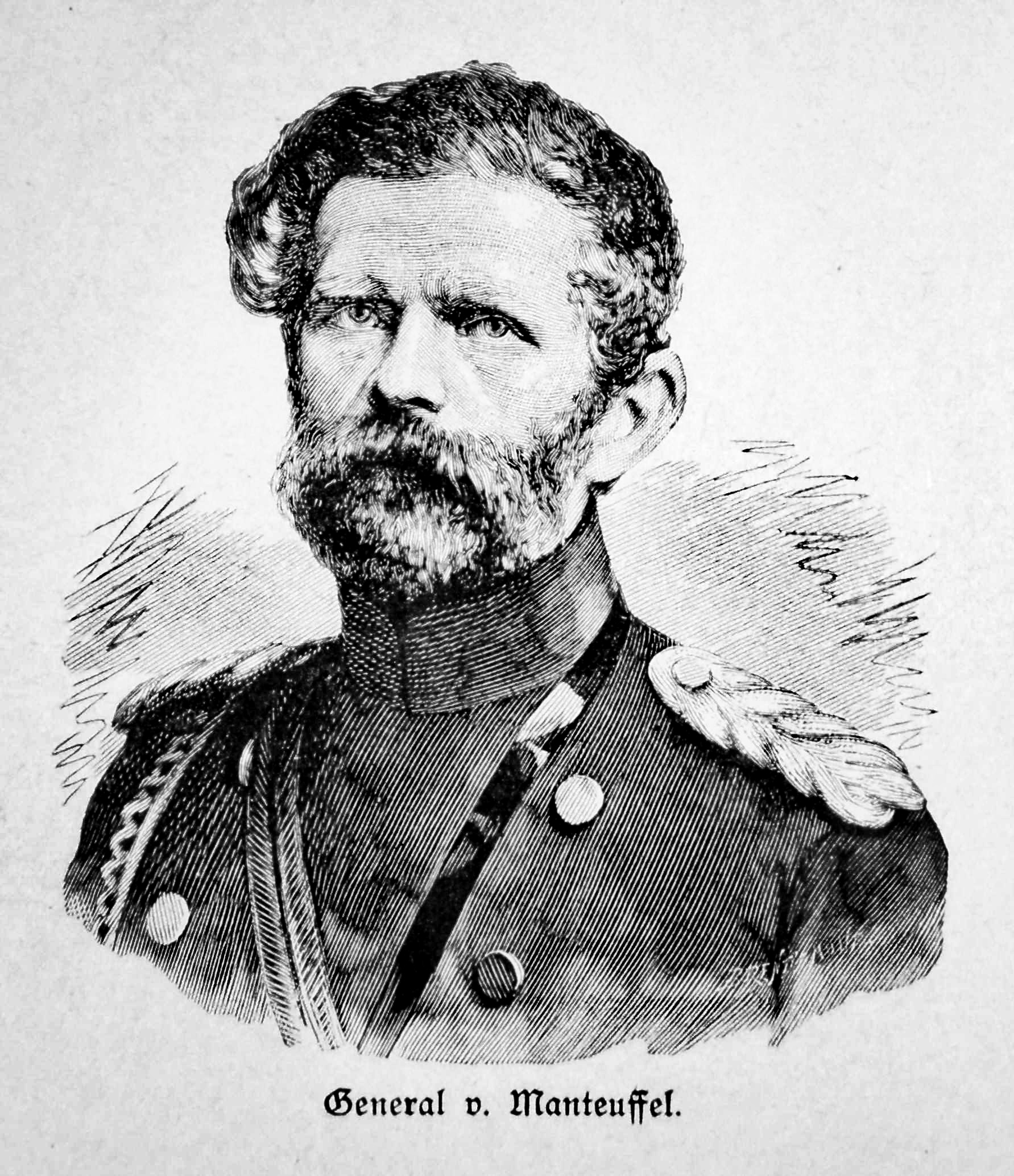
Edwin Freiherr Von Manteuffel
Edwin Karl Rochus Freiherr von Manteuffel (24 February 180917 June 1885) was a Prussian ''Generalfeldmarschall'' noted for his victories in the Franco-Prussian War, and the first Imperial Lieutenant (german: Reichsstatthalter) of Alsace–Lorraine from 1879 until his death. Biography Son of the president of the superior court of Magdeburg, Manteuffel was born at Dresden and brought up with his cousin, Otto von Manteuffel (1805–1882), the Prussian statesman. He entered the guards cavalry at Berlin in 1827 and became an officer in 1828. After attending the War Academy for two years, and serving successively as '' aide-de-camp'' to General von Müffling and to Prince Albert of Prussia, he was promoted captain in 1843 and major in 1848, when he became ''aide-de-camp'' to Frederick William IV, whose confidence he had gained during the revolutionary movement in Berlin. Promoted lieutenant-colonel in 1852, and colonel (and commanding officer of the 5th Uhlans) in 1853, Manteuff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
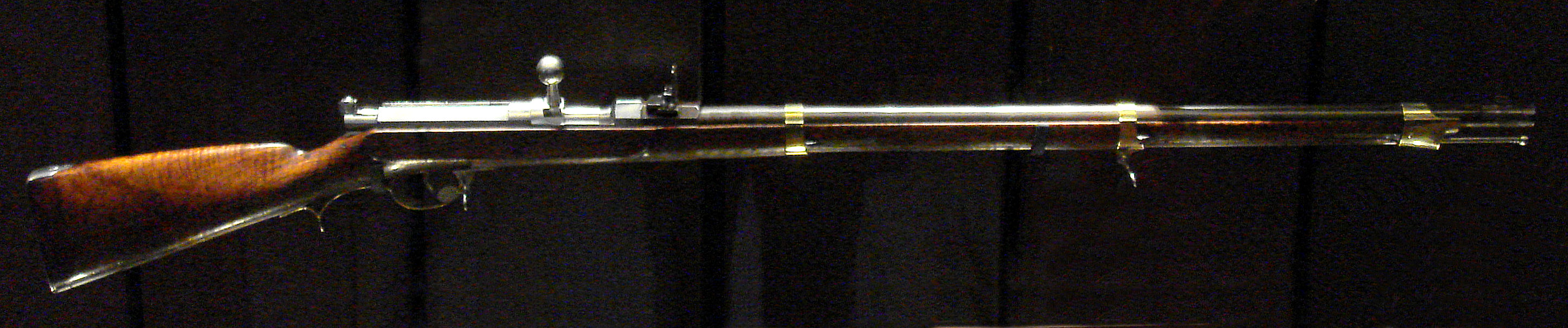
Needle Gun
A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with rifling) is a firearm that has a needle-like firing pin, which can pass through the paper cartridge case to strike a percussion cap at the bullet base. Types Pauly A diagram of a needle-gun cartridge, showing the paper cartridge case, the sabot, and acorn-shaped bullet. The first experimental needle gun was designed by Jean Samuel Pauly, a Swiss gunsmith. In Paris in 1808, in association with French gunsmith François Prélat, Pauly created the first fully self-contained cartridges: the cartridges incorporated a copper base with integrated mercury fulminate primer powder (the major innovation of Pauly), a round bullet and either brass or paper casing. The cartridge was loaded through the breech and fired with a needle. The needle-activated central-fire breech-loading gun became a major feature of firearms thereafter. The corresponding firearm was also developed by Pauly. Pauly made an improved version which was protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landwehr
''Landwehr'', or ''Landeswehr'', is a German language term used in referring to certain national army, armies, or militias found in nineteenth- and early twentieth-century Europe. In different context it refers to large-scale, low-strength fortifications. In German, the word means "defence of the country"; but the term as applied to an insurrectional militia is very ancient, and ''lantveri'' are mentioned in ''Baluzii Capitularia'', as quoted in Henry Hallam, Hallam's ''Middle Ages'', i. 262, 10th edition. The English term "home guard" may possibly derive from an attempt to translate the term ''landwehr'', the earliest unit calling itself "home guard" being formed by German Americans, German immigrants in Missouri in the events leading up to the American Civil War. Austria-Hungary Austrian ''Landwehr'' The Austrian Landwehr was one of three components that made up the Austro-Hungarian Army, ground forces of the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy between 1868 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Georg Albrecht Ernst Von Hake
250px, Karl von Hake Karl Georg Albrecht Ernst von Hake (8 August 1768 – 19 May 1835) was a Prussian general and Minister of War. Biography Hake was born on the estate of Flatow (now part of Kremmen) in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. He entered the Prussian Army in 1785. In 1793, while serving under the command of Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick, he distinguished himself in the Battle of Pirmasens during the French Revolutionary Wars against France. For his actions he was later to be decorated, on 3 April 1814, with the ''Pour le Mérite'' medal with Oak leaves. Hake was appointed to a post in the War Ministry in 1809, and served as Minister of War from 17 June 1810 until August 1813 when he was replaced by Boyen (during which time he attracted much attention by his efficient preparations for war). Subsequently, commanded a brigade in the Prussian IV Corps ( Bülow's) with rank of major-general, and played a distinguished part in the Battle of Waterloo. In 1819 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebhard Leberecht Von Blücher
Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Fürst von Wahlstatt (; 21 December 1742 – 12 September 1819), ''Graf'' (count), later elevated to ''Fürst'' (sovereign prince) von Wahlstatt, was a Prussian ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal). He earned his greatest recognition after leading his army against Napoleon I at the Battle of the Nations at Leipzig in 1813 and the Battle of Waterloo in 1815. Blücher was born in Rostock, the son of a retired army captain. His military career began in 1758 as a hussar in the Swedish Army. He was captured by the Prussians in 1760 during the Pomeranian Campaign and thereafter joined the Prussian Army, serving as a hussar officer for Prussia during the remainder of the Seven Years' War. In 1773, Blücher was forced to resign by Frederick the Great for insubordination. He worked as a farmer until the death of Frederick in 1786, when Blücher was reinstated and promoted to colonel. For his success in the French Revolutionary Wars, Blücher became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
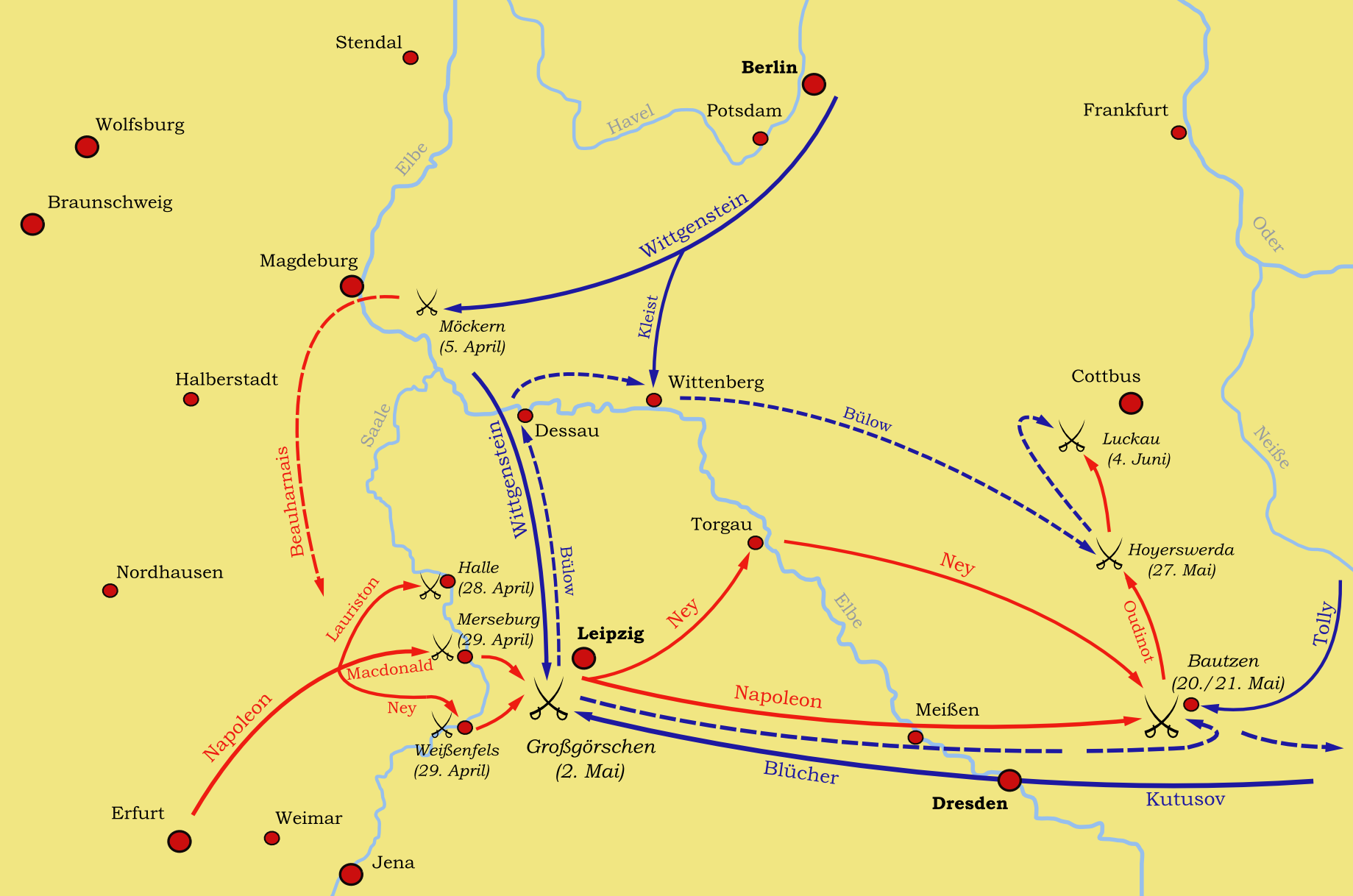
Battle Of Lützen (1813)
In the Battle of Lützen (German: ''Schlacht von Großgörschen'', 2 May 1813), Napoleon I of France defeated an allied army of the Sixth Coalition. The Russian commander, Prince Peter Wittgenstein, attempting to forestall Napoleon's capture of Leipzig, attacked the French right wing near Lützen, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, surprising Napoleon. Quickly recovering, he ordered a double envelopment of the allies. After a day of heavy fighting, the imminent encirclement of his army prompted Wittgenstein to retreat. Due to a shortage of cavalry, the French did not pursue. The next battle would be fought at Bautzen three weeks later. Prelude Following the disaster of French invasion of Russia in 1812, a new Coalition consisting of Britain, Sweden, Prussia and Russia formed against France. In response to this, Napoleon hastily assembled an army of just over 200,000 which included inexperienced recruits, troops from Spain and garrison battalions but was severely short of horses (a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabskapitän
''Stabskapitän'' (en: Staff captain), in the cavalry also ''Stabsrittmeister'' (en: "Staff riding master" or "Staff cavalry master"), or ''Kapitänleutnant'' (en: Captain lieutenant), was a historic military rank in the Prussian Army. In reference to the German ''Stabskapitän'' the equivalent rank in the Imperial Russian Army used to be the rank ''Stabs-kapitan'' (russian: штабс-капитан). It ranked between the Premierleutnant (later called Oberleutnant) and Hauptmann/Rittmeister in the Prussian army, and between ''poruchik'' and captain in the Russian army. Its holder represented the actual captain and company commander in his absence, frequently and often for long periods, should his (usually noble) Hauptmann show no interest in leading the company, though the Hauptmann would retain his rank, status and uniform. In the army of Frederick the Great, a regiment's regimentschef, oberst, staff officers, company commanders and those of nearby rank received a far high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard Von Scharnhorst
Gerhard Johann David von Scharnhorst (12 November 1755 – 28 June 1813) was a Hanoverian-born general in Prussian service from 1801. As the first Chief of the Prussian General Staff, he was noted for his military theories, his reforms of the Prussian army, and his leadership during the Napoleonic Wars. Scharnhorst limited the use of corporal punishments, established promotion for merit, abolished the enrollment of foreigners, began the organization of a reserve army, and organized and simplified the military administration. Biography Born at Bordenau (now a part of Neustadt am Rübenberge, Lower Saxony) near Hanover, into a small landowner's family, Scharnhorst succeeded in educating himself and in securing admission to the military academy of William, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe, at the Wilhelmstein fortress. In 1778 he received a commission into the Hanoverian service. He employed the intervals of regimental duty in further self-education and literary work. In 1783 he transferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Jena–Auerstedt
The twin battles of Jena and Auerstedt (; older spelling: ''Auerstädt'') were fought on 14 October 1806 on the plateau west of the river Saale in today's Germany, between the forces of Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Prussia. The defeat suffered by the Prussian Army subjugated the Kingdom of Prussia to the French Empire until the Sixth Coalition was formed in 1813. Several figures who were later integral to the reformation of the Prussian Army participated at Jena–Auerstedt, including Gebhard von Blücher, Carl von Clausewitz, August Neidhardt von Gneisenau, Gerhard von Scharnhorst, and Hermann von Boyen. Background Following the Prussian declaration of war, Napoleon initiated his campaign against the Fourth Coalition by thrusting a 180,000-strong force through the Frankenwald. The Prussian army, meanwhile, awaited Napoleon's advance with a force composed of about 130,000 Prussians and 20,000 Saxons. The Prussians were not organized well enough and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)