|
Japanese Occupation Of Kiska
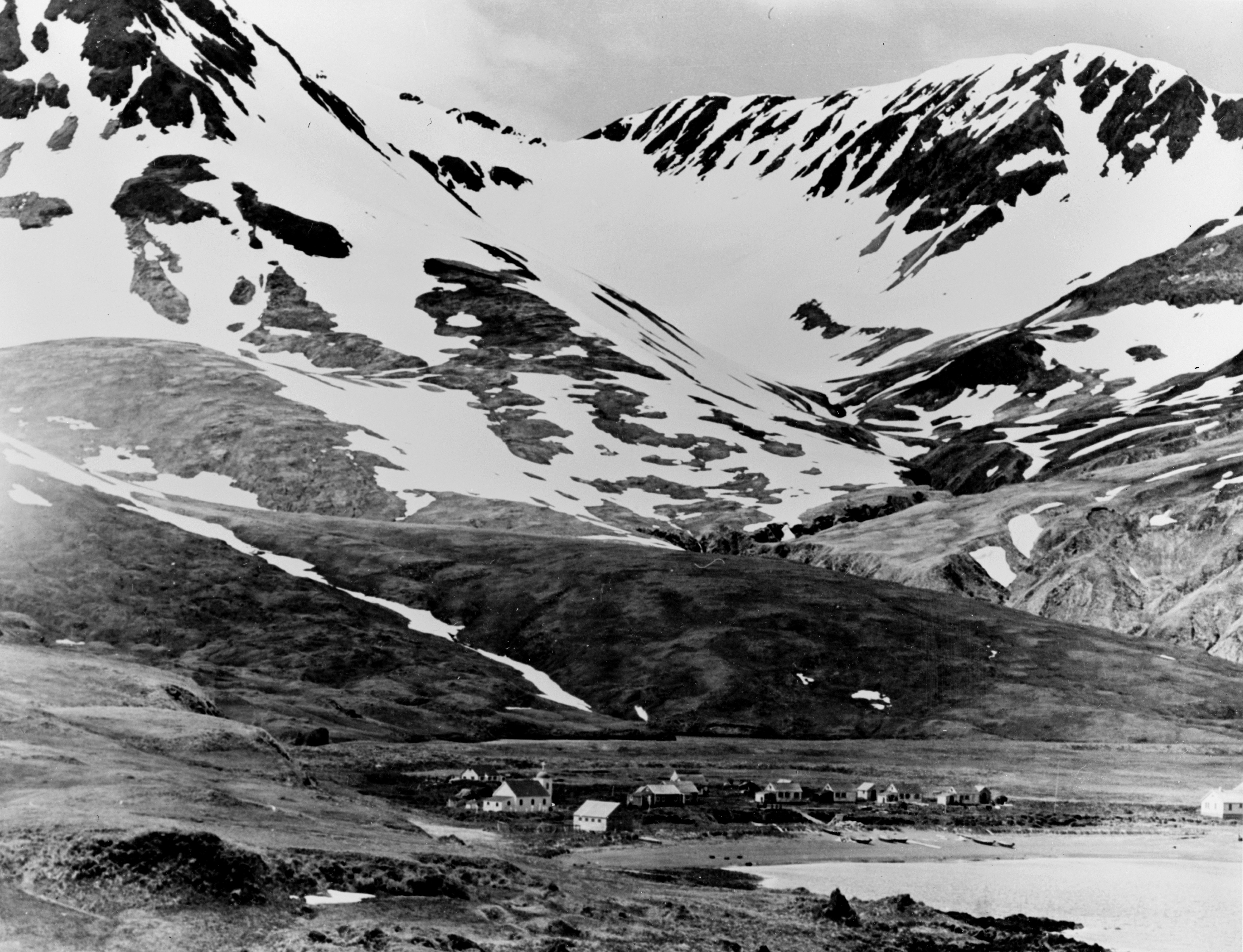
The Japanese occupation of Kiska took place between 6 June 1942 and 28 July 1943 during the Aleutian Islands Campaign of the American Theater and the Pacific Theater of World War II. The Japanese occupied Kiska and nearby Attu Island in order to protect the northern flank of the Japanese Empire. Along with the Attu landing the next day, it was the first time that the United States was occupied by a foreign power since the War of 1812, and was one of the two invasions of the United States during World War II. Background For the Imperial Navy, the North Pacific had a vast frontage from North-Kuril Islands to Minami-Tori-shima, and patrols in this vast sea area with few islands had not been easy. The Imperial Navy Fifth Fleet, which conducted patrols of the ocean off east of Japan, had begun to advocate since the end of January 1942 that the Imperial Navy occupy the western Aleutian Islands and advance the patrol line. In addition, the air raid on Minami-Tori-shima by the US Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Theater (World War II)
The American Theater was a theater of operations during World War II including all continental American territory, and extending into the ocean. Owing to North and South America's geographical separation from the central theaters of conflict (in Europe, the Mediterranean and Middle East, and the Pacific) the threat of an invasion of the continental U.S. or other areas in the Americas by the Axis Powers was negligible and the theater saw relatively little conflict. However, despite the relative unimportance of the American Theater, some battles took place within it, including the Battle of the River Plate, submarine attacks off the East Coast, the Aleutian Islands campaign, the Battle of the St. Lawrence, and the attacks on Newfoundland. Espionage efforts included Operation Bolívar. German operations South America ''See also Latin America during World War II'' Battle of the River Plate The first naval battle during the war was fought on December 13, 1939, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attu Island
Attu ( ale, Atan, russian: Атту, link=no) is an island in the Near Islands (part of the Aleutian Islands chain). It is the westernmost point of the U.S. state of Alaska. The island became uninhabited in 2010, making it the largest uninhabited island to be politically part of the United States. (archived June 25, 2017) The Battle of Attu was the site of the only World War II land battle fought in the United States. The battlefield area is a U.S. National Historic Landmark. Attu Station, a former Coast Guard LORAN station, is located at , making it one of the westernmost points of the United States relative to the rest of the country. However, since it is in the Eastern Hemisphere, being on the opposite side of the 180° longitude line of the contiguous 48 states, it can also be considered one of the easternmost points of the country (a second Aleutian Island, Semisopochnoi Island at 179°46′E, is the easternmost location in the United States by this definition). For purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guns Of Kiska
A gun is a ranged weapon designed to use a shooting tube (gun barrel) to launch projectiles. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns/water cannon, cannons, spray nozzle, spray guns for spray painting, painting or pressure washing, projected water disruptors, and technically also flamethrowers), gas (e.g. light-gas gun) or even charged particles (e.g. plasma torch, plasma gun). Solid projectiles may be free-flying (as with bullets and artillery shells) or tethered (as with Taser guns, spearguns and harpoon guns). A large-caliber gun is also called a ''cannon''. The means of projectile propulsion vary according to designs, but are traditionally effected pneumatically by a high gas pressure contained within the barrel tube, produced either through the rapid exothermic combustion of propellants (as with firearms), or by mechanical compression (as with air guns). The high-pressure gas is introduced behind the projectile, pushing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin D
Franklin may refer to: People * Franklin (given name) * Franklin (surname) * Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class Places Australia * Franklin, Tasmania, a township * Division of Franklin, federal electoral division in Tasmania * Division of Franklin (state), state electoral division in Tasmania * Franklin, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Gungahlin * Franklin River, river of Tasmania * Franklin Sound, waterway of Tasmania Canada * District of Franklin, a former district of the Northwest Territories * Franklin, Quebec, a municipality in the Montérégie region * Rural Municipality of Franklin, Manitoba * Franklin, Manitoba, an unincorporated community in the Rural Municipality of Rosedale, Manitoba * Franklin Glacier Complex, a volcano in southwestern British Columbia * Franklin Range, a mountain range on Vancouver Island, British Columbia * Franklin River (Vancouver Island), British Columbia * Franklin Strai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Of The United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S. states of California, Oregon, and Washington, but sometimes includes Alaska and Hawaii, especially by the United States Census Bureau as a U.S. geographic division. Definition There are conflicting definitions of which states comprise the West Coast of the United States, but the West Coast always includes California, Oregon, and Washington as part of that definition. Under most circumstances, however, the term encompasses the three contiguous states and Alaska, as they are all located in North America. For census purposes, Hawaii is part of the West Coast, along with the other four states. ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' refers to the North American region as part of the Pacific Coast, including Alaska and British Columbia. Although the enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Petty Officer
A chief petty officer (CPO) is a senior non-commissioned officer in many navies and coast guards. Canada "Chief petty officer" refers to two ranks in the Royal Canadian Navy. A chief petty officer 2nd class (CPO2) (''premier maître de deuxième classe'' or ''pm2'' in French) is equivalent to a master warrant officer in the Army and Air Force, and chief petty officer 1st class (CPO1) (''premier maître de première classe'' or ''pm1'') is equivalent to a chief warrant officer in the Army and Air Force. In spoken references, chief petty officers may be addressed as "chief" but are never addressed as "sir". Australia "Chief Petty Officer" is the second highest non-commissioned rank in the Royal Australian Navy. India A Chief Petty Officer in Indian Navy is a junior-commissioned officer, equivalent to the NATO rank enlisted grade of E-6 ( Staff Sergeant ) . This rank is equivalent to Naib Subedar in Indian Army and Junior Warrant Officer in Indian Air force. The two highest e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
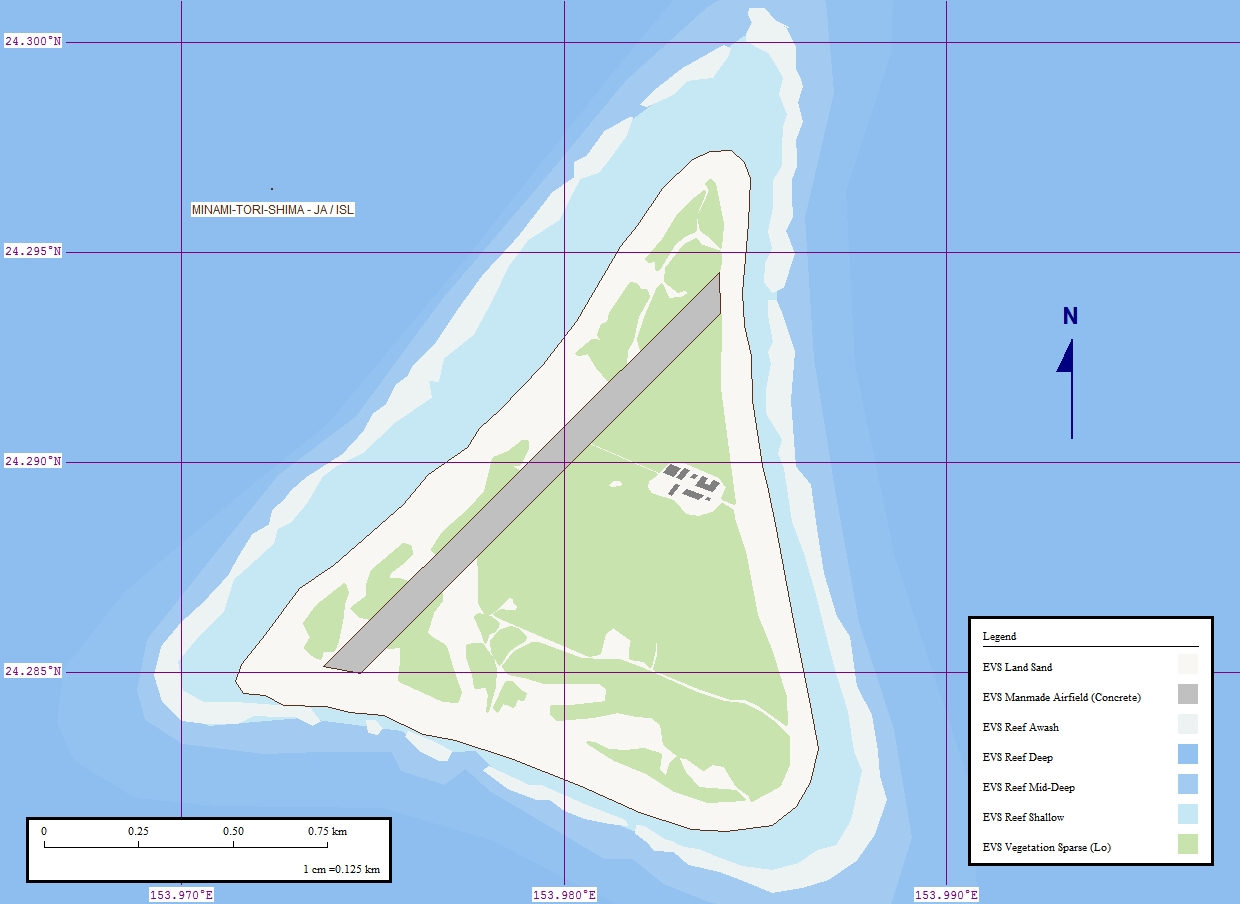
Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line between mainland Tokyo and Wake Island, further to the east-southeast. The closest island to Minamitorishima is East Island in the Mariana Islands, which is to the west-southwest. It is the easternmost territory belonging to Japan, and the only Japanese territory on the Pacific Plate, past the Japan Trench. Although small () it is of strategic importance, as it enables Japan to claim a exclusive economic zone in the surrounding waters. It is also the easternmost territory of Tokyo, being administratively part of Ogasawara village. There is no civilian population, except personnel of the Japan Meteorological Agency, JSDF, and Japan Coast Guard serving temporary tours of duty on the island. Access The island is off-limits to ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. It stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. They cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000. The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion as the Soviet Union towards the end of World War II. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest ( Iturup and Kunashir), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan and the Habomai islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute. The disputed islands are k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of The United States
The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the United States. The country has been physically invaded on several occasions—once during the War of 1812, once during the Mexican–American War, several times during the Mexican Border War, and three times during World War II, two of which were air attacks on American soil. During the Cold War, most of the US military strategy was geared towards repelling an attack by the Warsaw Pact against NATO allies in Europe. Early attacks The military history of the United States began with a foreign power on US soil: the British Army during the American Revolutionary War. After American independence, the next attack on American soil was during the War of 1812, also with Britain, the first and only time since the end of the Revolutionary War in which a foreign power occupied the American capital ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)