|
Jalal Al-Mulk Abu'l Hasan
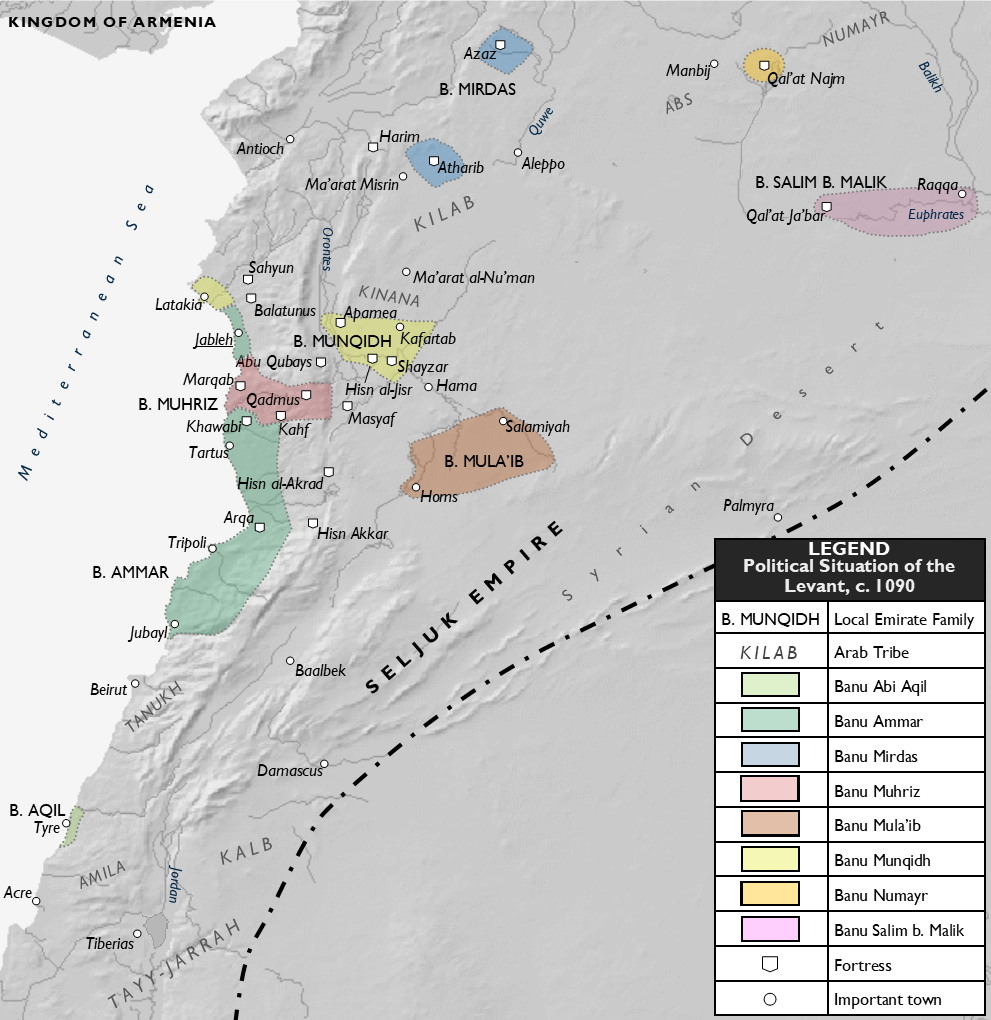
Jalal al-Mulk Ali ibn Muhammad ibn Ammar ( ar, جلال الملك علي بن محمد بن عمار) was the ruler (''qadi'') of Tripoli during the First Crusade. Ali belonged to the house of the Banu Ammar, which was known more for its learning than for warfare. The dynasty had been founded by his uncle, Amin al-Dawla Abu Talib al-Hasan ibn Ammar, who as ''qadi'' of Tripoli had declared himself independent from the Fatimid Caliphate c. 1065. Ali came to power in Tripoli after his uncle's death in 1072, after a brief succession struggle with his brother, whom he expelled from the city. He was able to maintain his precarious independence by playing the Fatimids off the Seljuks. In 1081, he captured Jableh from the Byzantine Empire. Under Ali's reign, the First Crusade came to the Levant. Following the Siege of Antioch, the Crusaders began to make their way down to Jerusalem in early 1099. Soon, the party of Raymond IV approached Tripoli. Fearing the advancing Crusaders, he atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amin Al-Dawla Abu Talib Al-Hasan Ibn Ammar
Amin may refer to: People * Amin (name), a masculine given name and also a surname * Al-Amin, the sixth Abbasid caliph, who ruled from 809 to 813 * Amin (Qing dynasty), an Imperial Prince of the Qing Dynasty * Amin, an arbitrator who assessed and collected revenue in the Parganas Other uses * Amin, Kurukshetra, now known as Abhimanyupur, a village in Haryana state, India * AMIN, or Anak Mindanao, a political party in the Philippines * "Amin" (song), a song by Anna Vissi * AMIN Worldwide, an alliance of independently owned advertising agencies * ''Amin'' (film), a 2018 French drama film * Amen in religion See also * Amine (other) * Amen (other) * Aming (J-pop) Aming (あみん) is female Japanese pop/folk duo composed of Takako Okamura and Haruko Kato that debuted in 1982 with their hit "Matsu wa is the debut single by Aming released on July 21, 1982 in Japan. Track list # "Matsu wa" (待つわ) ..., a Japanese singing duo popular in the early 1980s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond IV, Count Of Toulouse
Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse ( 1041 – 28 February 1105), sometimes called Raymond of Saint-Gilles or Raymond I of Tripoli, was a powerful noble in southern France and one of the leaders of the First Crusade (1096–1099). He was the Count of Toulouse, Duke of Narbonne and Margrave of Provence from 1094, and he spent the last five years of his life establishing the County of Tripoli in the Near East.Bréhier, Louis (1911). " Raymond IV, of Saint-Gilles". In Herbermann, Charles (ed.). ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 12. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Early years Raymond was a son of Pons of Toulouse and Almodis de La Marche. He received Saint-Gilles with the title of "count" from his father and displaced his niece Philippa, Duchess of Aquitaine, his brother William IV's daughter, in 1094 from inheriting Toulouse. In 1094, William Bertrand of Provence died and his margravial title to Provence passed to Raymond. A bull of Urban's dated 22 July 1096 names Raymond ''comes Nimirum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tripoli, Lebanon
Evidence of settlement in Tripoli dates back as early as 1400 BCE. In the 9th century, the Phoenicians established a trading station in Tripoli and later, under Persian rule, the city became the center of a confederation of the Phoenician city-states of Sidon, Tyre, and Arados Island. Under Hellenistic rule, Tripoli was used as a naval shipyard and the city enjoyed a period of autonomy. It came under Roman rule around 64 BCE. The 551 Beirut earthquake and tsunami destroyed the Byzantine city of Tripoli along with other Mediterranean coastal cities. During Umayyad rule, Tripoli became a commercial and shipbuilding center. It achieved semi-independence under Fatimid rule, when it developed into a center of learning. The Crusaders laid siege to the city at the beginning of the 12th century and were able finally to enter it in 1109. This caused extensive destruction, including the burning of Tripoli's famous library, Dar al-'Ilm (House of Knowledge), with its thousands of volumes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims Of The First Crusade
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century Arabs
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongst th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1099 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tripoli
The siege of Tripoli lasted from 1102 until July 12, 1109. It took place on the site of the present day Lebanese city of Tripoli, in the aftermath of the First Crusade. It led to the establishment of the fourth crusader state, the County of Tripoli. Background After the capture of Antioch (June 1098) and the destruction of Ma'arrat al-Numan (January 13, 1099), the Syrian emirs were terrified of the advancing crusaders and quickly handed over their cities to the Franks. On January 14, Sultan ibn Munqidh, emir of Shaizar, dispatched an embassy to Raymond IV of Toulouse, one of the leaders of the crusade, to offer provisions and food for men and horses, as well as guides to Jerusalem. In February, the emir of Homs, Janah ad-Dawla, who had fought bravely at the siege of Antioch, offered horses to Raymond. The ''qadi'' of Tripoli, Jalal al-Mulk, from the Banu Ammar, sent rich gifts and invited the Franks to send an embassy to his city. The ambassadors marvelled at the splendors of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bezants
In the Middle Ages, the term bezant (Old French ''besant'', from Middle Latin, Latin ''bizantius aureus'') was used in Western Europe to describe several gold coins of the east, all derived ultimately from the Solidus (coin), Roman ''solidus''. The word itself comes from the Greek Byzantion, ancient name of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. The original "bezants" were the gold coins produced by the government of the Byzantine Empire, first the ''nomisma'' and from the 11th century the ''hyperpyron''. Later, the term was used to cover the gold dinars produced by Islamic governments. In turn, the gold coins minted in the Kingdom of Jerusalem and County of Tripoli were termed "Saracen bezants", since they were modelled on the gold dinar. A completely different electrum coin based on Byzantine ''Trachy (currency), trachea'' was minted in the Kingdom of Cyprus and called the "white bezant". The term "bezant" in reference to coins is common in sources from the 10th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartus
) , settlement_type = City , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium Citadel of Tartus , image_seal = Emblem of Tartus.svg , seal_size = 60px , mapsize1 = TarusSeadefence.jpg , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Asia , pushpin_label_position = bottom , pushpin_mapsize = 250 , pushpin_map_caption = Location in Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Tartus Governorate , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_name2 = Tartus District , subdivision_type3 = Subdistrict , subdivision_name3 = Tartus Subdistrict , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Abdel Halim Khalil , est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond I Of Turenne
Raymond I of Turenne ( – ) was the 7th Viscount of Turenne. He participated along with his vassals in the First Crusade as part of the Army of Raymond of Saint-Gilles. Family Raymond was born around 1074, in the viscounty of Turenne, in Limousin. He succeeded his father, Boson of Turenne, who died during a pilgrimage to Jerusalem in 1091, and thus he became the 7th viscount of Turenne. His mother Gerberge, daughter of Bernard of Terrasson-Lavilledieu, became a nun at the Abbey of Saint-Martin de Tulle in 1103 and died in the same year. First Crusade In 1095, Raymond joined the crusaders led by Raymond de Saint-Gilles, Count of Toulouse. Before his departure, he entrusted the viscounty of Turenne to his mother. However, he prevailed in arms in many sieges, especially in Antioch and Jerusalem. During the Battle of Antioch that followed the siege, Raymond de Saint-Gilles decided to defend the fort of Mahomerie, the most attacked by Kerbogha's army, to put an end to the accusations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Pilet D'Alès
Raymond Pilet (Raymond de Narbonnne-Pelet) (1075–1120), the only child of Bernard I Pilet of Narbonne and his wife, whose name is unknown. Seigneur of Alès. Bernard was the son of Raymond II, Viscounts of Narbonne, Viscount of Narbone from 1066 to 1067. The name “pilet” refers to a fur that the nobility wore over their cuirass and coats-of-arms. Raymond distinguished himself as a combatant during the First Crusade. Joining the First Crusade Many of the chroniclers of the Crusades, including William of Tyre, have praised the valor and piety of Raymond. Guibert of Nogent, Guibert of Nogent’s ''Dei gesta per Francos, Dei Gesta per Francos'' goes so far as to describe him as a mythological hero. Raymond’s exploits in the crusade are recorded in ''Historia Francorum qui ceperunt Iherusalem,'' the chronicle of Raymond of Aguilers. Raymond was first under the command of Hugh, Count of Vermandois, Hugh the Great, Count of Vermandois, as part of his The Crusader Army of Hug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Arqa
Arqa ( ar, عرقا; akk, 𒅕𒋡𒋫, translit=Irqata) is a Lebanese village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast. The town was a notable city-state during the Iron Age. The city of ''Irqata'' sent 10,000 soldiers to the coalition against the Assyrian king in the Battle of Qarqar. The former bishopric became a double Catholic titular see (Latin and Maronite). The Roman Emperor Alexander Severus was born there. It is significant for the Tell Arqa, an archaeological site that goes back to Neolithic times, and during the Crusades there was a strategically significant castle. Names It is mentioned in Antiquity in the Amarna letters of Egypt-(as ''Irqata''), as well as in Assyrian documents. The Roman town was named Caesarea (of Lebanon/Phoenicia) or Arca Caesarea. History Early Bronze In the Early Bronze IV, the Akkar Plain had three major sites in Tell Arqa, Tell Kazel, and Tell Jamous. The cultural focus had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |