|
Jaccard Distance
The Jaccard index, also known as the Jaccard similarity coefficient, is a statistic used for gauging the Similarity measure, similarity and diversity index, diversity of Sample (statistics), sample sets. It was developed by Grove Karl Gilbert in 1884 as his ratio of verification (v) and now is frequently referred to as the Critical Success Index in meteorology. It was later developed independently by Paul Jaccard, originally giving the French name ''coefficient de communauté'', and independently formulated again by T. Tanimoto. Thus, the Tanimoto index or Tanimoto coefficient are also used in some fields. However, they are identical in generally taking the ratio of Intersection over Union. The Jaccard coefficient measures similarity between finite sample sets, and is defined as the size of the intersection (set theory), intersection divided by the size of the Union (set theory), union of the sample sets: : J(A,B) = = . Note that by design, 0\le J(A,B)\le 1. If ''A'' intersec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Detection
Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos. Well-researched domains of object detection include face detection and pedestrian detection. Object detection has applications in many areas of computer vision, including image retrieval and video surveillance. Uses It is widely used in computer vision tasks such as image annotation, vehicle counting, activity recognition, face detection, face recognition, video object co-segmentation. It is also used in tracking objects, for example tracking a ball during a football match, tracking movement of a cricket bat, or tracking a person in a video. Concept Every object class has its own special features that helps in classifying the class – for example all circles are round. Object class detection uses these special features. For example, when looking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Measure
In mathematics, a probability measure is a real-valued function defined on a set of events in a probability space that satisfies measure properties such as ''countable additivity''. The difference between a probability measure and the more general notion of measure (which includes concepts like area or volume) is that a probability measure must assign value 1 to the entire probability space. Intuitively, the additivity property says that the probability assigned to the union of two disjoint events by the measure should be the sum of the probabilities of the events; for example, the value assigned to "1 or 2" in a throw of a dice should be the sum of the values assigned to "1" and "2". Probability measures have applications in diverse fields, from physics to finance and biology. Definition The requirements for a function \mu to be a probability measure on a probability space are that: * \mu must return results in the unit interval , 1 returning 0 for the empty set and 1 for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sørensen–Dice Coefficient
The Sørensen–Dice coefficient (see below for other names) is a statistic used to gauge the similarity of two samples. It was independently developed by the botanists Thorvald Sørensen and Lee Raymond Dice, who published in 1948 and 1945 respectively. Name The index is known by several other names, especially Sørensen–Dice index, Sørensen index and Dice's coefficient. Other variations include the "similarity coefficient" or "index", such as Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). Common alternate spellings for Sørensen are ''Sorenson'', ''Soerenson'' and ''Sörenson'', and all three can also be seen with the ''–sen'' ending. Other names include: * F1 score * Czekanowski's binary (non-quantitative) index * Measure of genetic similarity * Zijdenbos similarity index, referring to a 1994 paper of Zijdenbos et al. Formula Sørensen's original formula was intended to be applied to discrete data. Given two sets, X and Y, it is defined as : DSC = \frac where , ''X'', and , ''Y' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
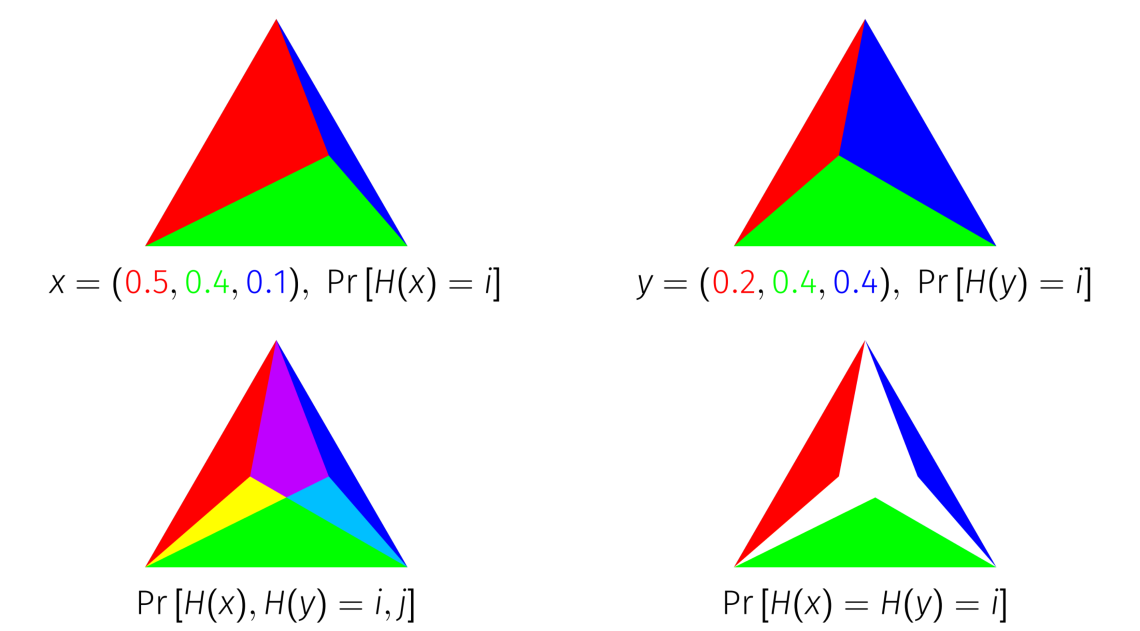
Geometric Interpretation Of The Probability Jaccard Index As Simplices
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a '' geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicator Function
In mathematics, an indicator function or a characteristic function of a subset of a set is a function that maps elements of the subset to one, and all other elements to zero. That is, if is a subset of some set , one has \mathbf_(x)=1 if x\in A, and \mathbf_(x)=0 otherwise, where \mathbf_A is a common notation for the indicator function. Other common notations are I_A, and \chi_A. The indicator function of is the Iverson bracket of the property of belonging to ; that is, :\mathbf_(x)= \in A For example, the Dirichlet function is the indicator function of the rational numbers as a subset of the real numbers. Definition The indicator function of a subset of a set is a function \mathbf_A \colon X \to \ defined as \mathbf_A(x) := \begin 1 ~&\text~ x \in A~, \\ 0 ~&\text~ x \notin A~. \end The Iverson bracket provides the equivalent notation, \in A/math> or to be used instead of \mathbf_(x)\,. The function \mathbf_A is sometimes denoted , , , or even just . Nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dummy Variable (statistics)
In regression analysis, a dummy variable (also known as indicator variable or just dummy) is one that takes the values 0 or 1 to indicate the absence or presence of some categorical effect that may be expected to shift the outcome. For example, if we were studying the relationship between gender and income, we could use a dummy variable to represent the gender of each individual in the study. The variable would take on a value of 1 for males and 0 for females. Dummy variables are commonly used in regression analysis to represent categorical variables that have more than two levels, such as education level or occupation. In this case, multiple dummy variables would be created to represent each level of the variable, and only one dummy variable would take on a value of 1 for each observation. Dummy variables are useful because they allow us to include categorical variables in our analysis, which would otherwise be difficult to include due to their non-numeric nature. They can also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity Analysis
Affinity analysis falls under the umbrella term of data mining which uncovers meaningful correlations between different entities according to their co-occurrence in a data set. In almost all systems and processes, the application of affinity analysis can extract significant knowledge about the unexpected trends. In fact, affinity analysis takes advantages of studying attributes that go together which helps uncover the hidden pattens in a big data through generating association rules. Association rules mining procedure is two-fold: first, it finds all frequent attributes in a data set and, then generates association rules satisfying some predefined criteria, support and confidence, to identify the most important relationships in the frequent itemset. The first step in the process is to count the co-occurrence of attributes in the data set. Next, a subset is created called the frequent itemset. The association rules mining takes the form of ''if'' a condition or feature (A) is presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Matching Coefficient
The simple matching coefficient (SMC) or Rand similarity coefficient is a statistic used for comparing the similarity and diversity of sample sets. Given two objects, A and B, each with ''n'' binary attributes, SMC is defined as: : \begin \text & = \frac \\ pt& = \frac \end where: :M_ is the total number of attributes where ''A'' and ''B'' both have a value of 0. :M_ is the total number of attributes where ''A'' and ''B'' both have a value of 1. :M_ is the total number of attributes where the attribute of ''A'' is 0 and the attribute of ''B'' is 1. :M_ is the total number of attributes where the attribute of ''A'' is 1 and the attribute of ''B'' is 0. The simple matching distance (SMD), which measures dissimilarity between sample sets, is given by 1 - \text. SMC is linearly related to Hamann similarity: SMC = (Hamann+1)/2. Also, SMC = 1-D^2/n, where D^2 is the squared Euclidean distance between the two objects (binary vectors) and n is the number of attributes. The SMC i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinomial Distribution
In probability theory, the multinomial distribution is a generalization of the binomial distribution. For example, it models the probability of counts for each side of a ''k''-sided dice rolled ''n'' times. For ''n'' independent trials each of which leads to a success for exactly one of ''k'' categories, with each category having a given fixed success probability, the multinomial distribution gives the probability of any particular combination of numbers of successes for the various categories. When ''k'' is 2 and ''n'' is 1, the multinomial distribution is the Bernoulli distribution. When ''k'' is 2 and ''n'' is bigger than 1, it is the binomial distribution. When ''k'' is bigger than 2 and ''n'' is 1, it is the categorical distribution. The term "multinoulli" is sometimes used for the categorical distribution to emphasize this four-way relationship (so ''n'' determines the prefix, and ''k'' the suffix). The Bernoulli distribution models the outcome of a single Bernoulli trial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
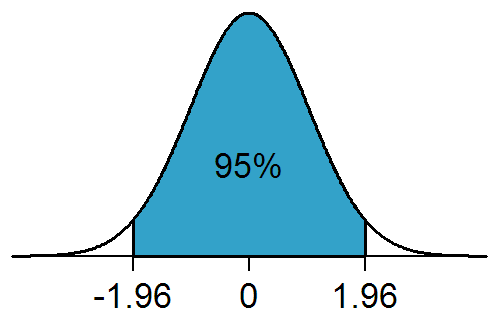
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ''p''-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Numeral System
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" ( one). The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language and the noise immunity in physical implementation. History The modern binary number system was studied in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries by Thomas Harriot, Juan Caramuel y Lobkowitz, and Gottfried Leibniz. However, systems related to binary numbers have appeared earlier in multiple cultures including ancient Egypt, China, and India. Leibniz was specifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hash Function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values. The values returned by a hash function are called ''hash values'', ''hash codes'', ''digests'', or simply ''hashes''. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a ''hash table''. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called ''hashing'' or ''scatter storage addressing''. Hash functions and their associated hash tables are used in data storage and retrieval applications to access data in a small and nearly constant time per retrieval. They require an amount of storage space only fractionally greater than the total space required for the data or records themselves. Hashing is a computationally and storage space-efficient form of data access that avoids the non-constant access time of ordered and unordered lists and structured trees, and the often exponential storage requirements of direct access of state spaces of large or variable-length keys. Use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |