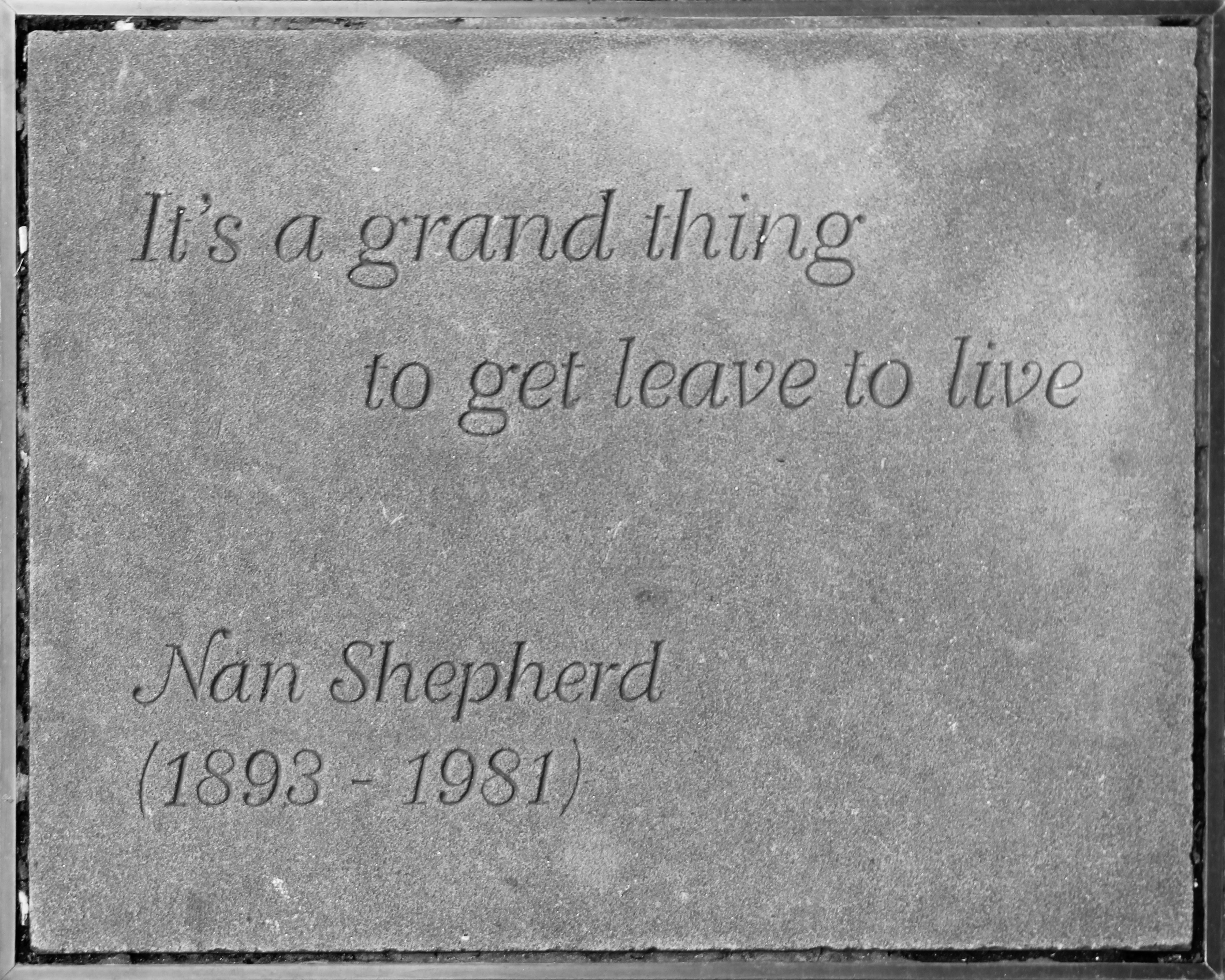|
J. C. Milne
John Clark Milne (1897–1962) was a Scottish poet who wrote in the Doric dialect of the Scots language. He was also a teacher and educationalist. Some of his poetry was written for children. Life John Milne was born at Memsie, near Fraserburgh in Aberdeenshire in 1897 to a farming family. He attended the University of Aberdeen where he excelled academically, then became a teacher. In later years he was Master of Method at Aberdeen College of Education. His collection of verses, ''The Orra Loon'' was published in 1946 and his collected ''Poems'' in 1963. The northeastern poet and novelist Nan Shepherd helped prepare the latter edition of Milne's poetry, published after his death. In 2009 the Buchan Heritage Society launched a CD on which well-known local performers and artists had collaborated in recording samples of his work. The society hoped that through hearing Milne's unique poetry children would help preserve the Doric tongue, which many in the area have forgotten. Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memsie
Memsie, Aberdeenshire, is a small community near Fraserburgh, Scotland. On Memsie Moor there is a very large stone cairn, Memsie Cairn, which has been opened, but nothing found inside. - There were two other cairns, but they have been removed.''Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland A Graphic and Accurate Description of Every Place in Scotland'' (1901) - p. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish People
The Scots ( sco, Scots Fowk; gd, Albannaich) are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic-speaking peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who founded the Kingdom of Scotland (or ''Alba'') in the 9th century. In the following two centuries, the Celtic-speaking Cumbrians of Strathclyde and the Germanic-speaking Angles of north Northumbria became part of Scotland. In the High Middle Ages, during the 12th-century Davidian Revolution, small numbers of Norman nobles migrated to the Lowlands. In the 13th century, the Norse-Gaels of the Western Isles became part of Scotland, followed by the Norse of the Northern Isles in the 15th century. In modern usage, "Scottish people" or "Scots" refers to anyone whose linguistic, cultural, family ancestral or genetic origins are from Scotland. The Latin word ''Scoti'' originally referred to the Gaels, but came to describe all inhabitants of Scotland. Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Dialect (Scotland)
Doric, the popular name for Mid Northern Scots or Northeast Scots, refers to the Scots language as spoken in the northeast of Scotland. There is an extensive body of literature, mostly poetry, ballads, and songs, written in Doric. In some literary works, Doric is used as the language of conversation while the rest of the work is in Lallans Scots or British English. A number of 20th and 21st century poets have written poetry in the Doric dialect. Nomenclature The term "Doric" was formerly used to refer to all dialects of Lowland Scots, but during the twentieth century it became increasingly associated with Mid Northern Scots. The name possibly originated as a jocular reference to the Doric dialect of the Ancient Greek language. Greek Dorians lived in Laconia, including Sparta, and other more rural areas, and were alleged by the ancient Greeks to have spoken laconically and in a language thought harsher in tone and more phonetically conservative than the Attic spoken in Athens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Language
Scots ( endonym: ''Scots''; gd, Albais, ) is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland (where the local dialect is known as Ulster Scots). Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300). Scots is recognised as an indigenous language of Scotland, a regional or minority language of Europe, as well as a vulnerable language by UNESCO. In the 2011 United Kingdom census, 2011 Scottish Census, over 1.5 million people in Scotland reported being able to speak Scots. As there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraserburgh
Fraserburgh (; sco, The Broch or ; gd, A' Bhruaich) is a town in Aberdeenshire (unitary), Aberdeenshire, Scotland with a population recorded in the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census at 13,100. It lies at the far northeast corner of Aberdeenshire, about north of Aberdeen, and north of Peterhead. It is the biggest shellfish port in Scotland and one of the largest in Europe, landing over in 2016. Fraserburgh is also a major port for whitefish (fisheries term), white and pelagic fish. History 16th and 17th century: Origins The name of the town means, literally, 'burgh of Fraser', after the Frasers of Philorth, Fraser family that bought the lands of Philorth in 1504 and thereafter brought about major improvement due to investment over the next century. By 1570, the Fraser family had built Fraserburgh Castle at Kinnaird Head and within a year a church was built for the area. Alexander Fraser (died 1623), Sir Alexander Fraser built a port in the town in 1579, obtained a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Aberdeen
The University of Aberdeen ( sco, University o' 'Aiberdeen; abbreviated as ''Aberd.'' in List of post-nominal letters (United Kingdom), post-nominals; gd, Oilthigh Obar Dheathain) is a public university, public research university in Aberdeen, Scotland. It is an Ancient universities of Scotland, ancient university founded in 1495 when William Elphinstone, Bishop of Aberdeen and Lord Chancellor of Scotland, Chancellor of Scotland, petitioned Pope Alexander VI on behalf of James IV of Scotland, James IV, King of Scots to establish King's College, Aberdeen, King's College, making it Scotland's 3rd oldest university and the 5th oldest in the English-speaking world and the United Kingdom. Aberdeen is consistently ranked among the top 160 universities in the world and is ranked within the top 20 universities in the United Kingdom according to ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', and 13th in the UK according to ''The Guardian''. The university comprises three colleges—King's College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nan Shepherd
Anna "Nan" Shepherd (11 February 1893 – 27 February 1981) was a Scottish Modernist writer and poet, best known for her seminal mountain memoir, ''The Living Mountain'', based on experiences of hill walking in the Cairngorms. This is noted as an influence by nature writers who include Robert Macfarlane and Richard Mabey. She also wrote poetry and three novels set in small fictional communities in Northern Scotland. The landscape and weather of this area played a major role in her novels and provided a focus for her poetry. Shepherd served as a lecturer in English at the Aberdeen College of Education for most of her working life. Life Nan Shepherd was born on 11 February 1893 at Westerton Cottage, Cults, now a suburb of Aberdeen, to John and Jane Shepherd. Shortly after her birth, the family moved to Dunvegan, Cults, the house she then lived in for most of her life. She attended Aberdeen High School for Girls and graduated from the University of Aberdeen in 1915. Shepherd subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Murray (poet)
Charles Murray (27 September 1864 – 12 April 1941) was a poet who wrote in the Doric dialect of Scots. He was one of three rural poets from the north-east of Scotland, the others being Flora Garry and John C. Milne, who did much to validate the literary use of Scots. Biography Charles Murray was born and raised in Alford in north-east Scotland. However he wrote much of his poetry while living in South Africa where he spent most of his working life as a successful civil engineer. His first volume, ''A Handful of Heather'' (1893), was privately printed and he withdrew it shortly after publication to rework many of the poems within it. His second volume, ''Hamewith'' (1900), was much more successful. It was republished five times before he died and it is this volume for which he is best known. The title of the volume, which means ''Homewards'' in English, reflects his expatriate situation. He served in the Armed Forces during the Second Boer War and the First World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Garry
Flora Garry (30 September 1900 – 16 June 2000) was a Scottish poet who mostly wrote in the Scots dialect of Aberdeenshire. Well known for her poetry, she played an important role along with Charles Murray and John C. Milne in validating the literary use of Scots. Biography Flora Garry was the daughter of Archie Campbell, a freelance writer who used the ''nom de plume'' of "The Buchan Farmer", and Helen Campbell, who wrote plays for radio. She was brought up at Mains of Auchmunziel, near to New Deer, Buchan in Abderdeenshire. She went to school in New Deer, then went on to the Peterhead Academy and the University of Aberdeen. She became a school teacher, and taught at Dumfries and Strichen. She married Robert Campbell Garry, who was the first to use insulin in Scotland while a house doctor at Western Infirmary, Glasgow and who became Regius Professor of Physiology at the University of Glasgow. They had one son, Frank. Flora Garry did not start to write poetry until World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1897 Births
Events January–March * January 2 – The International Alpha Omicron Pi sorority is founded, in New York City. * January 4 – A British force is ambushed by Chief Ologbosere, son-in-law of the ruler. This leads to a punitive expedition against Benin. * January 7 – A cyclone destroys Darwin, Australia. * January 8 – Lady Flora Shaw, future wife of Governor General Lord Lugard, officially proposes the name "Nigeria" in a newspaper contest, to be given to the British Niger Coast Protectorate. * January 22 – In this date's issue of the journal ''Engineering'', the word ''computer'' is first used to refer to a mechanical calculation device. * January 23 – Elva Zona Heaster is found dead in Greenbrier County, West Virginia. The resulting murder trial of her husband is perhaps the only capital case in United States history, where spectral evidence helps secure a conviction. * January 31 – The Czechoslovak Trade Union Association is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1962 Deaths
Year 196 ( CXCVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Dexter and Messalla (or, less frequently, year 949 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 196 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus attempts to assassinate Clodius Albinus but fails, causing Albinus to retaliate militarily. * Emperor Septimius Severus captures and sacks Byzantium; the city is rebuilt and regains its previous prosperity. * In order to assure the support of the Roman legion in Germany on his march to Rome, Clodius Albinus is declared Augustus by his army while crossing Gaul. * Hadrian's wall in Britain is partially destroyed. China * First year of the '' Jian'an era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * Emperor Xian of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Poets
Doric may refer to: * Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece ** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians * Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture * Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode * Doric dialect (Scotland) * Doric Club, a paramilitary organization which fought against the Lower Canada Rebellion * Doric Park, a park in Liverpool, England * Doric Organ, a 1960s Combo organ produced in Italy * Doric String Quartet, a string quartet based in the UK * SS ''Doric'' (1883), a British ocean liner operated by White Star Line * SS ''Doric'' (1923), another ship operated by White Star Line See also * Dorian (other), a synonym {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)