|
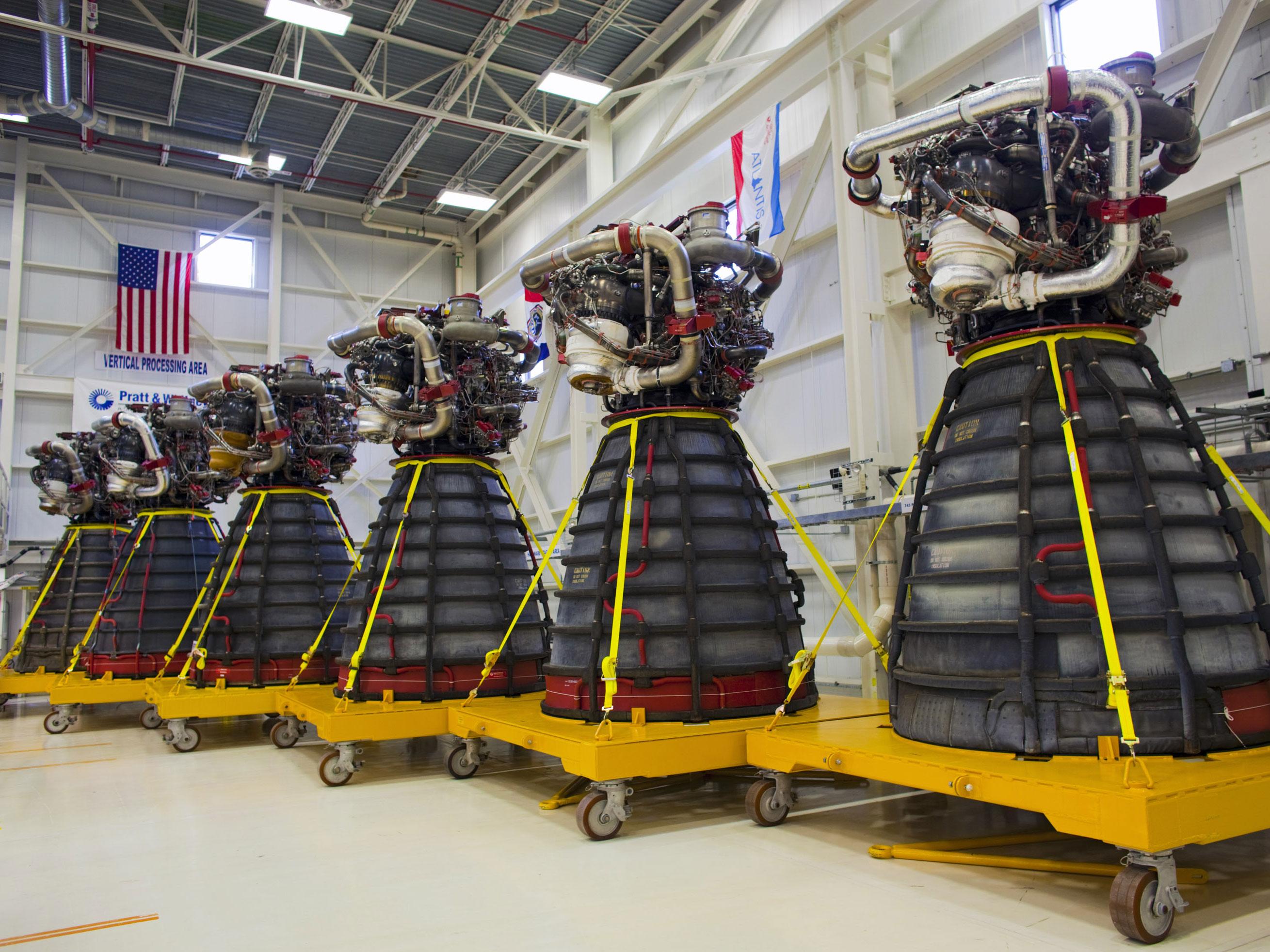
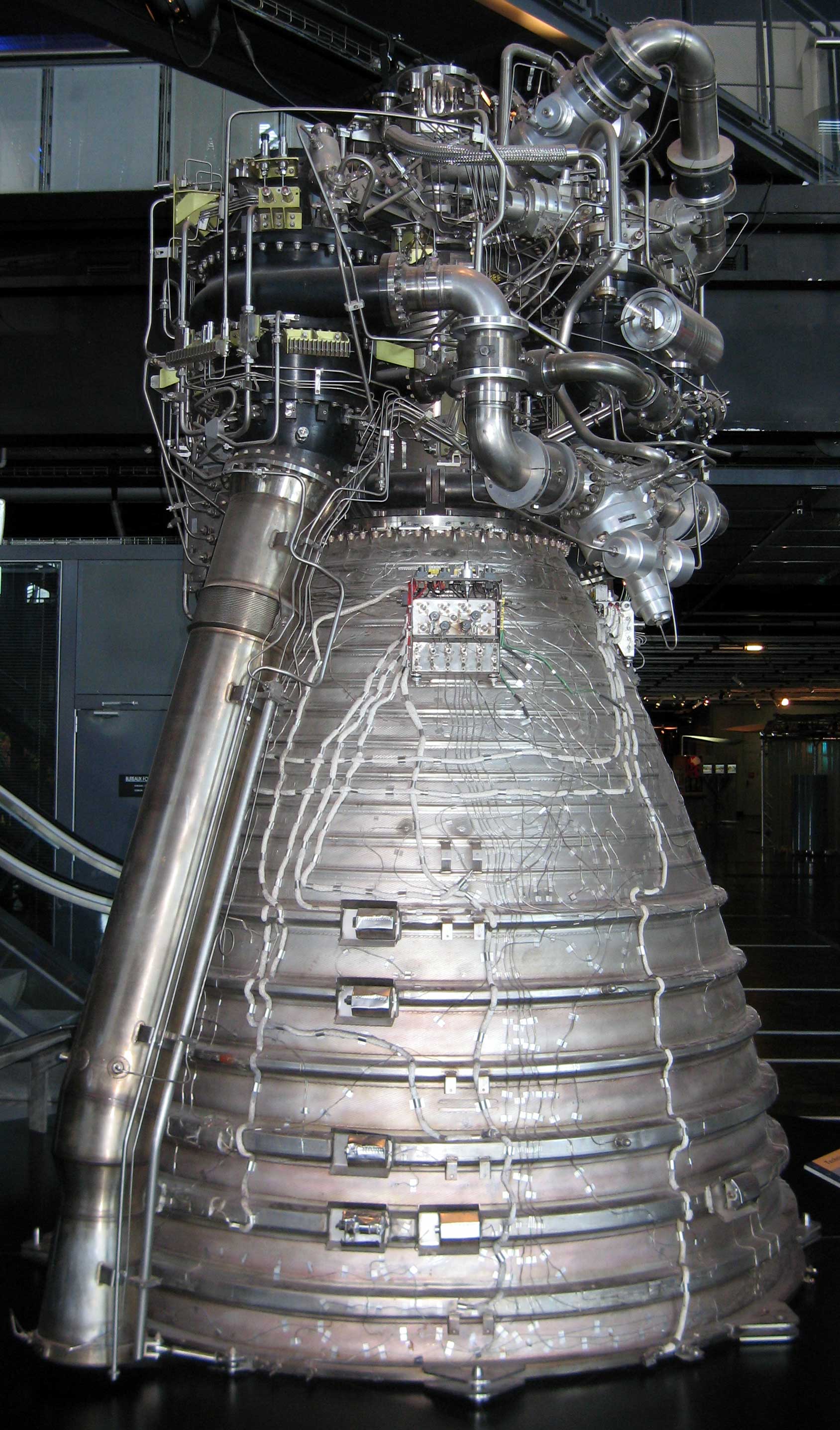
J-2X
The J-2X is a liquid-fueled cryogenic rocket engine that was planned for use on the Ares rockets of NASA's Constellation program, and later the Space Launch System. Built in the United States by Aerojet Rocketdyne (formerly, Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne), the J-2X burns cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants, with each engine producing of thrust in vacuum at a specific impulse (''I''sp) of . The engine's mass is approximately 2,470 kg (5,450 Lb), significantly heavier than its predecessors. The J-2X was intended to be based on the J-2 used on the S-II and S-IVB stages of the Saturn rockets used during the Apollo program, but as required thrust for the Ares I increased due to weight problems it became a clean-sheet design. It entered development in 2007 as part of the now-cancelled Constellation program. Originally planned for use on the upper stages of the Ares I and Ares V rockets, the J-2X was later intended for use in the Earth Departure Stage of the Blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-2 (rocket Engine)
The J-2 is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine used on NASA's Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles. Built in the U.S. by Rocketdyne, the J-2 burned cryogenic liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, with each engine producing of thrust in vacuum. The engine's preliminary design dates back to recommendations of the 1959 Silverstein Committee. Rocketdyne won approval to develop the J-2 in June 1960 and the first flight, AS-201, occurred on 26 February 1966. The J-2 underwent several minor upgrades over its operational history to improve the engine's performance, with two major upgrade programs, the de Laval nozzle-type J-2S and aerospike-type J-2T, which were cancelled after the conclusion of the Apollo program. The engine produced a specific impulse (''I''sp) of in a vacuum (or at sea level) and had a mass of approximately . Five J-2 engines were used on the Saturn V's S-II second stage, and one J-2 was used on the S-IVB upper stage used on both the Satu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
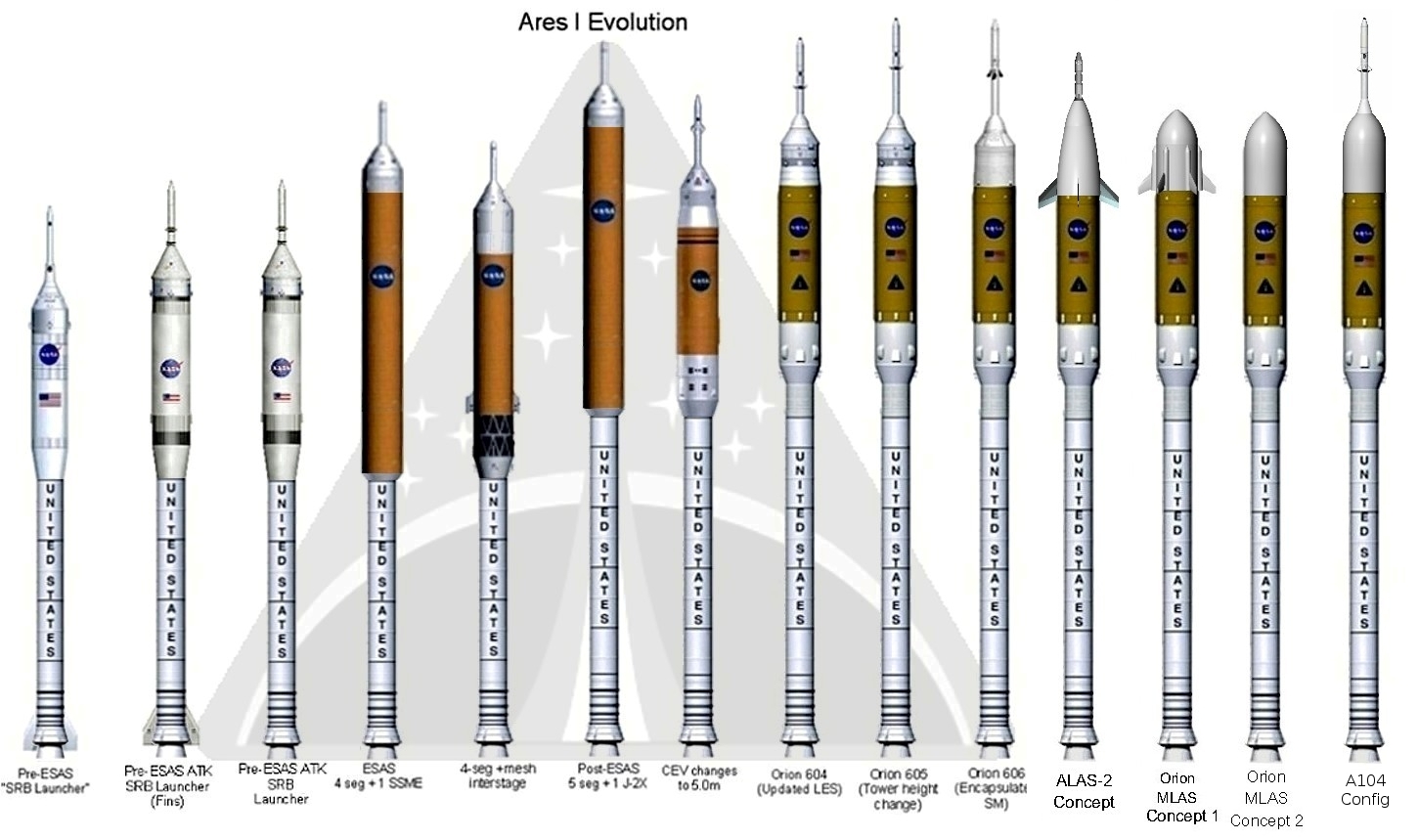
Ares I
Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars. Ares I was originally known as the "Crew Launch Vehicle" (CLV). NASA planned to use Ares I to launch Orion, the spacecraft intended for NASA human spaceflight missions after the Space Shuttle was retired in 2011. Ares I was to complement the larger, uncrewed Ares V, which was the cargo launch vehicle for Constellation. NASA selected the Ares designs for their anticipated overall safety, reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, the Constellation program, including Ares I, was cancelled by U.S. president Barack Obama in October 2010 with the passage of his 2010 NASA authorization bill. In September 2011, NASA detailed the Space Launch System as its new vehicle for human exploration beyond Earth's orbit. Development Advanced Transportation System Studies In 1995 Lockheed Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Departure Stage
The Earth Departure Stage (EDS) is the name given to the proposed second stage of the Block 2 Space Launch System. The EDS is intended to boost the rocket's payload into a parking orbit around the Earth and from there send the payload out of low Earth orbit to its destination in a manner similar to that of the S-IVB rocket stage used on the Saturn V rockets that propelled the Apollo spacecraft to the Moon. Its development has been put on hold (though not abandoned) until stages capable of transferring heavy payloads to Mars are required (currently expected in the 2030s). Ares V Design The EDS used on the cancelled Ares V would have been propelled by a single J-2X main engine fuelled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2), and was to have been designed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama as part of Project Constellation. Originally, the stage would have been based on the Space Shuttle's external tank, and would have used ''two'' J-2X engines, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a "return to the Moon no later than 2020" with a crewed flight to the planet Mars as the ultimate goal. The program's logo reflected the three stages of the program: the Earth (ISS), the Moon, and finally Mars—while the Mars goal also found expression in the name given to the program's booster rockets: Ares (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Mars). The technological aims of the program included the regaining of significant astronaut experience beyond low Earth orbit and the development of technologies necessary to enable sustained human presence on other planetary bodies. Constellation began in response to the goals laid out in the Vision for Space Exploration under NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and President George W. Bush. O'Keef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle developed by NASA. As of 2022, SLS has the highest payload capacity of any rocket in operational service, as well as the greatest liftoff thrust of any rocket in operation. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis moon landing program, SLS is designed to launch the crewed Orion spacecraft on a trans-lunar trajectory. The first uncrewed launch, Artemis 1, took place on 16 November 2022. Development of SLS began in 2011, as a replacement for the retired Space Shuttle as well as the cancelled Ares I and Ares V launch vehicles. As a Shuttle-derived vehicle, the Space Launch System reuses hardware from the Space Shuttle program, including the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters and RS-25, RS-25 first stage engines. An original flight date of late 2016 was delayed by nearly 6 years. The SLS program has Space Launch System#Criticism, attracted criticism for such de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ares V
The Ares V (formerly known as the Cargo Launch Vehicle or CaLV) was the planned cargo launch component of the cancelled NASA Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars. Ares V and the smaller Ares I were named after Ares, the Greek god of war. The Ares V was to launch the Earth Departure Stage and Altair lunar lander for NASA's return to the Moon, which was planned for 2019. It would also have served as the principal launcher for missions beyond the Earth-Moon system, including the program's ultimate goal, a crewed mission to Mars. The uncrewed Ares V would complement the smaller, and human-rated Ares I rocket for the launching of the 4–6 person Orion spacecraft. Both rockets, deemed safer than the then-current Space Shuttle, would have employed technologies developed for the Apollo program, the Shuttle program, and the Delta IV EELV program. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas-generator Cycle (rocket)
The gas-generator cycle is a power cycle of a pumped liquid bipropellant rocket engine. Part of the unburned propellant is burned in a gas generator (or preburner) and the resulting hot gas is used to power the propellant pumps before being exhausted overboard, and lost. Because of this loss, this type of engine is termed open cycle. Usage Gas-generator combustion engines include the following: * Vulcain, HM7B * Merlin *RS-68 *RS-27A *J-2X * F-1 *RD-107 * CE-20 * Rocket launch systems that use gas-generator combustion engines: * Ariane 5 *Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy *Delta IV *Saturn V *Soyuz * Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle III *Long March 3B, Long March 2F *Rocket Lab Neutron *Miura 5 See also * Combustion tap-off cycle * Expander cycle * Pressure-fed engine * Rocket engine A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-25
The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-25, also known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME), is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine that was used on NASA's Space Shuttle and is currently used on the Space Launch System (SLS). Designed and manufactured in the United States by Rocketdyne (later Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne and Aerojet Rocketdyne), the RS-25 burns Cryogenic fuel, cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants, with each engine producing thrust at liftoff. Although RS-25 heritage traces back to the 1960s, its concerted development began in the 1970s with the first flight, STS-1, on April 12, 1981. The RS-25 has undergone upgrades over its operational history to improve the engine's reliability, safety, and maintenance load. The engine produces a specific impulse (''I''sp) of in a vacuum, or at sea level, has a mass of approximately , and is capable of throttling between 67% and 109% of its #Engine throttle/output, rated power level in one-percent increments. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerojet Rocketdyne
Aerojet Rocketdyne is an American manufacturer of rocket, Hypersonic flight, hypersonic, and electric propulsive systems for space, defense, civil and commercial applications. Headquartered in Sacramento, California, the company is owned by Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings. Aerojet Rocketdyne was formed in 2013 when Aerojet (then owned by GenCorp) and Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne were merged, following the latter's acquisition by GenCorp from Pratt & Whitney. On April 27, 2015, the name of the holding company, GenCorp, was changed from ''GenCorp, Inc.'' to ''Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc''. Lockheed Martin announced plans to take over Aerojet Rocketdyne on December 20, 2020 as part of a $4.4 billion acquisition; however this was abandoned by Lockheed on February 13, 2022 after opposition from Raytheon Technologies, Raytheon led the Federal Trade Commission, FTC to move to block the acquisition. Products Current engines * RS-25 (LH2/LOX) – Previously known as the Space Shuttle ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne
Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne (PWR) was an American company that designed and produced rocket engines that use liquid rocket propellants, liquid propellants. It was a division of Pratt & Whitney, a fully owned subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation. It was headquartered in Canoga Park, California, Canoga Park, Los Angeles, California. In 2013, the company was sold to GenCorp, becoming part of Aerojet Rocketdyne. History Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne was formed in 2005 when Pratt & Whitney Space Propulsion and Boeing Rocketdyne, Rocketdyne Propulsion & Power were merged, following the latter's acquisition from Boeing by United Technologies Corporation. Boeing retained the 2,800 acre Rocketdyne Santa Susana Field Laboratory property above Canoga Park while a majority of the engineering and design continued to be carried out at the Pratt & Whitney Space Propulsion facility located on Beeline Highway outside West Palm Beach, Florida. In July 2012, United Technologies Corporation ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Rocket Engine
A cryogenic rocket engine is a rocket engine that uses a cryogenic fuel and oxidizer; that is, both its fuel and oxidizer are gases which have been liquefied and are stored at very low temperatures. These highly efficient engines were first flown on the US Atlas-Centaur and were one of the main factors of NASA's success in reaching the Moon by the Saturn V rocket. Rocket engines burning cryogenic propellants remain in use today on high performance upper stages and boosters. Upper stages are numerous. Boosters include ESA's Ariane 5, JAXA's H-II, and the United States Delta IV and Space Launch System. The United States, Russia, Japan, India, France and China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ... are the only countries that have operational cryogenic rocket engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-IVB
The S-IVB (pronounced "S-four-B") was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 (rocket engine), J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twice: first for Earth orbit insertion after second stage cutoff, and then for translunar injection (TLI). History The S-IVB evolved from the upper stage of the Saturn I rocket, the S-IV, and was the first stage of the Saturn V to be designed. The S-IV used a cluster of six engines but used the same fuels as the S-IVB – liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. It was also originally meant to be the fourth stage of a planned rocket called the Saturn C-4, C-4, hence the name S-IV. Eleven companies submitted proposals for being the lead contractor on the stage by the deadline of 29 February 1960. NASA administrator T. Keith Glennan decided on 19 April that Douglas Aircraft Company would be awarded the contract. Convair had come a close second but G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |