|
Ivy Hooks
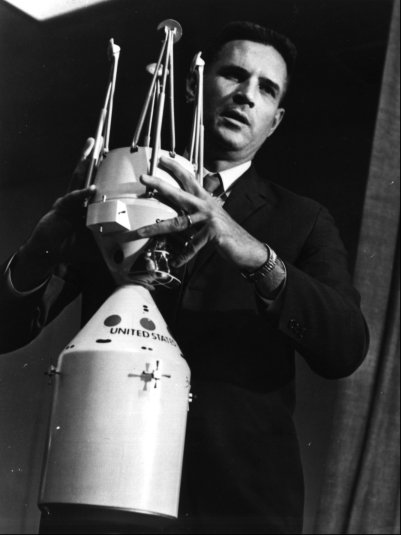
Ivy Fay Hooks (born November 17, 1941) is an American mathematician and engineer who worked for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). She joined NASA after graduating from the University of Houston with a master's degree in mathematics and physics in 1965. Her first assignment was with the Apollo program, where she worked on the modeling of lighting on the Moon and the dynamics of the launch escape system, among other projects. She then went on to play an important role in the design and development of the Space Shuttle, being one of only two women engineers assigned to the original design team for the orbiter. Early life Ivy Fay Hooks was born in Houston, Texas, on November 17, 1941, and grew up in Livingston, Texas. She was named after Ivy Parker, one of the founding members of the Society of Women Engineers, and a close friend of her parents. She graduated from Livingston High School and entered Southwestern University in Georgetown, Texas, where she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in 2020. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the seat and largest city of Harris County and the principal city of the Greater Houston metropolitan area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States and the second-most populous in Texas after Dallas–Fort Worth. Houston is the southeast anchor of the greater megaregion known as the Texas Triangle. Comprising a land area of , Houston is the ninth-most expansive city in the United States (including consolidated city-counties). It is the largest city in the United States by total area whose government is not consolidated with a county, parish, or borough. Though primarily in Harris County, small portions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin College
Austin College is a private liberal arts college affiliated with the Presbyterian Church (USA) and located in Sherman, Texas.Austin College , Austin College History. About 1,300 students are enrolled at the college.Austin College , Austin College Life. Students are required to live on campus for the first three years of their education in order to foster a close-knit and community oriented campus lifestyle. Austin College actively promotes study abroad programs; 70% of graduates have at least one international study experience during college, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balsa Wood
''Ochroma pyramidale'', commonly known as the balsa tree, is a large, fast-growing tree native to the Americas. It is the sole member of the genus ''Ochroma''. The tree is famous for its wide usage in woodworking, with the name ''balsa'' being the Spanish word for "raft." A deciduous angiosperm, ''Ochroma pyramidale'' can grow up to 30 m tall, and is classified as a hardwood despite the wood itself being very soft; it is the softest commercial hardwood and is widely used because of its light weight. Biology Balsa on Bota Hill, Limbe Botanical Garden, Cameroon">Limbe_Botanical_Garden.html" ;"title="Bota Hill, Limbe Botanical Garden">Bota Hill, Limbe Botanical Garden, Cameroon A member of the mallow family, ''Ochroma pyramidale'' is native from southern Mexico to southern Brazil, but can now be found in many other countries (Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, Thailand, Solomon Islands). It is a pioneer plant, which establishes itself in clearings in forests, either man-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Faget
Maxime Allen "Max" Faget (pronounced ''fah-ZHAY''; August 26, 1921 – October 9, 2004) was a Belizean-born American mechanical engineer. Faget was the designer of the Mercury spacecraft, and contributed to the later Gemini and Apollo spacecraft as well as the Space Shuttle. Life Faget was the son of American doctor Guy Henry Faget, and great-grandson of another prominent physician, Jean Charles Faget. Born in Dangriga, Belize (then known as British Honduras), he attended City College of San Francisco in San Francisco, California, and he received a Bachelor of Science degree in mechanical engineering from Louisiana State University in 1943. After three years as a submariner aboard in the U.S. Navy, Faget joined the Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia as a research scientist. While working for NACA at Langley, he worked on the design of the X-15 hypersonic spacecraft. In 1958, Faget became one of the 35 engineers who formed the Space Task Group, creating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Orbiter
The Space Shuttle orbiter is the spaceplane component of the Space Shuttle, a partially reusable orbital spacecraft system that was part of the discontinued Space Shuttle program. Operated from 1977 to 2011 by NASA, the U.S. space agency, this vehicle could carry astronauts and payloads into low Earth orbit, perform in-space operations, then re-enter the atmosphere and land as a glider, returning its crew and any on-board payload to the Earth. Six orbiters were built for flight: ''Enterprise'', ''Columbia'', ''Challenger'', ''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'', and '' Endeavour''. All were built in Palmdale, California, by the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania-based Rockwell International company. The first orbiter, ''Enterprise'', made its maiden flight in 1977. An unpowered glider, it was carried by a modified Boeing 747 airliner called the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft and released for a series of atmospheric test flights and landings. ''Enterprise'' was partially disassembled and retired after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descent Propulsion System
The descent propulsion system (DPS - pronounced 'dips') or lunar module descent engine (LMDE), internal designation VTR-10, is a variable- throttle hypergolic rocket engine invented by Gerard W. Elverum Jr. and developed by Space Technology Laboratories (TRW) for use in the Apollo Lunar Module descent stage. It used Aerozine 50 fuel and dinitrogen tetroxide () oxidizer. This engine used a pintle injector, which paved the way for other engines to use similar designs. Requirements The propulsion system for the descent stage of the lunar module was designed to transfer the vehicle, containing two crewmen, from a circular lunar parking orbit to an elliptical descent orbit with a pericynthion of , then provide a powered descent to the lunar surface, with hover time above the lunar surface to select the exact landing site. To accomplish these maneuvers, a propulsion system was developed that used hypergolic propellants and a gimballed pressure-fed ablative cooled engine that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascent Propulsion System
The ascent propulsion system (APS) or lunar module ascent engine (LMAE) is a fixed-thrust hypergolic rocket engine developed by Bell Aerosystems for use in the Apollo Lunar Module ascent stage. It used Aerozine 50 fuel, and oxidizer. Rocketdyne provided the injector system, at the request of NASA, when Bell could not solve combustion instability problems. Origins The LMAE traces its origin to the earlier Bell Aerosystems engines (8096, 8247) used in the RM-81 Agena, the rocket upper stage and satellite support bus developed by Lockheed initially for the canceled WS-117L reconnaissance satellite program. The Agena served as an upper stage for several defense, intelligence, and exploration programs: SAMOS-E, SAMOS-F (ELINT Ferret) and MIDAS (Missile Defense Alarm System) military early-warning satellites, Corona photo intelligence program, and the Ranger and Lunar Orbiter lunar probes. The Lockheed Agena target vehicle using the Bell 8247 engine was qualified for 15 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed spacecraft to operate exclusively in the airless vacuum of space, and remains the only crewed vehicle to land anywhere beyond Earth. Structurally and aerodynamically incapable of flight through Earth's atmosphere, the two-stage lunar module was ferried to lunar orbit attached to the Apollo command and service module (CSM), about twice its mass. Its crew of two flew the complete lunar module from lunar orbit to the Moon's surface. During takeoff, the spent descent stage was used as a launch pad for the ascent stage which then flew back to the command module, after which it was also discarded. Overseen by Grumman, the LM's development was plagued with problems that delayed its first uncrewed flight by about ten months and its first cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to the Master of Arts degree, the Master of Science degree is typically granted for studies in sciences, engineering and medicine and is usually for programs that are more focused on scientific and mathematical subjects; however, different universities have different conventions and may also offer the degree for fields typically considered within the humanities and social sciences. While it ultimately depends upon the specific program, earning a Master of Science degree typically includes writing a thesis. The Master of Science degree was first introduced at the University of Michigan in 1858. One of the first recipients of the degree was De Volson Wood, who was conferred a Master of Science degree at the University of Michigan in 1859. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation. Surface albedo is defined as the ratio of radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While bi-hemispherical reflectance is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as obtained from flux measurements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed spacecraft to operate exclusively in the airless vacuum of space, and remains the only crewed vehicle to land anywhere beyond Earth. Structurally and aerodynamically incapable of flight through Earth's atmosphere, the two-stage lunar module was ferried to lunar orbit attached to the Apollo command and service module (CSM), about twice its mass. Its crew of two flew the complete lunar module from lunar orbit to the Moon's surface. During takeoff, the spent descent stage was used as a launch pad for the ascent stage which then flew back to the command module, after which it was also discarded. Overseen by Grumman, the LM's development was plagued with problems that delayed its first uncrewed flight by about ten months and its first cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manned Spaceflight Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late US president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973. It consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on in the Clear Lake Area of Houston, which acquired the official nickname "Space City" in 1967. The center is home to NASA's astronaut corps, and is responsible for training astronauts from both the US and its international partners. It houses the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, which has provided the flight control function for every NASA human spaceflight since Gemini 4 (including Apollo, Skylab, Apollo–Soyuz, and Space Shuttle). It is popularly known by its radio call signs "Mission Control" and "Houston". The original Manned Spacecraft Center grew out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |