|
Ivan Skoropadskyi
Ivan Skoropadsky ( uk, Іван Скоропадський) (1646 – 3 July 1722) was a Cossack Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host (in office: 1708–1722), and the successor to the famous Hetman Ivan Mazepa. Biography Born into a noble Cossack family in Uman, Ukraine in 1646, Skoropadsky was educated in Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. In 1675 he joined Cossack military service under Hetman Ivan Samoylovych and distinguished himself in Russo-Turkish War of 1676–1681 and once again in the Crimean expedition against the Ottoman Empire and Crimean Khanate in 1688. Ivan Skoropadsky was briefly an ambassador representing Cossack Hetmanate in negotiations with the Russian Tsar Peter the Great. During the Great Northern War Skoropadsky was a Cossack colonel of the Ukrainian Starodub regiment and after Swedish army crossed into Ukraine in 1708, refused to join Ivan Mazepa who decided to switch sides and fight against Russia. Only about 3,000 Cossacks, mostly Zaporozhians, followed Mazepa, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenians
Ruthenian and Ruthene are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term Rutheni was used in medieval sources to describe all Eastern Slavs of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, as an exonym for people of the former Kievan Rus', thus including ancestors of the modern Belarusians, Rusyns and Ukrainians. The use of ''Ruthenian'' and related exonyms continued through the early modern period, developing several distinctive meanings, both in terms of their regional scopes and additional religious connotations (such as affiliation with the Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church). In medieval sources, the Latin term ''Rutheni'' was commonly applied to East Slavs in general, thus encompassing all endonyms and their various forms (Ukrainian: ''—Ä—É—Å–∏–Ω–∏'', Belarusian: ''—Ä—É—Å—ñ–Ω—ã''). By opting for the use of exonymic terms, authors who wrote in Latin were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlo Skoropadsky
Pavlo Petrovych Skoropadskyi ( uk, Павло Петрович Скоропадський, Pavlo Petrovych Skoropadskyi; – 26 April 1945) was a Ukrainian aristocrat, military and state leader, decorated Imperial Russian Army and Ukrainian Army general of Cossack heritage. Skoropadskyi became Hetman of Ukraine following a coup on 29 April 1918. Origin Pavlo Skoropadskyi was born into the Skoropadsky family of Ukrainian military leaders and statesmen, that distinguished themselves since the 17th century when Fedir Skoropadsky participated in the Battle of Zhovti Vody. His grandson Ivan Skoropadsky (1646-1722) was Hetman of the Ukrainian Cossacks from 1708. The present Skoropadskys descend from his brother. His patrilineal great-grandfather was Mikhail Yakivich Skoropadskyi, son of Yakiv Mikhailovich Skoropadskyi and wife, and his patrilineal great-grandmother was Pulcheria ...vna Markevicha. Skoropadskyi's father Petro Skoropadsky (1834–1885) was a Cavalry Guard Colonel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Andreyevich Tolstoy
Count Pyotr Andreyevich Tolstoy (russian: Граф Пётр Андреевич Толстой; 1645–1729) was a Russian statesman and diplomat, prominent during and after the reign of Peter the Great. He was the ancestor of all the Counts Tolstoy, including the novelist Leo Tolstoy (September 9 .S. August 28 1828 – November 20 .S. November 7 1910) and Alexei Tolstoy the writer. His wife was Solomonida Timofeevna Dubrovskaya born 1660 and died 1722; he had two sons with her, Ivan (born 1685) and Peter (born 1680). Both his sons died in exile with him the year before his own death. He was, however, survived by many grandchildren: the family was recalled by the Empress Elizabeth, daughter of Peter the Great in 1760, and had all honors and land restored. Background Some historians assume Pyotr Tolstoy to have been an "okolnichy", while others consider he came from a " boyar" background. He served in 1682 as Chamberlain at the court of childless Tsar Feodor III Alekseevich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
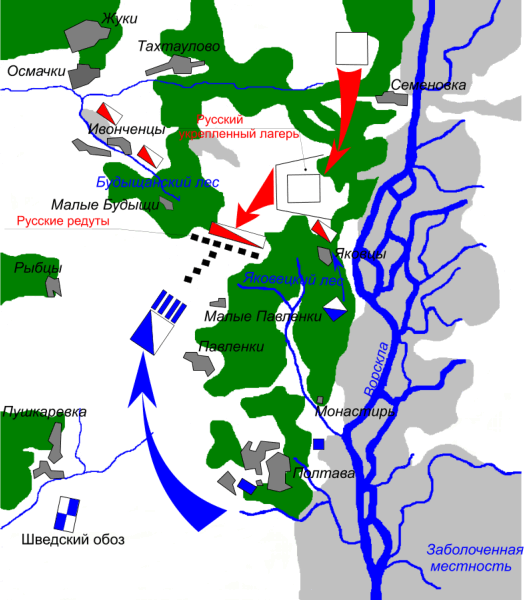
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated a Swedish army, under the command of Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle put an end to the status of the Swedish Empire as a European great power, as well as its eastbound expansion, and marked the beginning of Russian hegemony in Northern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter under Tsar Peter I's rule was the only one still undefeated. Charles XII therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hlukhiv, Ukraine
Hlukhiv ( uk, Глу́хів, ) or Glukhov (russian: Глухов, translit=Glukhov) is a small historic town on the Esman River. It is a city of regional significance in the Sumy region of Ukraine. Hlukhiv is administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance. Hlukhiv Municipality includes Hlukhiv and the village of Sliporod. Hlukhiv also serves as administrative center of Hlukhiv Raion but does not belong to the raion. Population: It is known for being a capital of the Cossack Hetmanate after deposition of Ivan Mazepa in 1708–1764. The former Soviet Chervone-Pustohorod air base is located near Hlukhiv. History First noticed by chroniclers as a Severian town in 1152. Sometime in 1247 Hlukhiv became the seat of a branch of the princely house of Chernigov following the Mongol invasion of Rus. Between 1320 and 1503 it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania before being conquered by the Grand Duchy of Moscow. In 1618 it became part of the Polish–Lithuanian C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baturyn
Baturyn ( uk, Бату́рин, ), is a historic city in Chernihiv Oblast (province) of northern Ukraine. It is located in Nizhyn Raion (district) on the banks of the Seym River. Baturyn lost its city status in 1923 and received it back only in 2008. It hosts the administration of Baturyn urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: History Evidence of settlement in the area of present-day Baturyn dates back to the Neolithic era, with digging having also revealed Bronze Age and Scythian remains. According to some modern writers, the earliest fortress at Baturyn would have been created by the Grand Principality of Chernihiv in the 11th century. The contemporary name for the settlement, however, was first mentioned in the 1625, likely referring to the fortress of Stefan Batory (1533-1586, King of Poland, Prince of Transylvania, and Grand Duke of Lithuania), which was built and named in his honor. The area had been part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles XII Of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of Wittelsbach. Charles was the only surviving son of Charles XI and Ulrika Eleonora the Elder. He assumed power, after a seven-month caretaker government, at the age of fifteen. In 1700, a triple alliance of Denmark–Norway, Saxony– Poland–Lithuania and Russia launched a threefold attack on the Swedish protectorate of Holstein-Gottorp and provinces of Livonia and Ingria, aiming to draw advantage as the Swedish Empire was unaligned and ruled by a young and inexperienced king, thus initiating the Great Northern War. Leading the Swedish army against the alliance, Charles won multiple victories despite being usually significantly outnumbered. A major victory over a Russian army some three times the size in 1700, at the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporozhtsi, translit-std=ungegn) were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids, the land also known historically as the Wild Fields in what is today central and eastern Ukraine. Much of this territory is now flooded by the waters of the Kakhovka Reservoir. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th century, the Zaporozhian Cossacks were a strong political and military force that challenged the authority of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Tsardom of Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starodub
Starodub ( rus, links=no, –°—Ç–∞—Ä–æ–¥—ÉÃÅ–±, p=st…ôr…êÀàdup, ''old oak'') is a town in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, on the Babinets River (the Dnieper basin), southwest of Bryansk. Population: 16,000 (1975). History Starodub has been known since the 11th century, when it was a part of the Principality of Chernigov. It was plundered by the Cumans in 1080. It was burned to the ground by the Mongols in the 13th century. It became a part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 14th century (soon part of the Polish‚ÄìLithuanian union), and Grand Duke Algirdas rebuilt it as a defensive stronghold against Muscovites and Tatars. In 1408, it was granted to Duke ≈Ývitrigaila. In 1503, it passed to the Grand Duchy of Moscow. In 1535, it was besieged and captured by Polish-Lithuanian forces and the defenders were executed however, it soon fell back to Muscovy. In 1616, it was recaptured by the Polish‚ÄìLithuanian Commonwealth, within which it became a county seat in the Smolensk Voivod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony– Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, several Polish magnates under Stanislaus I Leszczyński (1704–1710) and Cossacks under the Ukrainian Hetman Ivan Mazepa (1708–17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter I Of Russia
Peter I ( ‚Äì ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Aleks√©yevich ( rus, –ü—ë—Ç—Ä –ê–ª–µ–∫—Å–µÃÅ–µ–≤–∏—á, p=Ààp ≤…µtr …êl ≤…™Ààks ≤ej…™v ≤…™t…ï, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power. Through a number of successful wars, he captured ports at Azov and the Baltic Sea, laying the groundwork for the Imperial Russian Navy, ending uncontested Swedish supremacy in the Baltic and beginning the Tsardom's expansion into a much larger empire that became a major European power. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment. Peter's reforms had a lastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)
