|
Ivan Fomin
Ivan Aleksandrovich Fomin (3 February 1872 – 12 June 1936) was a Russian architect and educator. He began his career in 1899 in Moscow, working in the Art Nouveau style. After relocating to Saint Petersburg in 1905, he became an established master of the Neoclassical Revival movement. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917 Fomin developed a Soviet adaptation of Neoclassicism and became one of the key contributors to an early phase of Stalinist architecture known as postconstructivism. Early years Born in Oryol, Fomin received a ''classical'' education at a high school in Riga, and studied mathematics at the Moscow University. In 1894, he joined the Imperial Academy of Arts in Saint Petersburg but was expelled in 1896Russian bio: Лисовский В.Г., "И.А. Фомин", М, 1979. Other sources place expulsion in 1897 for political activities. After a year of studies in France, Fomin settled in Moscow and passed the tests for a contractor's license. He worked for Lev Kek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryol
Oryol ( rus, Орёл, p=ɐˈrʲɵl, lit. ''eagle''), also transliterated as Orel or Oriol, is a city and the administrative center of Oryol Oblast situated on the Oka River, approximately south-southwest of Moscow. It is part of the Central Federal District, as well as the Central Economic Region. History Kievan Rus While there are no historical records, archaeological evidence shows that a fortress settlement existed between the Oka River and Orlik Rivers as early as the 12th century, when the land was a part of the Principality of Chernigov. The name of the fortress is unknown; it may not have been called Oryol at the time. In the 13th century, the fortress became a part of the Zvenigorod district of the Karachev Principality. In the early 15th century, the territory was conquered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The city was soon abandoned by its population after being sacked either by Lithuanians or the Golden Horde. The territory became a part of the Tsardom of Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Kekushev
Lev Nikolayevich Kekushev (russian: Лев Николаевич Кекушев) was a Russian architect, notable for his Art Nouveau buildings in Moscow, built in the 1890s and early 1900s in the original, Franco-Belgian variety of this style. Kekushev's buildings are notable for his skillful use of metal ornaments and his signature with a lion (''Lev'') ornament or sculpture. Biography Education Kekushev was born in the family of a Russian officer in Vilnius (Maria Naschokina, p. 253; Simbirsk according to other sources). Kekushev graduated high school in Vilnius, and the Institute of Civil Engineers in Saint Petersburg (1883–1889). For one year, he worked as a state-employed construction engineer in Saint Petersburg, but relocated to Moscow in 1890. At first an assistant to architect Semyon Eybushits, he started independent practice in 1893. At the same time, Kekushev became a master in applied art technologies - iron forging, silver galvanization and chemical frosting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Iskusstva
''Mir iskusstva'' ( rus, «Мир искусства», p=ˈmʲir ɪˈskustvə, ''World of Art'') was a Russian magazine and the artistic movement it inspired and embodied, which was a major influence on the Russians who helped revolutionize European art during the first decade of the 20th century. The magazine had limited circulation outside Russia. From 1909, several of the ''miriskusniki'' (i.e., members of the movement) also participated in productions of Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes company based in Paris. Foundation The artistic group was founded in November 1898 by a group of students that included Alexandre Benois, Konstantin Somov, Dmitry Filosofov, Léon Bakst, and Eugene Lansere. The starting moments for the new artistic group was organization of the ''Exhibition of Russian and Finnish Artists'' in the Stieglitz Museum of Applied Arts in Saint-Petersburg. The magazine was co-founded in 1899 in St. Petersburg by Alexandre Benois, Léon Bakst, and Sergei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkonsky
Volkonsky is a Russian language locational surname, named after the Volkona river south of Moscow, and borne by a Russian noble family.Ziegler, Dominic. ''Black Dragon River: A Journey Down the Amur River at the Borderlands of Empires.'' New York: Penguin Press. 2015. p. 139. Alternative spellings include Volkonskaya, Volkonski and Wolkonsky. The name Volkonsky may refer to: *Alexander Volkonsky (1866–1934), Russian diplomat *Alexey Volkonsky (born 1978), Russian canoer *Andrei Volkonsky (1933–2008), Russian composer *Maria Mikhailovich Volkonskaya (1863–1943), Russian aristocrat *Maria Volkonsky (1805–1863), Russian aristocrat *Nikita Volkonsky (1781–1844), Russian general *Peeter Volkonski (born 1954), Estonian musician *Peter Volkonsky (1861–1948), Russian aristocrat *Pyotr Mikhailovich Volkonsky (1776–1852), Russian general *Serge Wolkonsky (1860–1937), Russian theatre director *Sergei Volkonsky (1788–1865), Russian general *Zinaida Volkonskaya Princess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Benois
Leon Benois (russian: Леонтий Николаевич Бенуа; 1856 in Peterhof – 1928 in Leningrad) was a Russian architect from the Benois family. Biography He was the son of architect Nicholas Benois, the brother of artists Alexandre Benois and Albert Benois. He built the Roman Catholic cathedral of Notre-Dame in St Petersburg, the mausoleum of the Grand Dukes of Russia in the Peter and Paul Fortress, the Russian Chapel in Darmstadt, and the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Warsaw, among many other works. Benois served as Dean of the Imperial Academy of Arts (1903–06, 1911–17) and edited the architecture magazine ''Zodchii''. He gave his name to Leonardo da Vinci's painting ''Benois Madonna'' which he inherited from his father-in-law and presented to the Hermitage Museum. The painter Nadia Benois was his daughter, and the actor Sir Peter Ustinov was his grandson. See also * Benois family External links Cathedral of Notre-Dame de St Petersburg [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
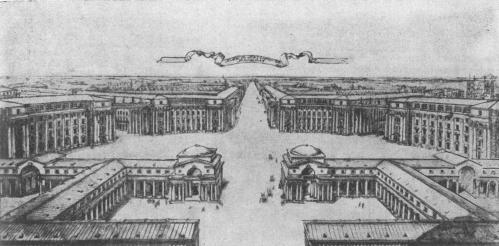
Fomin Golodai 01
Fomin (russian: Фомин), or Fomina (feminine; Фомина), is a common Russian surname that is derived from the male given name Foma and literally means ''Foma's''. It may refer to: Masculine form *Aleksandr Fomin (botanist) (1869–1935), Russian/Soviet botanist and academician *Aleksandr Fomin, alias of Soviet spy Alexander Feklisov (1914–2007), known for receiving information from Julius Rosenberg and his contacts during the Cuban Missile Crisis * Andriy Fomin (born 1977), Ukrainian Olympic speedskater *Artyom Fomin (born 1988), Russian football player *Boris Fomin (1900–1948), Russian composer of folk music *Daniil Fomin (born 1997), Russian football player * Denis Fomin (born 1996), Russian football defender *Dmitry Fomin (born 1968), Russian Olympic volleyball player * Fedor Fomin (born 1968), Russian/Norwegian computer scientist *Ivan Fomin (1872–1936), a Russian/Soviet architect *Margarita Fomina (born 1988), Russian curler *Mitya Fomin (born 1974), Russian sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fomin Golodai 00
Fomin (russian: Фомин), or Fomina (feminine; Фомина), is a common Russian surname that is derived from the male given name Foma and literally means ''Foma's''. It may refer to: Masculine form *Aleksandr Fomin (botanist) (1869–1935), Russian/Soviet botanist and academician *Aleksandr Fomin, alias of Soviet spy Alexander Feklisov (1914–2007), known for receiving information from Julius Rosenberg and his contacts during the Cuban Missile Crisis * Andriy Fomin (born 1977), Ukrainian Olympic speedskater *Artyom Fomin (born 1988), Russian football player *Boris Fomin (1900–1948), Russian composer of folk music *Daniil Fomin (born 1997), Russian football player * Denis Fomin (born 1996), Russian football defender *Dmitry Fomin (born 1968), Russian Olympic volleyball player * Fedor Fomin (born 1968), Russian/Norwegian computer scientist *Ivan Fomin (1872–1936), a Russian/Soviet architect *Margarita Fomina (born 1988), Russian curler *Mitya Fomin (born 1974), Russian sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koloman Moser
Koloman Moser (; 30 March 1868 – 18 October 1918) was an Austrian artist who exerted considerable influence on twentieth-century graphic art. He was one of the foremost artists of the Vienna Secession movement and a co-founder of Wiener Werkstätte. Moser designed a wide array of art works, including books and graphic works from postage stamps to magazine vignettes; fashion; stained glass windows, porcelains and ceramics, blown glass, tableware, silver, jewelry, and furniture. Biography Moser was born in Vienna in 1868 to parents Josef and Thresia Moser (née Hirsch); he was the oldest of three siblings. studied at the Wiener Akademie and the Kunstgewerbeschule, where he also taught from 1899. Moser's designs in architecture, furniture, jewellery, graphics, and tapestries helped characterise the work of this era. He drew upon the clean lines and repetitive motifs of classical Greek and Roman art and architecture in reaction to the Baroque decadence of his turn-of-the-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Maria Olbrich
Joseph Maria Olbrich (22 December 1867 – 8 August 1908) was an Austrian architect and one of the Vienna Secession founders. Early life Olbrich was born in Opava, Austrian Silesia (now Czech Republic), the third child of Edmund and Aloisia Olbrich. He had two sisters, who died before he was born, and two younger brothers, John and Edmund. His father was a prosperous confectioner and wax manufacturer who also owned a brick works, where Olbrich's interest in the construction industry has its early origin. Career Olbrich studied architecture at the University of Applied Arts Vienna (''Wiener Staatsgewerbeschule'') and the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna, where he won several prizes. These included the Prix de Rome, for which he traveled in Italy and North Africa. In 1893, he started working for Otto Wagner, the Austrian architect, and probably did the detailed construction for most of Wagner's Wiener Stadtbahn (Metropolitan Railway) buildings. In 1897, Gustav Klimt, Olbrich, Josef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Rennie Mackintosh
Charles Rennie Mackintosh (7 June 1868 – 10 December 1928) was a Scottish architect, designer, water colourist and artist. His artistic approach had much in common with European Symbolism. His work, alongside that of his wife Margaret Macdonald, was influential on European design movements such as Art Nouveau and Secessionism and praised by great modernists such as Josef Hoffmann. Mackintosh was born in Glasgow and died in London. He is among the most important figures of Modern Style (British Art Nouveau style). Early life and education Charles Rennie Mackintosh was born at 70 Parson Street, Townhead, Glasgow, on 7 June 1868, the fourth of eleven children and second son of William McIntosh, a superintendent and chief clerk of the City of Glasgow Police. He attended Reid's Public School and the Allan Glen's Institution from 1880 to 1883. William's wife Margaret Mackintosh née 'Rennie' grew up in the Townhead and Dennistoun (Firpark Terrace) areas of Glasgow. Name He cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Majolica
Victorian majolica properly refers to two types of majolica made in the second half of the 19th century in Europe and America. Firstly, and best known, there is the mass-produced majolica decorated with coloured lead glazes, made in Britain, Europe and the US; typically hard-wearing, surfaces moulded in relief, vibrant translucent glazes, in occasionally classical but mostly naturalistic styles, often with an element of High Victorian whimsy. Secondly, there is the much less common tin-glazed majolica made primarily by Mintons from 1848 to circa 1880, typically with flat surfaces, opaque white glaze with fine brush painted decoration in imitation of the Italian Renaissance maiolica process and styles. Glazes Glaze is a vitreous coating on a ceramic. There are four types of glazing: feldspathic or alkali-glazed, salt-glazed, lead-glazed, and tin-glazed. It is important to understand that lead oxide is the main ingredient of both lead ''and'' tin glazes. Lead oxide is a flux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Endell
August Endell (1871–1925) was a designer, writer, teacher, and German architect. He was one of the founders of the Jugendstil movement, the German counterpart of Art Nouveau. His first marriage was with Elsa von Freytag-Loringhoven. Life August Endell was born on April 12, 1871, in Berlin. In 1892 Endell moved to Munich, where he gave up his dream of being a teacher and instead became a scholar. He studied aesthetics, psychology and philosophy, German literature, and art at the University of Munich. He had the intention to pursue a doctorate degree in academics, but changed direction when he met Hermann Obrist, who became a close friend, and whose work was characterized by expressive ornamentation of observed submarine flora and fauna. Although influenced and encouraged by Obrist, Endell was primarily concerned with translating his idea of mobile space into architecture and decorations. Endell expressed important ideas on the stylistic intention underlying the work of Jugendstil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



