|
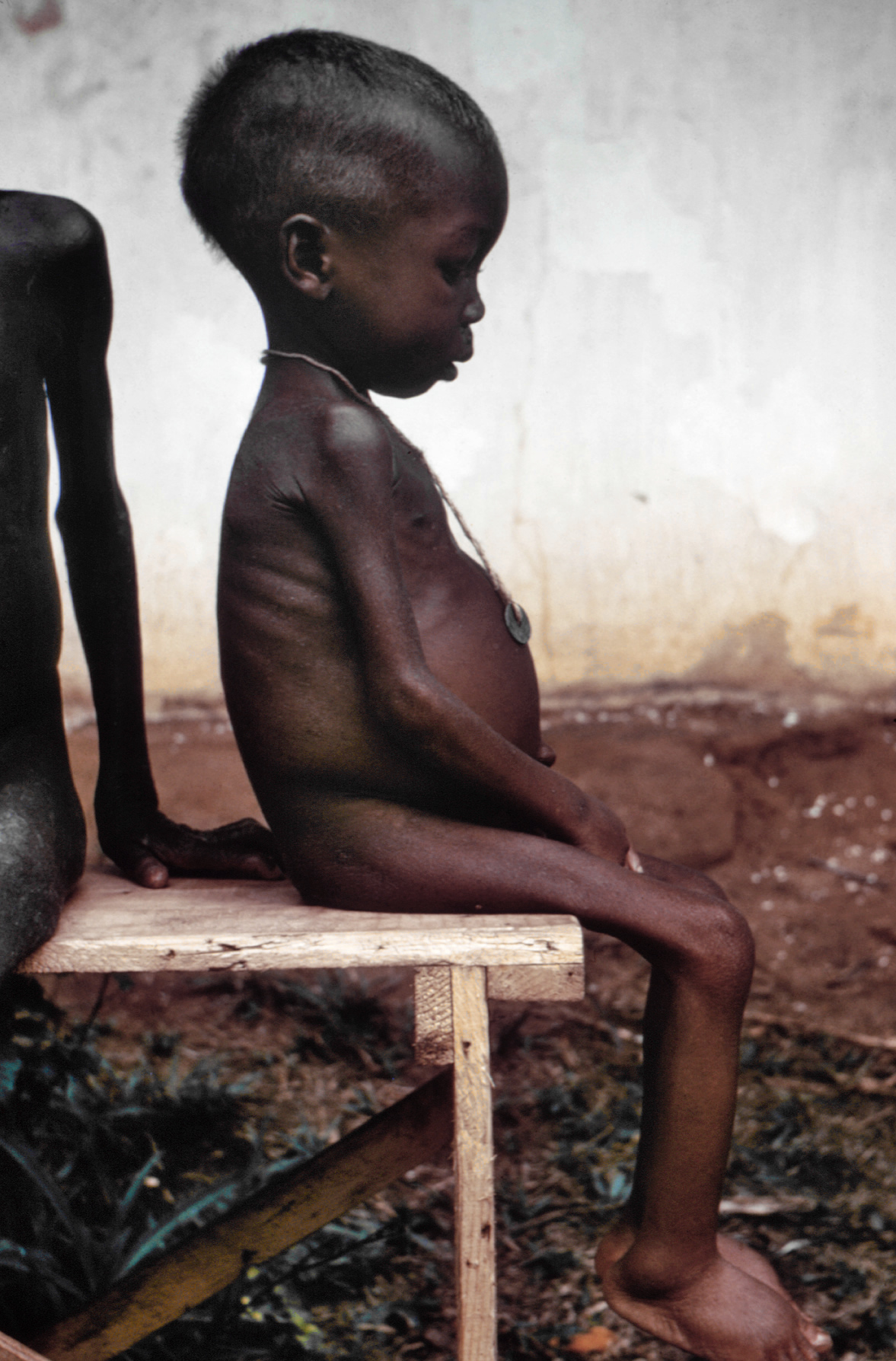
Israeli War Crimes
Israeli war crimes are the violations of international criminal law, including war crimes and crimes against humanity, which the Israel Defense Forces, the military branch of the state of Israel, has been accused of committing since the founding of Israel in 1948. These have included murder, intentional targeting of civilians, killing of prisoners of war and surrendered combatants, indiscriminate attacks, collective punishment, starvation of civilians, the use of human shields, torture, pillage, forced transfer, breach of medical neutrality, targeting of journalists, unlawful attacks against civilian objects and protected objects, wanton destruction, and incitement to genocide. Israel ratified the Geneva Conventions on July 6, 1951, and on January 2, 2015, the State of Palestine acceded to the Rome Statute, granting the International Criminal Court (ICC) jurisdiction over war crimes committed in the Occupied Palestinian Territories (OPT). Human rights experts argue that acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyed Ambulance In The CIty Of Shijaiyah In The Gaza Strip
Destroyed may refer to: * Destroyed (Sloppy Seconds album), ''Destroyed'' (Sloppy Seconds album), a 1989 album by Sloppy Seconds * Destroyed (Moby album), ''Destroyed'' (Moby album), a 2011 album by Moby See also * Destruction (other) * Ruined (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incitement To Genocide
Incitement to genocide is a crime under international law which prohibits inciting (encouraging) the commission of genocide. An extreme form of hate speech, incitement to genocide is considered an inchoate offense and is theoretically subject to prosecution even if genocide does not occur, although charges have never been brought in an international court without mass violence having occurred. "Direct and public incitement to commit genocide" was forbidden by the Genocide Convention in 1948. Incitement to genocide is often cloaked in metaphor and euphemism and may take many forms beyond direct advocacy, including dehumanization and "accusation in a mirror". Historically, incitement to genocide has played a significant role in the commission of genocide, including the Armenian genocide, the Holocaust and the Rwandan genocide. Definitions "Direct and public incitement to commit genocide" is forbidden by the Genocide Convention (1948), Article 3(c). If genocide were to be committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent United Nations Fact Finding Mission On The Israel Palestine Conflict
Following the 2021 Israel–Palestine crisis, the United Nations Human Rights Council voted on 27 May 2021 to set up a United Nations fact-finding mission to investigate possible war crimes and other abuses committed in Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories. Mission members Navi Pillay (South Africa), serves as chair, Miloon Kothari (India) and Chris Sidoti (Australia) serve as members of the commission. Mandate The commission will report to the Human Rights Council annually from June 2022. Unlike previous fact finding missions the inquiry is open ended and will examine "all underlying root causes of recurrent tensions, instability and protraction of conflict, including systematic discrimination and repression based on national, ethnic, racial or religious identity." Manpower was reduced from 24 to 18 persons following a US-Israel campaign to reduce the Commission budget. On 17 February 2022, Israel said it will not cooperate with the commission, alleging bias. At the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Fact-finding Mission
A United Nations fact-finding mission, also called a United Nations commission of inquiry, is a United Nations mission carried out with the intention to discover facts. They are often sent to troubled areas. Fact-finding missions have been sent by the UN to a number of trouble-spots over the past 50 years, on a pragmatic, occasional, case-by-case basis. There are legal and political parameters for fact-finding, which stresses its value and opens the door for more comprehensive, ongoing use of this tool, particularly by the Secretary-General. History Fact-finding was first established during the Hague Convention of 1907, which dealt with international commissions of inquiry. Declaration The draft declaration, was adopted without a vote by a Special United Nations Committee at the end of a three-week sessions in New York held 4–22 February 1991. On 9 December 1991, the General Assembly adopted resolution 46/59; ''Declaration on Fact-finding by the United Nations in the Field o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Human Rights Council
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), CDH is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. The headquarters of the Council are at the United Nations Office at Geneva in Switzerland. The Council investigates allegations of breaches of human rights in United Nations member states and addresses thematic human rights issues like freedom of association and assembly, freedom of expression, freedom of belief and religion, women's rights, LGBT rights, and the rights of racial and ethnic minorities. The Council was established by the United Nations General Assembly on 15 March 2006 to replace the United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR, herein CHR). The Council works closely with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and engages the United Nations ''special procedures''. The Council has been strongly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and supporters around the world. The stated mission of the organization is to campaign for "a world in which every person enjoys all of the human rights enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and other international human rights instruments." The organization has played a notable role on human rights issues due to its frequent citation in media and by world leaders. AI was founded in London in 1961 by the lawyer Peter Benenson. Its original focus was prisoners of conscience, with its remit widening in the 1970s, under the leadership of Seán MacBride and Martin Ennals to include miscarriages of justice and torture. In 1977, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. In the 1980s, its secretary general was Thomas Hammarberg, succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Médecins Sans Frontières
(MSF; pronounced ), also known as Doctors Without Borders, is a humanitarian medical non-governmental organisation (NGO) or charity of French origin known for its projects in conflict zones and in countries affected by endemic diseases. Main areas of work include diabetes, drug-resistant infections, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, tropical and neglected diseases, tuberculosis, vaccines and COVID-19. In 2019, the charity was active in 70 countries with over 35,000 personnel; mostly local doctors, nurses and other medical professionals, logistical experts, water and sanitation engineers, and administrators. Private donors provide about 90% of the organisation's funding, while corporate donations provide the rest, giving MSF an annual budget of approximately US$1.63 billion. MSF was founded in 1971, in the aftermath of the Biafran famine of the Nigerian Civil War, by a small group of French doctors and journalists who sought to expand accessibility to medical care across nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human rights abusers to denounce abuse and respect human rights, and the group often works on behalf of refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners. Human Rights Watch, in 1997, shared the Nobel Peace Prize as a founding member of the International Campaign to Ban Landmines, and it played a leading role in the 2008 treaty banning cluster munitions. The organization's annual expenses totaled $50.6 million in 2011, $69.2 million in 2014, and $75.5 million in 2017. History Human Rights Watch was co-founded by Robert L. Bernstein Jeri Laber and Aryeh Neier as a private American NGO in 1978, under the name Helsinki Watch, to monitor the then-Soviet Union's compliance with the Helsinki Accords. Helsinki Watch adopted a practice of public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquarters of the United Nations, headquartered on extraterritoriality, international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and Peace Palace, The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with Dumbarton Oaks Conference, the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for United Nations Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupied Palestinian Territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has referred to the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, as "the Occupied Palestinian Territory", and this term was used as the legal definition by the ICJ in its advisory opinion of July 2004. The term occupied Palestinian territory was used by the United Nations and other international organizations between October 1999 and December 2012 to refer to areas controlled by the Palestinian National Authority, but from 2012, when Palestine was admitted as one of its non-member observer states, the United Nations started using exclusively the name State of Palestine. The European Union (EU) also adopts the term occupied Palestinian territory, with a parallel term Palestinian Authority territories also occasiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
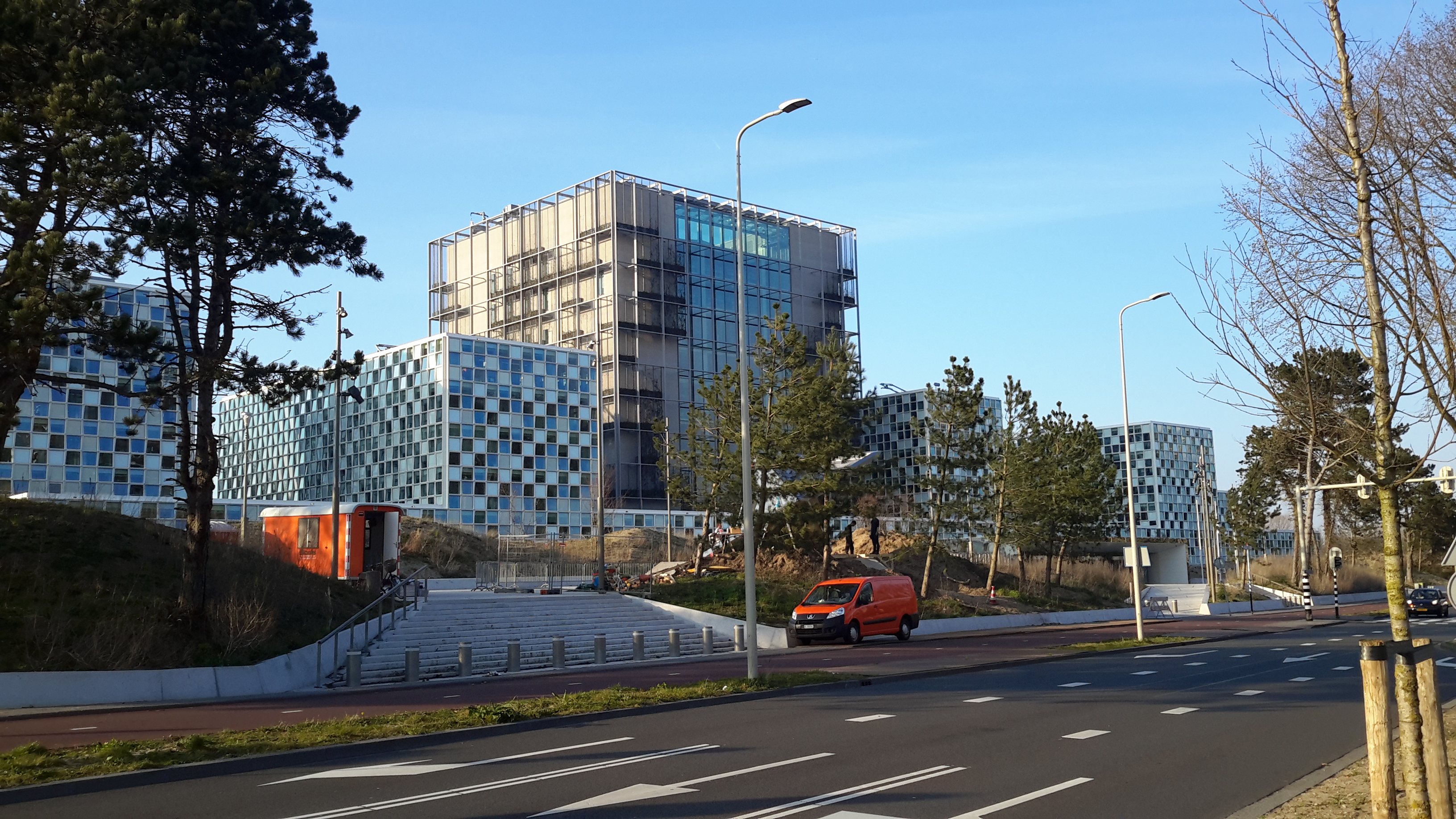
International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals for the international crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes and the crime of aggression. It is distinct from the International Court of Justice, an organ of the United Nations that hears disputes between states. While praised as a major step towards justice, and as an innovation in international law and human rights, the ICC has faced a number of criticisms from governments and civil society, including objections to its jurisdiction, accusations of bias, Eurocentrism and racism, questioning of the fairness of its case-selection and trial procedures, and doubts about its effectiveness. History The establishment of an international tribunal to judge political leaders accused of international crimes was first proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |