|
Israeli Casualties Of War
Israeli casualties of war, in addition to those of Israel's nine major wars, include 9,745 soldiers and security forces personnel killed in "miscellaneous engagements and terrorist attacks", which includes security forces members killed during military operations, by fighting crime, natural disasters, diseases, traffic or labor accidents and disabled veterans whose disabilities contributed to their deaths. Between 1948 and 1997, 20,093 Israeli soldiers were killed in combat, 75,000 Israelis were wounded, and nearly 100,000 Israelis were considered disabled army veterans. On the other hand, in 2010 Yom Hazikaron, Israel honored the memory of 22,684 Israeli soldiers and pre-Israeli Palestinian Jews killed since 1860 in the line of duty for the independence, preservation and protection of the nation, and 3,971 civilian terror victims. The memorial roll, in addition to IDF members deceased, also include fallen members of the Shin Bet security service, the Mossad intelligence serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Of Fallen Soldiers From The Yom Kippur War - Flickr - Israel Defense Forces
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of art such as sculptures, statues or fountains and parks. Larger memorials may be known as monuments. Types The most common type of memorial is the gravestone or the memorial plaque. Also common are war memorials commemorating those who have died in wars. Memorials in the form of a cross are called intending crosses. Online memorials are often created on websites and social media to allow digital access as an alternative to physical memorials which may not be feasible or easily accessible. When somebody has died, the family may request that a memorial gift (usually money) be given to a designated charity, or that a tree be planted in memory of the person. Those temporary or makeshift memorials are also called grassroots memorials.''Grassroo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Foreign Affairs (Israel)
The Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs ( he, מִשְׂרַד הַחוּץ, translit. ''Misrad HaHutz''; ar, وزارة الخارجية الإسرائيلية) is one of the most important ministries in the Israeli government. The ministry's role is to implement Israel's foreign policy, and promote economic, cultural, and scientific relations with other countries. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is located in the government complex in Givat Ram, Jerusalem. Yair Lapid currently holds the Foreign Ministry post. History In the early months of 1948, when the government of the future State of Israel was being formed, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs was housed in a building in the abandoned Templer village of Sarona, on the outskirts of Tel Aviv. Moshe Sharett, formerly head of the Political Department of the Jewish Agency, was placed in charge of foreign relations, with Walter Eytan as Director General. In November 2013, the longest labor dispute in the history of the Foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Insurgency In Palestine
A successful paramilitary campaign was carried out by Zionist underground groups against British rule in Mandatory Palestine from 1944 to 1948. The tensions between the Zionist underground and the British mandatory authorities rose from 1938 and intensified with the publication of the White Paper of 1939. The Paper outlined new government policies to place further restrictions on Jewish immigration and land purchases, and declared the intention of giving independence to Palestine, with an Arab majority, within ten years. Though World War II brought relative calm, tensions again escalated into an armed struggle towards the end of the war, when it became clear that the Axis powers were close to defeat. The Haganah, the largest of the Jewish underground militias, which was under the control of the officially recognised Jewish leadership of Palestine, remained cooperative with the British. But in 1944 the Irgun launched a rebellion against British rule, thus joining Lehi (group), Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
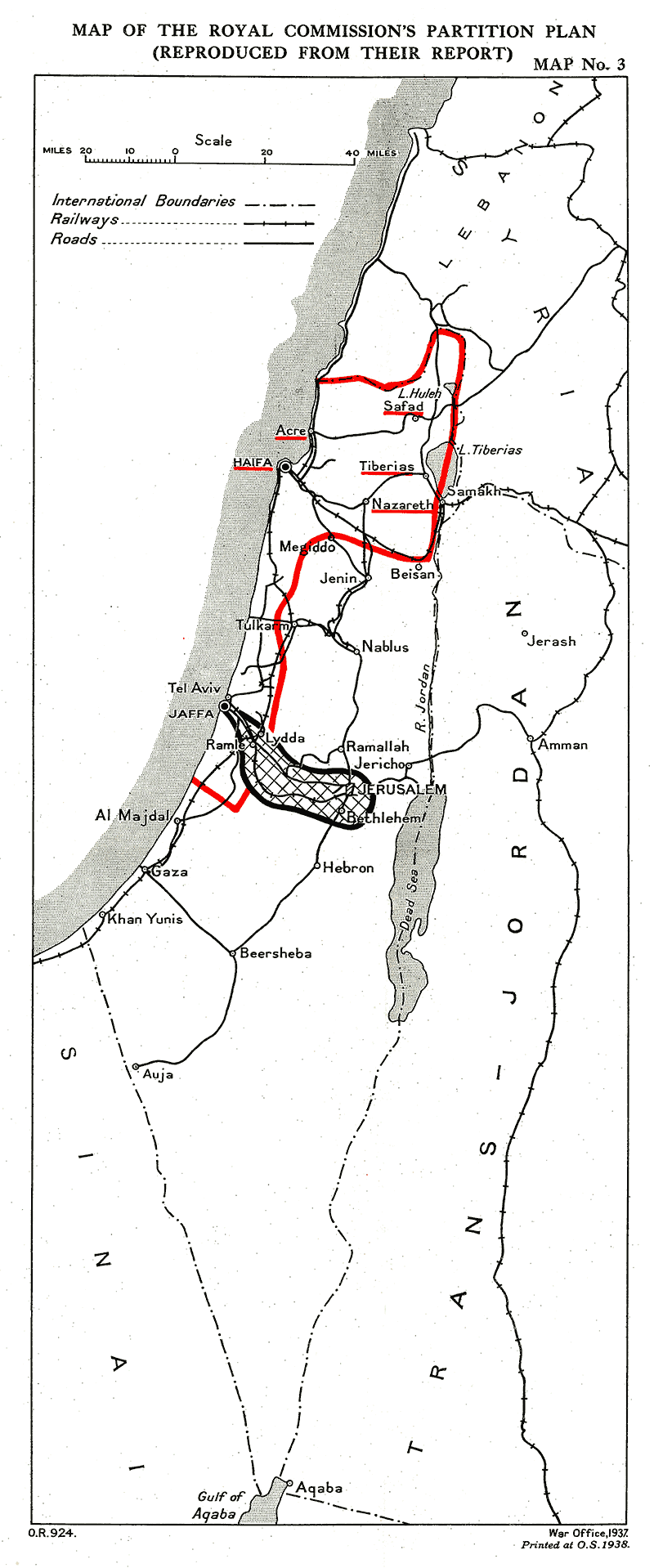
1936–1939 Arab Revolt In Palestine
The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine, later known as The Great Revolt (''al-Thawra al- Kubra'') or The Great Palestinian Revolt (''Thawrat Filastin al-Kubra''), was a popular nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration of the Palestine Mandate, demanding Arab independence and the end of the policy of open-ended Jewish immigration and land purchases with the stated goal of establishing a "Jewish National Home". The uprising coincided with a peak in the influx of immigrant Jews, some 60,000 that year –the Jewish population having grown under British auspices from 57,000 to 320,000 in 1935 – and with the growing plight of the rural fellahin rendered landless, who as they moved to metropolitan centers to escape their abject poverty found themselves socially marginalized. Since 1920 Jews and Arabs had been involved in a cycle of attacks and counter-attacks, and the immediate spark for the uprising was the murder of two Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 Palestine Riots
The 1933 Palestine riots ( he, מאורעות תרצ"ד, Me'oraot Tartsad) were a series of violent riots in Mandatory Palestine, as part of the intercommunal conflict in Mandatory Palestine. The riots erupted on 13 October 1933 when the police broke up a banned demonstration organized by the Arab Executive Committee. The riots came as the culmination of Arab resentment at Jewish migration after it surged to new heights following the rise of Nazi Germany, and at the British Mandate authorities for allegedly facilitating Jewish land purchases. The second mass demonstration, at Jaffa in October, turned into a bloodbath when police fired on the thousands-strong crowd, killing 19 and injuring some 70. The "Jaffa massacre", as Palestinians called it, quickly triggered further unrest, including a week-long general strike and urban insurrections that resulted in police killing 7 more Arabs and wounding another 130 with gunfire. Background The sectarian violence in Mandatory Palestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Palestine Riots
The 1929 Palestine riots, Buraq Uprising ( ar, ثورة البراق, ) or the Events of 1929 ( he, מאורעות תרפ"ט, , ''lit.'' Events of 5689 Anno Mundi), was a series of demonstrations and riots in late August 1929 in which a longstanding dispute between Muslims and Jews over access to the Western Wall in Jerusalem escalated into violence. The riots took the form, for the most part, of attacks by Arabs on Jews accompanied by destruction of Jewish property. During the week of riots, from 23 to 29 August, 133 Jews were killed by Arabs, and 339 Jews were injured, most of whom were unarmed. There were 116 Arabs killed and at least 232 wounded, mostly by the Mandate police suppressing the riots. Around 20 Arabs were killed by Jewish attackers and indiscriminate British gunfire. After the riots, 174 Arabs and 109 Jews were charged with murder or attempted murder; around 40% of Arabs and 3% of Jews were subsequently convicted. During the riots, 17 Jewish communities were e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920 Palestine Riots
The 1920 Nebi Musa riots or 1920 Jerusalem riots took place in British-controlled part of Occupied Enemy Territory Administration between Sunday, 4 April, and Wednesday, 7 April 1920 in and around the Old City of Jerusalem. Five Jews and four Arabs were killed, and several hundred were injured. The riots coincided with and are named after the Nebi Musa festival, which was held every year on Easter Sunday, and followed rising tensions in Arab-Jewish relations. The events came shortly after the Battle of Tel Hai and the increasing pressure on Arab nationalists in Syria in the course of the Franco-Syrian War. Speeches were given by Arab religious leaders during the festival (in which large numbers of Muslims traditionally gathered for a religious procession), which included slogans referencing Zionist immigration and previous confrontations around outlying Jewish villages in the Galilee. The trigger which turned the procession into a riot is not known with certainty. The British m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tel Hai
The Battle of Tel Hai was fought on 1 March 1920 between Arab irregulars and a Jewish defensive paramilitary force protecting the village of Tel Hai in Northern Galilee. In the course of the event, a Shiite Arab militia, accompanied by Bedouin from a nearby village, attacked the Jewish agricultural locality of Tel Hai. In the aftermath of the battle eight Jews and five Arabs were killed. Joseph Trumpeldor, the commander of Jewish defenders of Tel Hai, was shot in the hand and stomach, and died while being evacuated to Kfar Giladi that evening. Tel Hai was eventually abandoned by the Jews and burned by the Arab militia. The event is perceived by some scholars as part of the Franco-Syrian War and by some as an outbreak of violence, in the later developing Sectarian conflict in Mandatory Palestine. Background Tel Hai had been intermittently inhabited since 1905 and was permanently settled as a border outpost in 1918, following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. The are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
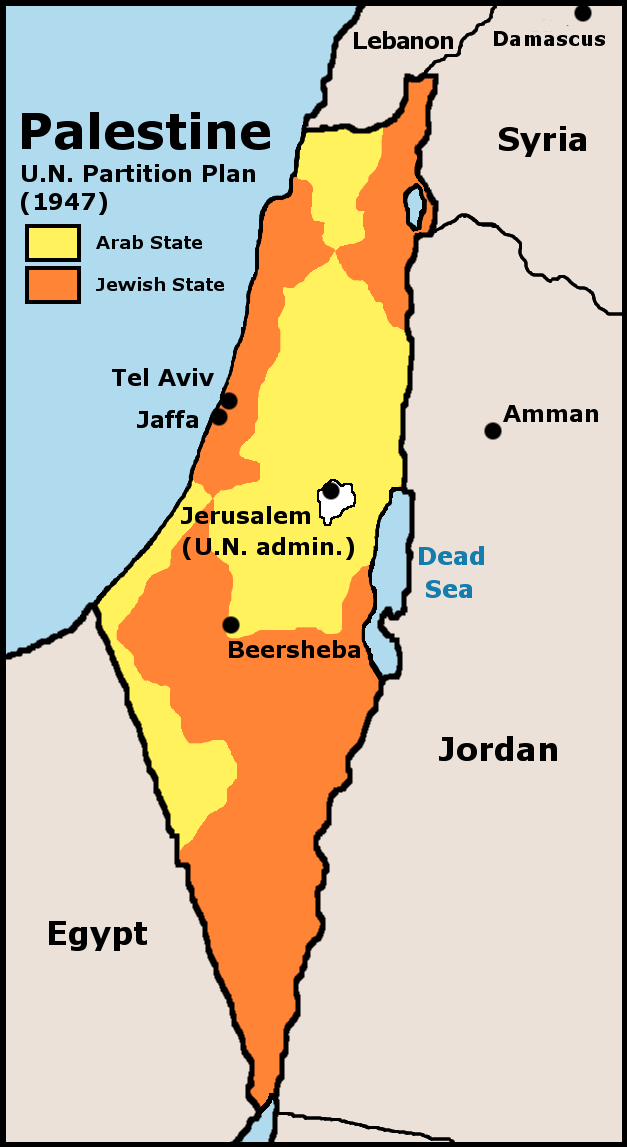
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Palestine In World War II
The Italian bombing of Mandatory Palestine in World War II was part of an effort by the Italian Royal Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica'') to strike at the United Kingdom and its overseas empire throughout the Middle East during World War II. Background On 10 June 1940, the Kingdom of Italy declared war on the French Republic and the United Kingdom. The Italian invasion of France was short-lived and the French signed an armistice with the Italians on 25 June, three days after France's armistice with Germany. This left the British and the forces of the Commonwealth of Nations for the Italians to contend with in the Middle East. Successively on 19 October 1940, four Italian SM.82s bombers attacked American-operated oil refineries in the British Protectorate of Bahrain, damaging the local refineries.Air Raid! A Sequel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British–Zionist Conflict
A successful paramilitary campaign was carried out by Zionist underground groups against British rule in Mandatory Palestine from 1944 to 1948. The tensions between the Zionist underground and the British mandatory authorities rose from 1938 and intensified with the publication of the White Paper of 1939. The Paper outlined new government policies to place further restrictions on Jewish immigration and land purchases, and declared the intention of giving independence to Palestine, with an Arab majority, within ten years. Though World War II brought relative calm, tensions again escalated into an armed struggle towards the end of the war, when it became clear that the Axis powers were close to defeat. The Haganah, the largest of the Jewish underground militias, which was under the control of the officially recognised Jewish leadership of Palestine, remained cooperative with the British. But in 1944 the Irgun launched a rebellion against British rule, thus joining Lehi, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |