|
Isotropic Radiator
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical point source of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source. Isotropic radiators are used as reference radiators with which other sources are compared, for example in determining the gain of antennas. A coherent isotropic radiator of electromagnetic waves is theoretically impossible, but incoherent radiators can be built. An isotropic sound radiator is possible because sound is a longitudinal wave. The unrelated term '' isotropic radiation'' refers to radiation which has the same intensity in all directions, thus an isotropic radiator does ''not'' radiate isotropic radiation. Physics In physics, an isotropic radiator is a point radiation or sound source. At a distance, the sun is an isotropic radiator of electromagnetic radiation. Antenna theory In anten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropic Radiator Animation 240x240x8frame 0
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented. Mathematics Within mathematics, ''isotropy'' has a few different meanings: ; Isotropic manifolds: A manifold is isotropic if the geometry on the manifold is the same regardless of direction. A similar concept is homogeneity. ; Isotropic quadratic form: A quadratic form ''q'' is said to be isotropic if there is a non-zero vector ''v'' such that ; such a ''v'' is an isotropic vector or null vector. In complex geometry, a line through the origin in the direction of an isotropic vector is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
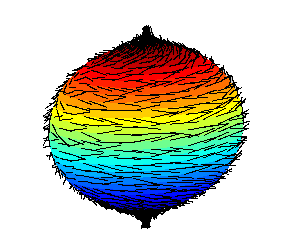
Hairy Ball Theorem
The hairy ball theorem of algebraic topology (sometimes called the hedgehog theorem in Europe) states that there is no nonvanishing continuous tangent vector field on even-dimensional ''n''-spheres. For the ordinary sphere, or 2‑sphere, if ''f'' is a continuous function that assigns a vector in R3 to every point ''p'' on a sphere such that ''f''(''p'') is always tangent to the sphere at ''p'', then there is at least one pole, a point where the field vanishes (a ''p'' such that ''f''(''p'') = 0). The theorem was first proved by Henri Poincaré for the 2-sphere in 1885, and extended to higher dimensions in 1912 by Luitzen Egbertus Jan Brouwer. The theorem has been expressed colloquially as "you can't comb a hairy ball flat without creating a cowlick" or "you can't comb the hair on a coconut". Counting zeros Every zero of a vector field has a (non-zero) "index", and it can be shown that the sum of all of the indices at all of the zeros must be two, because the Euler c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
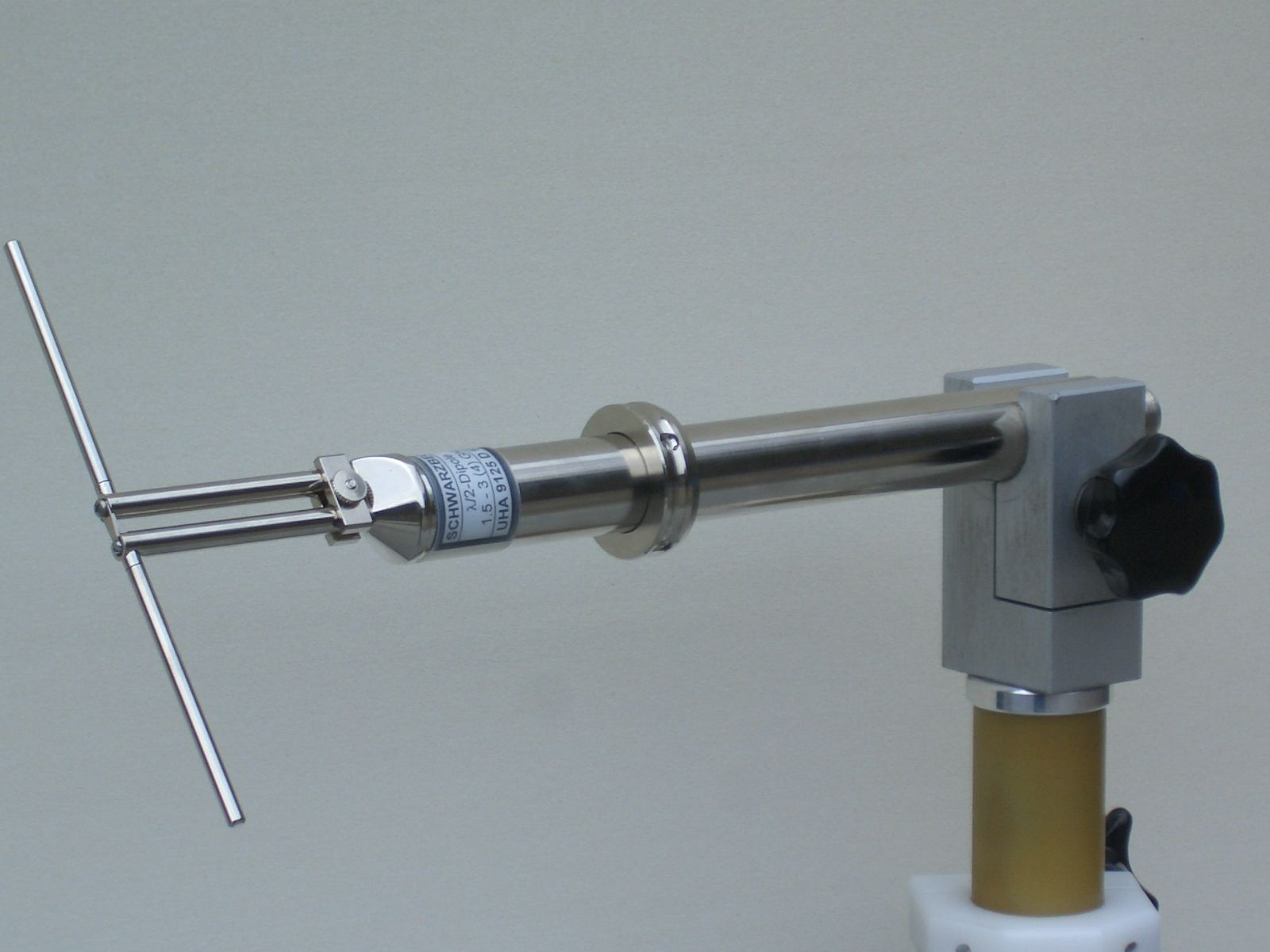
Hertzian Dipole
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of ground. A common example of a dipole is the "rabbit ears" television antenna found on broadcast te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnidirectional Antenna
In radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is a class of antenna which radiates equal radio power in all directions perpendicular to an axis (azimuthal directions), with power varying with angle to the axis ( elevation angle), declining to zero on the axis. When graphed in three dimensions ''(see graph)'' this radiation pattern is often described as ''doughnut-shaped''. Note that this is different from an isotropic antenna, which radiates equal power in ''all'' directions, having a ''spherical'' radiation pattern. Omnidirectional antennas oriented vertically are widely used for nondirectional antennas on the surface of the Earth because they radiate equally in all horizontal directions, while the power radiated drops off with elevation angle so little radio energy is aimed into the sky or down toward the earth and wasted. Omnidirectional antennas are widely used for radio broadcasting antennas, and in mobile devices that use radio such as cell phones, FM radios, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: “Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd ed. 1982 David K Cheng: “Field and Wave Electromagnetics”, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Edition 2, 1998. Edward C. Jordan & Keith G. Balmain; “Electromagnetic Waves and Radiating Systems” (2nd ed. 1968) Prentice-Hall. Particularly in the fields of fiber optics, lasers, and integrated optics, the term radiation pattern may also be used as a synonym for the near-field pattern or Fresnel pattern.Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves (electromagnetic waves of radio frequency) and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation. Radio receivers are essential components of all systems that use radio. The information produced by the receiver may be in the form of sound, video (television), or digital data. A radio receiver may be a separate piece of electronic equipment, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMF Measurement
EMF measurements are measurements of ambient (surrounding) electromagnetic fields that are performed using particular sensors or probes, such as EMF meters. These probes can be generally considered as ''antennas'' although with different characteristics. In fact, probes should not perturb the electromagnetic field and must prevent coupling and reflection as much as possible in order to obtain precise results. There are two main types of EMF measurements: *''broadband measurements'': performed using a broadband probe, that is a device which senses any signal across a wide range of frequencies and is usually made with three independent diode detectors; *''frequency selective measurements'': in which the measurement system consists of a field antenna and a frequency selective receiver or spectrum analyzer allowing to monitor the frequency range of interest. EMF probes may respond to fields only on one axis, or may be tri-axial, showing components of the field in three directions at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 10 (approximately ). The unit expresses a relative change or an absolute value. In the latter case, the numeric value expresses the ratio of a value to a fixed reference value; when used in this way, the unit symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is " V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). Two principal types of scaling of the decibel are in common use. When expressing a power ratio, it is defined as ten times the logarithm in base 10. That is, a change in ''power'' by a factor of 10 corresponds to a 10 dB change in level. When expressing root-power quantities, a change in ''ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensity (physics)
In physics, the intensity or flux of radiant energy is the power transferred per unit area, where the area is measured on the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the energy. In the SI system, it has units watts per square metre (W/m2), or kg⋅ s−3 in base units. Intensity is used most frequently with waves such as acoustic waves (sound) or electromagnetic waves such as light or radio waves, in which case the ''average'' power transfer over one period of the wave is used. ''Intensity'' can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with " strength", "amplitude", " magnitude", or " level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech. Intensity can be found by taking the energy density (energy per unit volume) at a point in space and multiplying it by the velocity at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Efficiency
Antenna ''apertureillumination efficiency is a measure of the extent to which an antenna or array is uniformly excited or illuminated. It is typical for an antenna pertureor array to be intentionally under-illuminated or under-excited in order to mitigate sidelobes and reduce antenna temperature. It is not to be confused with radiation efficiency or antenna efficiency. Definition Antenna pertureillumination efficiency is defined as "The ratio, usually expressed in percent, of the maximum directivity of an antenna pertureto its standard directivity." It is synonymous with normalized directivity. Standard eferencedirectivity is defined as "The maximum directivity from a planar aperture of area A, or from a line source of length L, when excited with a uniform-amplitude, equiphase distribution." Key to understanding these definitions is that "maximum" directivity refers to the direction of maximum radiation intensity, i.e., the main lobe. Therefore, illumination efficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's gain is a key performance parameter which combines the antenna's directivity and radiation efficiency. The term ''power gain'' has been deprecated by IEEE. In a transmitting antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction. In a receiving antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts radio waves arriving from a specified direction into electrical power. When no direction is specified, gain is understood to refer to the peak value of the gain, the gain in the direction of the antenna's main lobe. A plot of the gain as a function of direction is called the antenna pattern or radiation pattern. It is not to be confused with directivity, which does ''not'' take an antenna's radiation efficiency into account. Gain or 'absolute gain' is defined as "The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction to the radiation intensity that would be produced if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Wave
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations. Water waves are an example of transverse wave. A simple example is given by the waves that can be created on a horizontal length of string by anchoring one end and moving the other end up and down. Another example is the waves that are created on the membrane of a drum. The waves propagate in directions that are parallel to the membrane plane, but each point in the membrane itself gets displaced up and down, perpendicular to that plane. Light is another example of a transverse wave, where the oscillations are the electric and magnetic fields, which point at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the direction of propagation. Transverse waves commonly occur in elastic solids due to the shear stress generated; the oscillations in this case are the displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)