|
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet transplantation is the transplantation of isolated islets from a donor pancreas into another person. It is an experimental treatment for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Once transplanted, the islets begin to produce insulin, actively regulating the level of glucose in the blood. Islets are usually infused into the person's liver. If the cells are not from a genetically identical donor the person's body will recognize them as foreign and the immune system will begin to attack them as with any transplant rejection. To prevent this immunosuppressant drugs are used. A study from 2005 showed that islet transplantation has progressed to the point that 58% of the people were insulin independent one year after the operation. A review published 2016 reported a 50 – 70% rate of insulin independence after five years, in five studies from leading transplant centers published 2005 – 2012. In the period from 1999 to 2004, 471 people with type 1 diabetes received islet transplants at 43 inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, Liver transplantation, liver, Lung transplantation, lungs, Pancreas transplantation, pancreas, Intestinal transplant, intestine, Thymus transplantation, thymus and uterus transplantation, uterus. Tissues include Bone grafting, bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneal transplantation, corneae, skin grafting, skin, Artificial heart valve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways (local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle power) also can be achieved. Examples Short Duration & Low Potency Procaine Chloroprocaine Medium Duration & Potency Lidocaine Prilocaine High Duration & Potency Tetracaine Bupivacaine Cinchocaine Ropivacaine Clinical LAs belong to one of two classes: aminoamide and aminoester local anesthetics. Synthetic LAs are structurally related to cocaine. They differ from cocaine mainly in that they have a very low abuse potential and do not produce hypertension or (with few exceptions) vasoconstriction. They are used in various techniques of local anesthesia such as: * Topical anesthesia (surface) * Topical administration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of such a condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
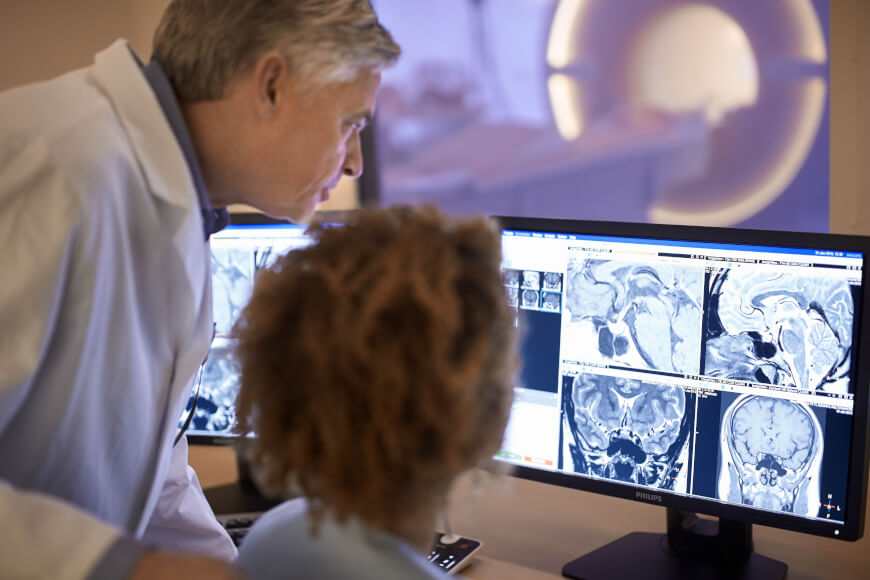
Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Because of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Duct
The pancreatic duct, or duct of Wirsung (also, the major pancreatic duct due to the existence of an accessory pancreatic duct), is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine pancreas, which aids in digestion. Structure The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct just prior to the ampulla of Vater, after which both ducts perforate the medial side of the second portion of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla. There are many anatomical variants reported, but these are quite rare. Accessory pancreatic duct Most people have just one pancreatic duct. However, some have an additional accessory pancreatic duct, also called the Duct of Santorini. An accessory pancreatic duct can be functional or non-functional. It may open separately into the second part of the duodenum,Moore KL, Dalley AF. 2006. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 5th Ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p 287.1. Mchonde GJ, Gesase AP. Termination patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagenase
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as ''Clostridium''. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of gas gangrene. They normally target the connective tissue in muscle cells and other body organs. Collagen, a key component of the animal extracellular matrix, is made through cleavage of pro-collagen by collagenase once it has been secreted from the cell. This stops large structures from forming inside the cell itself. In addition to being produced by some bacteria, collagenase can be made by the body as part of its normal immune response. This production is induced by cytokines, which stimulate cells such as fibroblasts and osteoblasts, and can cause indirect tissue damage. Therapeutic uses Collagenases have been approved for medical uses for: * treatment of Dupuytren's contracture and Peyronie's disease (Xiaflex). * wound healing (Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islet Transplantation PLoS Medicine
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanent or tidal (i.e. surfaced reef or seamount); and may exist in the sea, lakes, rivers or any other sizeable bodies of water. Definition As suggested by its origin ''islette'', an Old French diminutive of "isle", use of the term implies small size, but little attention is given to drawing an upper limit on its applicability. The World Landforms website says, "An islet landform is generally considered to be a rock or small island that has little vegetation and cannot sustain human habitation", and further that size may vary from a few square feet to several square miles, with no specific rule pertaining to size. Other terms * Ait (/eɪt/, like eight) or eyot (/aɪ(ə)t, eɪt/), a small island. It is especially used to refer to riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Diabetic hypoglycemia is a low blood glucose level occurring in a person with diabetes mellitus. It is one of the most common types of hypoglycemia seen in emergency departments and hospitals. According to the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP), and based on a sample examined between 2004 and 2005, an estimated 55,819 cases (8.0% of total admissions) involved insulin, and severe hypoglycemia is likely the single most common event. In general, hypoglycemia occurs when a treatment to lower the elevated blood glucose of diabetes inaccurately matches the body's physiological need, and therefore causes the glucose to fall to a below-normal level. Signs and symptoms Diabetic hypoglycemia can be mild, recognized easily by the patient, and reversed with a small amount of carbohydrates eaten or drunk, or it may be severe enough to cause unconsciousness requiring intravenous dextrose or an injection of glucagon. Severe hypoglycemic unconsciou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |