|
Isaac Galland
Isaac Galland (May 15, 1791 – September 27, 1858) was a merchant, postmaster, land speculator, and doctor. He is best known for selling large tracts of land around Commerce, Illinois, to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in 1839. Early life Galland was born in Somerset, Pennsylvania on May 15, 1791, to Matthew Galland and Hannah Fenno during their move from Norfolk, Virginia, to the Western frontier. He was the second of five children. His siblings were Abel (March 9, 1787 – 1857), Matthew Jr. (1794–1812), David (May 10, 1795 – November 26, 1872), and Mary (Polly) (September 8, 1798 – April 27, 1870). Shortly after his birth, his family relocated to land near Marietta, Ohio, which was located in Ohio's Donation Tract. "The remote location of the Galland homestead did not hinder Isaac's education, since his mother, an educated woman, took on the responsibility of teaching him as much as she could until he was thirteen." Although little is known of his tee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oquawka, Illinois
Oquawka is a village in Henderson County, Illinois, Henderson County, Illinois, United States. The population was 1,371 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Henderson County. Oquawka is part of the Burlington, Iowa, Burlington, Iowa, IA–IL Burlington micropolitan area, Micropolitan Statistical Area. Geography Oquawka is located at (40.938880, -90.949044). According to the 2010 census, Oquawka has a total area of , of which (or 79.07%) is land and (or 20.93%) is water. Demographics 2010 census As of the censusProfile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-17-08 of 2010, there were 1,371 people, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder (Latter Day Saints)
Elder is a priesthood office in the Melchizedek priesthood of denominations within the Latter Day Saint movement, including the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). LDS Church Office of the Melchizedek Priesthood In the LDS Church, "elder" is considered the introductory—or lowest—of five offices of the Melchizedek priesthood. Every person who receives the Melchizedek priesthood is simultaneously ordained to the office of elder; this may be done to male members who are at least 18 years old. In order to be ordained, the member must be determined to be worthy by his local bishop and stake president."Ordinance and Blessing Policies", '' Handbook 1: Stake Presidents and Bishops'' (Salt Lake City, Utah: LDS Church, 2010) § 16. The consent of the priesthood holders of the stake is also required before the ordination is performed, and this is usually done at a semiannual stake conference or an annual general stake priesthood meeting. Ordination is accomplis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauvoo, Illinois
Nauvoo ( ; from the ) is a small city in Hancock County, Illinois, United States, on the Mississippi River near Fort Madison, Iowa. The population of Nauvoo was 950 at the 2020 census. Nauvoo attracts visitors for its historic importance and its religious significance to members of several groups: The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints; the Community of Christ, formerly the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS); other groups stemming from the Latter Day Saint movement; and the Icarians. The city and its immediate surrounding area are listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Nauvoo Historic District. History The area of Nauvoo was first called Quashquema, named in honor of the Native American chief who headed a Sauk and Fox settlement numbering nearly 500 lodges. By 1827, white settlers had built cabins in the area. By 1829 this area of Hancock County had grown sufficiently so that a post office was needed and in 1832 the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, he had attracted tens of thousands of followers and founded a religion that continues to the present with millions of global adherents. Smith was born in Sharon, Vermont. By 1817, he had moved with his family to Western New York, the site of intense religious revivalism during the Second Great Awakening. Smith said he experienced a series of visions, including one in 1820 during which he saw "two personages" (whom he eventually described as God the Father and Jesus Christ), and another in 1823 in which an angel directed him to a buried book of golden plates inscribed with a Judeo-Christian history of an ancient American civilization. In 1830, Smith published what he said was an English translation of these plates called the ''Book of Mormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was initially chosen as the capital of the territory. In 1837, the territorial legislature met in Burlington, just north of the Skunk River on the Mississippi, which became part of the Iowa Territory in 1838. In that year, 1838, the territorial capital of Wisconsin was moved to Madison. Territorial area The Wisconsin Territory initially included all of the present-day states of Wisconsin, Minnesota, and Iowa, and part of the Dakotas east of the Missouri River. Much of the territory had originally been part of the Northwest Territory, which was ceded by Britain in 1783. The portion in what is now Iowa and the Dakotas was originally part of the Louisiana Purchase and was split off from the Missouri Territory in 1821 and attached to the Michi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keokuk, Iowa
Keokuk is a city in and a county seat of Lee County, Iowa, United States, along with Fort Madison. It is Iowa's southernmost city. The population was 9,900 at the time of the 2020 census. The city is named after the Sauk chief Keokuk, who is thought to be buried in Rand Park. It is in the extreme southeast corner of Iowa, where the Des Moines River meets the Mississippi. It is at the junction of U.S. Routes 61, 136 and 218. Just across the rivers are the towns of Hamilton and Warsaw, Illinois, and Alexandria, Missouri. Keokuk, along with the city of Fort Madison, is a principal city of the Fort Madison-Keokuk micropolitan area, which includes all of Lee County, Iowa, Hancock County, Illinois and Clark County, Missouri. History Situated between the Des Moines and Mississippi rivers, the area that became Keokuk had access to a large trading area and was an ideal location for settlers. In 1820, the US Army prohibited soldiers stationed along the Mississippi River from havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
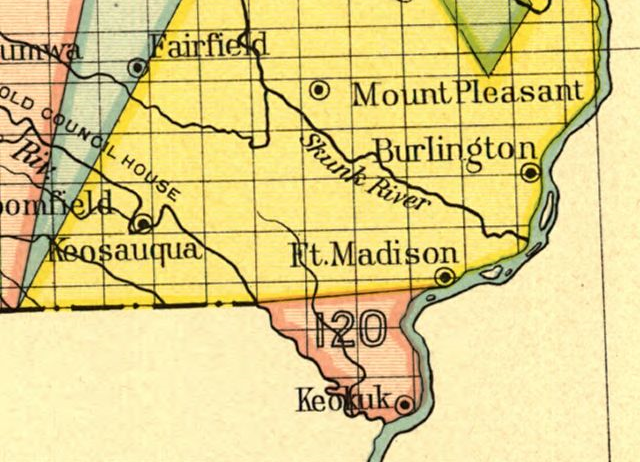
Half-Breed Tract
A Half-Breed Tract was a segment of land designated in the western states by the United States government in the 19th century specifically for Métis of American Indian and European or European-American ancestry, at the time commonly known as half-breeds. The government set aside such tracts in several parts of the Midwestern prairie region, including in Iowa Territory, Nebraska Territory, Kansas Territory, Minnesota Territory, and Wisconsin Territory. Overview Historically, the mixed-blood population in the ''Pays d'en Haut'' region surrounding the Great Lakes were typically the descendants of Native American women and White men, often men of French-Canadian or Scots (including Orcadian) origin, who dominated early fur trapping and trade. These men lived far from other Europeans. Others had fathers who were American trappers and traders. The children typically grew up in their mother's tribes, where the fathers and families were offered protection if not full membership. As r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Historical Museum Of Iowa
The State Historical Society of Iowa (SHSI), a division of the Iowa Department of Cultural Affairs, serves as the official historical repository for the State of Iowa and also provides grants, public education, and outreach about Iowa history and archaeology. The SHSI maintains a museum, library, archives, and research center in Des Moines and a research library in Iowa City, as well as several historic sites in Iowa. It was founded in 1857 in Iowa City, where it was first affiliated with the University of Iowa. As the organization grew in size and collections, it became a separate state agency headquartered near the Iowa Capitol in Des Moines. SHSI publications The SHSI currently publishes the ''Annals of Iowa''. In the past it published the ''Iowa Heritage Illustrated'', ''Goldfinch'', the ''Iowa Journal of History and Politics'', and the ''Iowa Historical Record''. It also currently produces an e-newsletter, the ''Iowa Historian''. State and federal regulation The SHSI is pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Caleb Bingham
George Caleb Bingham (March 20, 1811 – July 7, 1879) was an American artist, soldier and politician known in his lifetime as "the Missouri Artist". Initially a Whig Party (United States), Whig, he was elected as a delegate to the Missouri legislature before the American Civil War where he fought against the extension of slavery westward. During that war, although born in Virginia, Bingham was dedicated to the Union cause and became captain of a volunteer company which helped keep the state from joining the Confederacy, and then served four years as State Treasurer of Missouri, Missouri's Treasurer. During his final years, Bingham held several offices in Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, while also serving as Missouri's Adjutant General. His paintings of American frontier life along the Missouri River exemplify the Luminism (American art style), Luminist style.EM Bloch (1986) ''The Paintings of George Caleb Bingham: A Catalog Raissoné'', University of Missouri Press. Early life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw, Illinois
Warsaw is a city in Hancock County, Illinois, United States. The population was 1,607 at the 2010 census, a decline from 1,793 in 2000. The city is notable for its historic downtown and the Warsaw Brewery, which operated for more than 100 years beginning in 1861 and, after renovation, reopened as a bar, restaurant and microbrewery in 2006. History The city of Warsaw began in 1812, when young Major Zachary Taylor founded Fort Edwards on the eastern bank of the Mississippi River across from the mouth of the Des Moines River. Fort Johnson was occupied only for a few weeks before it was burned. In 1815 another military camp, Fort Edwards, was built nearby at a different location. Warsaw became an important fur trading post and one of the earliest American settlements in northern Illinois. During the 1840s, Warsaw was a center of opposition to Mormon settlement in Nauvoo and other areas in Hancock County during the conflict sometimes known as the " Mormon Illinois War". The local ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Johnson
Fort Johnson was a U.S. Army post built on bluffs overlooking the Mississippi River in modern-day Warsaw, Illinois, during the War of 1812. The fort was established in September 1814 by Major Zachary Taylor, future 12th President of the United States (1849-1850). Troops retreating from the Battle of Credit Island constructed the fort after effectively surrendering control of the upper Mississippi to the British and allied Indian tribes, including the Sauk. The fort, which held a full company of men, was completed in just a few weeks, and had a commanding view of the Mississippi valley, the mouth of the Des Moines River, and the foot of the Des Moines Rapids. Because of the chaotic situation along the Mississippi River frontier, the fort was abandoned in late October 1814 after provisions ran out. The company retreated to Cap au Gris near St. Louis. Black Hawk described the founding of the fort and a skirmish in his autobiography: A party of braves followed to watch where they lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |