|
Iron Response Element
In molecular biology, the iron response element or iron-responsive element (IRE) is a short conserved stem-loop which is bound by iron response proteins (IRPs, also named IRE-BP or IRBP). The IRE is found in UTRs (untranslated regions) of various mRNAs whose products are involved in iron metabolism. For example, the mRNA of ferritin (an iron storage protein) contains one IRE in its 5' UTR. When iron concentration is low, IRPs bind the IRE in the ferritin mRNA and cause reduced translation rates. In contrast, binding to multiple IREs in the 3' UTR of the transferrin receptor (involved in iron acquisition) leads to increased mRNA stability. Mechanism of action The two leading theories describe how iron probably interacts to impact posttranslational control of transcription. The classical theory suggests that IRPs, in the absence of iron, bind avidly to the mRNA IRE. When iron is present, it interacts with the protein to cause it to release the mRNA. For example, In high iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Biochemistry And Molecular Biology
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. Insect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
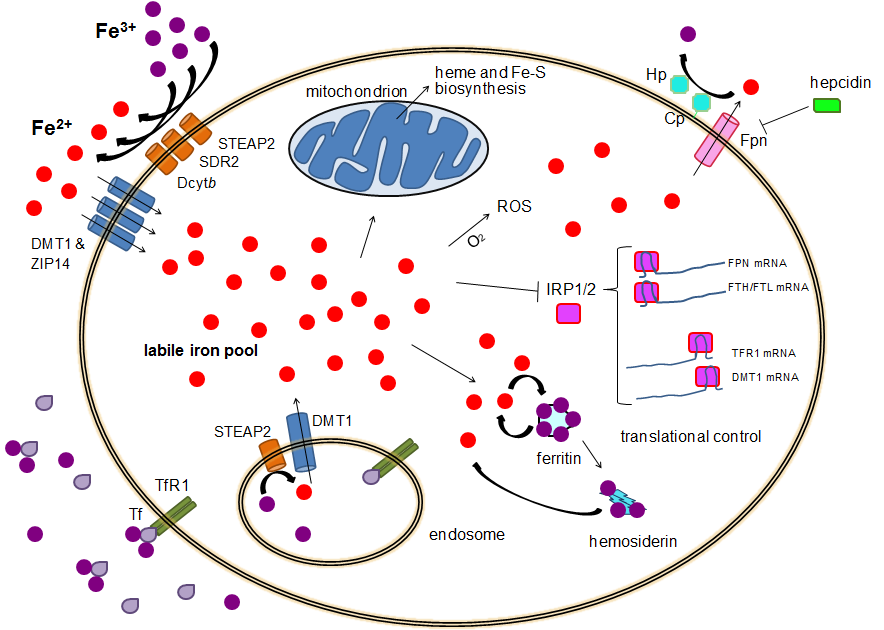
SLC40A1
Ferroportin-1, also known as solute carrier family 40 member 1 (SLC40A1) or iron-regulated transporter 1 (IREG1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC40A1'' gene, and is part of the Ferroportin (Fpn) FamilyTC# 2.A.100. Ferroportin is a transmembrane protein that transports iron from the inside of a cell to the outside of the cell. Ferroportin is the only known iron exporter. After dietary iron is absorbed into the cells of the small intestine, ferroportin allows that iron to be transported out of those cells and into the bloodstream. Fpn also mediates the efflux of iron recycled from macrophages resident in the spleen and liver. Ferroportin is regulated by hepcidin, a hormone produced by the liver; hepcidin binds to Fpn and limits its iron-efflux activity, thereby reducing iron delivery to the blood plasma. Therefore, the interaction between Fpn and hepcidin controls systemic iron homeostasis. Structure and function Members of the ferroportin family consist of 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC11A2
Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 2 (NRAMP 2), also known as divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) and divalent cation transporter 1 (DCT1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC11A2'' (solute carrier family 11, member 2) gene. DMT1 represents a large family of orthologous metal ion transporter proteins that are highly conserved from bacteria to humans. As its name suggests, DMT1 binds a variety of divalent metals including cadmium (Cd2+), copper (Cu2+), and zinc (Zn2+,); however, it is best known for its role in transporting ferrous iron (Fe2+). DMT1 expression is regulated by body iron stores to maintain iron homeostasis. DMT1 is also important in the absorption and transport of manganese (Mn2+). In the digestive tract, it is located on the apical membrane of enterocytes, where it carries out H+-coupled transport of divalent metal cations from the intestinal lumen into the cell. Function Iron is not only essential for the human body, it is required f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
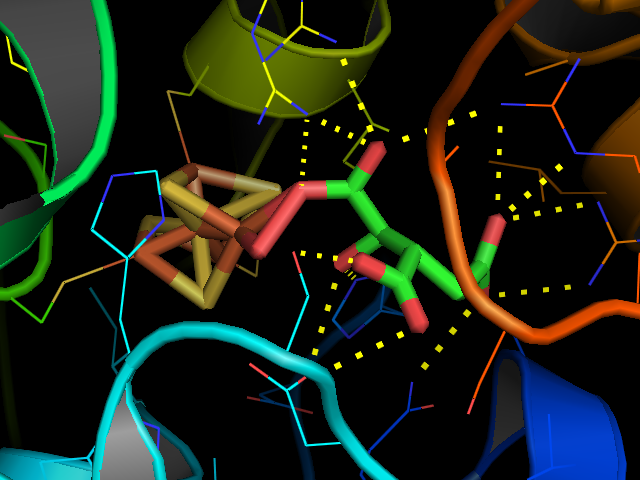
Aconitase
Aconitase (aconitate hydratase; ) is an enzyme that catalyses the stereo-specific isomerization of citrate to isocitrate via ''cis''- aconitate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, a non-redox-active process. Image:Citrate wpmp.png, Image:Cis-Aconitate wpmp.png, Image:isocitric acid.svg, Structure Aconitase, displayed in the structures in the right margin of this page, has two slightly different structures, depending on whether it is activated or inactivated. In the inactive form, its structure is divided into four domains. Counting from the N-terminus, only the first three of these domains are involved in close interactions with the Fe-4Scluster, but the active site consists of residues from all four domains, including the larger C-terminal domain. The Fe-S cluster and a anion also reside in the active site. When the enzyme is activated, it gains an additional iron atom, creating a Fe-4Scluster. However, the structure of the rest of the enzyme is nearly unchanged; the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Biological Chemistry
The ''Journal of Biological Chemistry'' (''JBC'') is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1905., jbc.org Since 1925, it is published by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. It covers research in areas of biochemistry and molecular biology. The editor is Alex Toker. As of January 2021, the journal is fully open access. In press articles are available free on its website immediately after acceptance. Editors The following individuals have served as editors of the journal: * 1906–1909: John Jacob Abel and Christian Archibald Herter * 1909–1910: Christian Archibald Herter * 1910–1914: Alfred Newton Richards * 1914–1925: Donald D. Van Slyke * 1925–1936: Stanley R. Benedict. After Benedict died, John T. Edsall served as temporary editor until the next editor was appointed. * 1937–1958: Rudolph J. Anderson * 1958–1967: John T. Edsall * 1968–1971: William Howard Stein * 1971–2011: Herbert Tabor * 2011–2015: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The EMBO Journal
''The EMBO Journal'' is a semi-monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on full-length papers describing original research of general interest in molecular biology and related areas. The editor-in-chief is Facundo D. Batista (Harvard Medical School). History The journal was established in 1982 and was published by Nature Publishing Group on behalf of the European Molecular Biology Organization until the launch of EMBO Press in 2013. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 13.783. See also *''EMBO Reports'' *''Molecular Systems Biology ''Molecular Systems Biology'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal covering systems biology at the molecular level (examples include: genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microbial systems, the integration of cell signaling and r ...'' References External links * * (1986–2003 issues from microfilm) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALAS2
Delta-aminolevulinate synthase 2 also known as ALAS2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ALAS2'' gene. ALAS2 is an aminolevulinic acid synthase. The product of this gene specifies an erythroid-specific mitochondrially located enzyme. The encoded protein catalyzes the first step in the heme biosynthetic pathway. Defects in this gene cause X-linked pyridoxine-responsive sideroblastic anemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. Its gene contains an IRE Ire or IRE may refer to: Ire * Extreme anger; intense fury * Irē, the Livonian name for Mazirbe, Latvia * A town in Oye, Nigeria * ''Ire'' (album), a 2015 album by the Australian metalcore band Parkway Drive * Ire (Iliad), a town mentioned in ... in its 5'-UTR region on which an IRP binds if the iron level is too low, thus inhibiting its translation. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFRC
Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TfR1), also known as Cluster of Differentiation 71 (CD71), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TFRC'' gene. TfR1 is required for iron import from transferrin into cells by endocytosis. Structure and function TfR1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein composed of two disulfide-linked monomers joined by two disulfide bonds. Each monomer binds one holo-transferrin molecule creating an iron-Tf-TfR complex which enters the cell by endocytosis. Clinical significance TfR1 as a potential new target in cases of human leukemia & lymphoma. InatherYs, in Évry, France, developed a candidate drug, INA01 antibody (anti-CD71) that showed efficacy in pre-clinical studies in the therapy of two incurable orphan oncohematological diseases: the adult T cell leukemia (ATLL) caused by HTLV-1 and the Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). TfR1 expressed on the endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier is used also in preclinical research to allow the delivery of large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 12.779. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the mass media, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferritin Light Chain
Ferritin light chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FTL'' gene. Ferritin is the major protein responsible for storing intracellular iron in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is a heteropolymer consisting of 24 subunits, heavy and light ferritin chains. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. It is abnormally expressed in fetuses of both IVF and ICSI, which may contribute to the increase risk of birth defects in these assisted reproductive technologies. Function Iron is extremely important in the development of neurons, transport through iron-sulfur clusters, the electron transport chain, and synthesis and breakdown of neurotransmitters. The function of the FTL is to act as both an iron reservoir and to remove excess iron from the body. Since iron plays a role in electron transfer, there is potential for the generation of free, highly toxic radicals which makes the role of the FTL as an iron detoxifier very significant. The rates of iron uptake and release may be affe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |