|
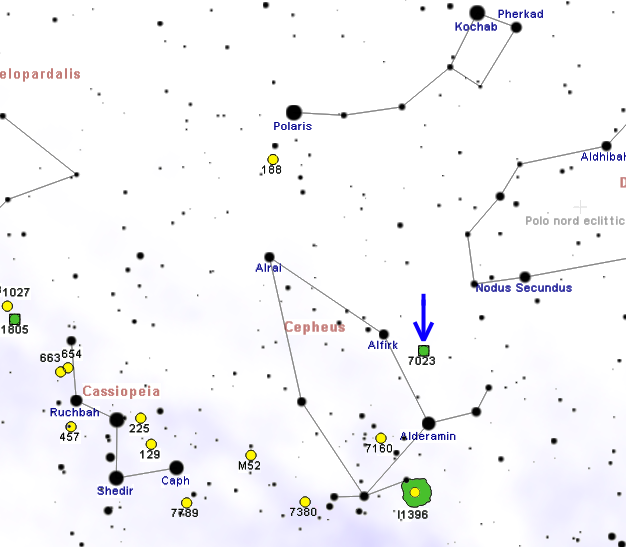
Iris Nebula
The Iris Nebula (also known as NGC 7023 and Caldwell 4) is a bright reflection nebula in the constellation Cepheus. The designation NGC 7023 refers to the open cluster within the larger reflection nebula designated LBN 487. The nebula, which shines at magnitude +6.8, is illuminated by a magnitude +7.4 star designated SAO 19158. It is located near the Mira-type variable star T Cephei, and near the bright magnitude +3.23 variable star Beta Cephei Beta Cephei (β Cephei, abbreviated Beta Cep, β Cep) is a triple star system of the third magnitude in the constellation of Cepheus. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 690 light-y ... (Alfirk). It lies 1,300 light-years away and is six light-years across. Notes References * * External links * SEDS – NGC 7023VizieR – NGC 7023NED – NGC 7023Dark Atmospheres Photography – Iris Nebula NGC 7023See NGC 7023 in WorldWide Telescope {{DEFAULTSORT:Iris N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheus (constellation)
Cepheus is a constellation in the far northern sky, named after Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the second century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 constellations in the modern times. The constellation's brightest star is Alpha Cephei, with an apparent magnitude of 2.5. Delta Cephei is the prototype of an important class of star known as a Cepheid variable. RW Cephei, an orange hypergiant, together with the red supergiants Mu Cephei, MY Cephei, SW Cephei, VV Cephei, and V354 Cephei are among the largest stars known. In addition, Cepheus also has the hyperluminous quasar S5 0014+81, which hosts an ultramassive black hole in its core, reported at 40 billion solar masses, about 10,000 times more massive than the central black hole of the Milky Way, making this among the most massive black holes currently known. This paper does acknowledge the possibility of an optical illusion that would cause an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldwell Catalogue
The Caldwell catalogue is an astronomical catalogue of 109 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers. The list was compiled by Patrick Moore as a complement to the Messier catalogue. While the Messier catalogue is used by amateur astronomers as a list of deep-sky objects for observation, Moore noted that Messier's list was not compiled for that purpose and excluded many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, such as the Hyades, the Double Cluster ( NGC 869 and NGC 884), and the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253). The Messier catalogue was actually compiled as a list of known objects that might be confused with comets. Moore also observed that since Messier compiled his list from observations in Paris, it did not include bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere, such as Omega Centauri, Centaurus A, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae. Moore compiled a list of 109 objects to match the commonly accepted number of Messier objects (he exclud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collinder Catalogue
In astronomy, the Collinder catalogue is a catalogue of 471 open clusters by Swedish astronomer Per Collinder. It was published in 1931 as an appendix to Collinder's paper ''On structural properties of open galactic clusters and their spatial distribution''. Catalogue objects are denoted by ''Collinder'', e.g. "Collinder 399". Dated prefixes include as ''Col + catalogue number'', or ''Cr + catalogue number'', e.g. "Cr 399". Vital statistics * The catalogue contains 471 objects: 452 open clusters, 11 globular clusters, 6 Asterism (astronomy), asterisms, 1 Stellar kinematics#Moving groups, stellar moving group, and 1 Stellar kinematics#Stellar associations, stellar association. * Objects are spread out across the entire celestial sphere. * NGC 188, Cr 8 is the northernmost Collinder object, located at a declination of +85º in the constellation Camelopardalis. * Cr 411 is the southernmost Collinder object, located at a declination of -79º in the constellation Octans. Collinder obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Nebula
Reflection or reflexion may refer to: Science and technology * Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon ** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface *** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water ** Signal reflection, in signal transmission * Elastic scattering, a process in nuclear and particle physics * Reflection nebula, a nebula that is extended and has no boundaries * Reflection seismology or seismic reflection, a method of exploration geophysics Mathematics * Reflection principle, in set theory * Point reflection, a reflection across a point * Reflection (mathematics), a transformation of a space * Reflection formula, a relation in a function * Reflective subcategory, in category theory Computing * Reflection (computer graphics), simulation of reflective surfaces * Reflection (computer programming), a program that accesses or modifies its own code * Reflection, terminal emulation software by Attachmate Arts and entertainment Film and television * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravity, gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the Galactic Center. This can result in a migration to the main body of the galaxy and a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral galaxy, spiral and irregular galaxy, irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mira Variable
Mira variables (named for the prototype star Mira) are a class of pulsating stars characterized by very red colours, pulsation periods longer than 100 days, and amplitudes greater than one magnitude in infrared and 2.5 magnitude at visual wavelengths. They are red giants in the very late stages of stellar evolution, on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), that will expel their outer envelopes as planetary nebulae and become white dwarfs within a few million years. Mira variables are stars massive enough that they have undergone helium fusion in their cores but are less than two solar masses, stars that have already lost about half their initial mass. However, they can be thousands of times more luminous than the Sun due to their very large distended envelopes. They are pulsating due to the entire star expanding and contracting. This produces a change in temperature along with radius, both of which factors cause the variation in luminosity. The pulsation depends on the mass and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cephei
T, or t, is the twentieth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''tee'' (pronounced ), plural ''tees''. It is derived from the Semitic Taw 𐤕 of the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician and Paleo-Hebrew script (Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic and Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew Taw ת/𐡕/, Syriac alphabet, Syriac Taw ܬ, and Arabic script, Arabic ت Tāʼ) via the Greek letter tau, τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most commonly used letter in English-language texts. History ''Taw'' was the last letter of the Western Semitic alphabets, Semitic and Hebrew alphabets. The sound value of Semitic ''Taw'', Greek alphabet Tαυ (''Tau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cephei
Beta Cephei (β Cephei, abbreviated Beta Cep, β Cep) is a triple star system of the third magnitude in the constellation of Cepheus. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 690 light-years distant from the Sun. It is the prototype of the Beta Cephei variable stars. It consists of a binary pair (designated Beta Cephei A) together with a third companion (B). The binary's two components are themselves designated Beta Cephei Aa (officially named Alfirk , the traditional name for the system) and Ab. Nomenclature ''β Cephei'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Cephei'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as ''Beta Cephei A'' and ''B'', and those of ''A's'' components - ''Beta Cephei Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Beta Cephei bore the traditional na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |