|
Irbit Fair
{{Unreferenced, date=March 2009 The Irbit fair (Russian: Ирби́тская я́рмарка, ''irbitskaya yarmarka'') was the second largest fair in Imperial Russia after the Makariev Fair. It was held annually in winter, trading with tea and fur brought along the Siberian trakt from Asia. As Thomas Wallace Knox (1835–96) writes in his book ''Overland through Asia; Pictures of Siberian, Chinese, and Tatar Life'' (1870): :We met many sledges laden with goods en route to the fair which takes place every February at Irbit. This fair is of great importance to Siberia, and attracts merchants from all the region west of Tomsk. From forty to fifty million rubles worth of goods are exchanged there during the four weeks devoted to traffic. The commodities from Siberia are chiefly furs and tea, those from Europe comprise a great many articles. Irbit is on the Asiatic side of the Ural mountains, about two hundred versts northeast of Ekaterineburg. It is a place of little consequence e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irbit - Fur Market
Irbit (russian: Ирби́тStress is given per the ''Dictionary of modern geographical names'', entry o().) is a town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located from Yekaterinburg by train or by car, on the right bank of the Nitsa. Population: It was previously known as ''Irbeyevskaya Sloboda'' (until 1662). History Founded in 1631 as Irbeyevskaya Sloboda (),''Geographical names of the Urals: Short Toponymic Dictionary'' () its name was changed in 1662 to Irbit. It was granted official town status by Catherine the Great in 1775 for the town's loyalty to the Empress during the Pugachev uprising of 1773–1774. In 1776, she awarded the town its official crest. In the 19th century, the Irbit Fair was an important event for the trade in Siberian fur and Chinese tea. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of the administrative divisions, Irbit serves as the administrative center of Irbitsky District, even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitsa River
The Nitsa () is a river in the Sverdlovsk Oblast in Russia. It is a tributary of the Tura. The river commences at the confluence of the Neyva and the Rezh, east of the city Alapayevsk and flows firstly in an easterly and then in southeasterly direction. It is long. However, if the Nitsa and Neyva are counted as one, the river is long. It has a drainage basin of . The Nitsa converges with the Tura at Ust-Nitsinskoye. The river has a mixed supply, which is dominated by snow. The discharge downstream from the start, at the city of Irbit, is . The river is usually frozen by the end of October, beginning of November until the end of April. The river is navigable along its entire length. The most important tributary is the Irbit Irbit (russian: Ирби́тStress is given per the ''Dictionary of modern geographical names'', entry o().) is a town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located from Yekaterinburg by train or by car, on the right bank of the Nitsa. Population: ..., whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Sverdlovsk Oblast
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irbitsky Uyezd
Irbitsky Uyezd (''Ирбитский уезд'') was one of the subdivisions of the Perm Governorate of the Russian Empire. It was situated in the southeastern part of the governorate. Its administrative centre was Irbit. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Irbitsky Uyezd had a population of 159,068. Of these, 98.1% spoke Russian, 1.1% Tatar, 0.2% Bashkir, 0.2% Mansi, 0.1% Yiddish Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ... and 0.1% Komi-Zyrian as their native language. References Uezds of Perm Governorate History of Sverdlovsk Oblast {{Russia-gov-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Fairs In Russia
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market. An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchange of goods and services for other goods and services, i.e. trading things without the use of money. Modern traders generally negotiate through a medium of exchange, such as money. As a result, buying can be separated from selling, or earning. The invention of money (and letter of credit, paper money, and non-physical money) greatly simplified and promoted trade. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade. In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labour, a predominant form of economic activity in which individuals and groups concentrate on a small aspect of production, but use their output in trades for other products and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Fairs , in biology
{{disambiguation ...
Annual may refer to: *Annual publication, periodical publications appearing regularly once per year **Yearbook **Literary annual *Annual plant *Annual report *Annual giving *Annual, Morocco, a settlement in northeastern Morocco *Annuals (band), a musical group See also * Annual Review (other) * Circannual cycle A circannual cycle is a biological process that occurs in living creatures over the period of approximately one year. This cycle was first discovered by Ebo Gwinner and Canadian biologist Ted Pengelley. It is classified as an Infradian rhythm, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Siberia
The early history of Siberia was greatly influenced by the sophisticated nomadic civilizations of the Scythians ( Pazyryk) on the west of the Ural Mountains and Xiongnu ( Noin-Ula) on the east of the Urals, both flourishing before the Christian era. The steppes of Siberia were occupied by a succession of nomadic peoples, including the Khitan people, various Turkic peoples, and the Mongol Empire. In the Late Middle Ages, Tibetan Buddhism spread into the areas south of Lake Baikal. During the Russian Empire, Siberia was chiefly developed as an agricultural province. The government also used it as a place of exile, sending Avvakum, Dostoevsky, and the Decemberists, among others, to work camps in the region. During the 19th century, the Trans-Siberian Railway was constructed, supporting industrialization. This was also aided by discovery and exploitation of vast reserves of Siberian mineral resources. Prehistory and antiquity According to the field of genetic genealogy, people f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of Russia
After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and collapse of Soviet Russia's controlled economy, a new Russian Federation was created under Boris Yeltsin in 1991. The Russian Federation had multiple economic reforms, including privatization and market and trade liberalization due to the collapse of communism. The economy is much more stable than in the early 1990s, but inflation still remains an issue for Russia. Historically and currently, the Russian economy has differed sharply from major developed economies in terms of a weak legal system, underdevelopment of modern economic activities, technological backwardness, and lower living standards. Historical background For about 69 years, the Russian economy and that of the rest of the Soviet Union operated on the basis of a centrally planned economy, with a state control over virtually all means of production and over investment, production, and consumption decisions throughout the economy. Economic policy was made accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Pasternak
Boris Leonidovich Pasternak (; rus, Бори́с Леони́дович Пастерна́к, p=bɐˈrʲis lʲɪɐˈnʲidəvʲɪtɕ pəstɛrˈnak; 30 May 1960) was a Russian poet, novelist, composer and literary translator. Composed in 1917, Pasternak's first book of poems, ''My Sister, Life'', was published in Berlin in 1922 and soon became an important collection in the Russian language. Pasternak's translations of stage plays by Goethe, Schiller, Calderón de la Barca and Shakespeare remain very popular with Russian audiences. Pasternak is the author of ''Doctor Zhivago'' (1957), a novel that takes place between the Russian Revolution of 1905 and the Second World War. ''Doctor Zhivago'' was rejected for publication in the USSR, but the manuscript was smuggled to Italy and was first published there in 1957. Pasternak was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1958, an event that enraged the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, which forced him to decline the prize. In 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
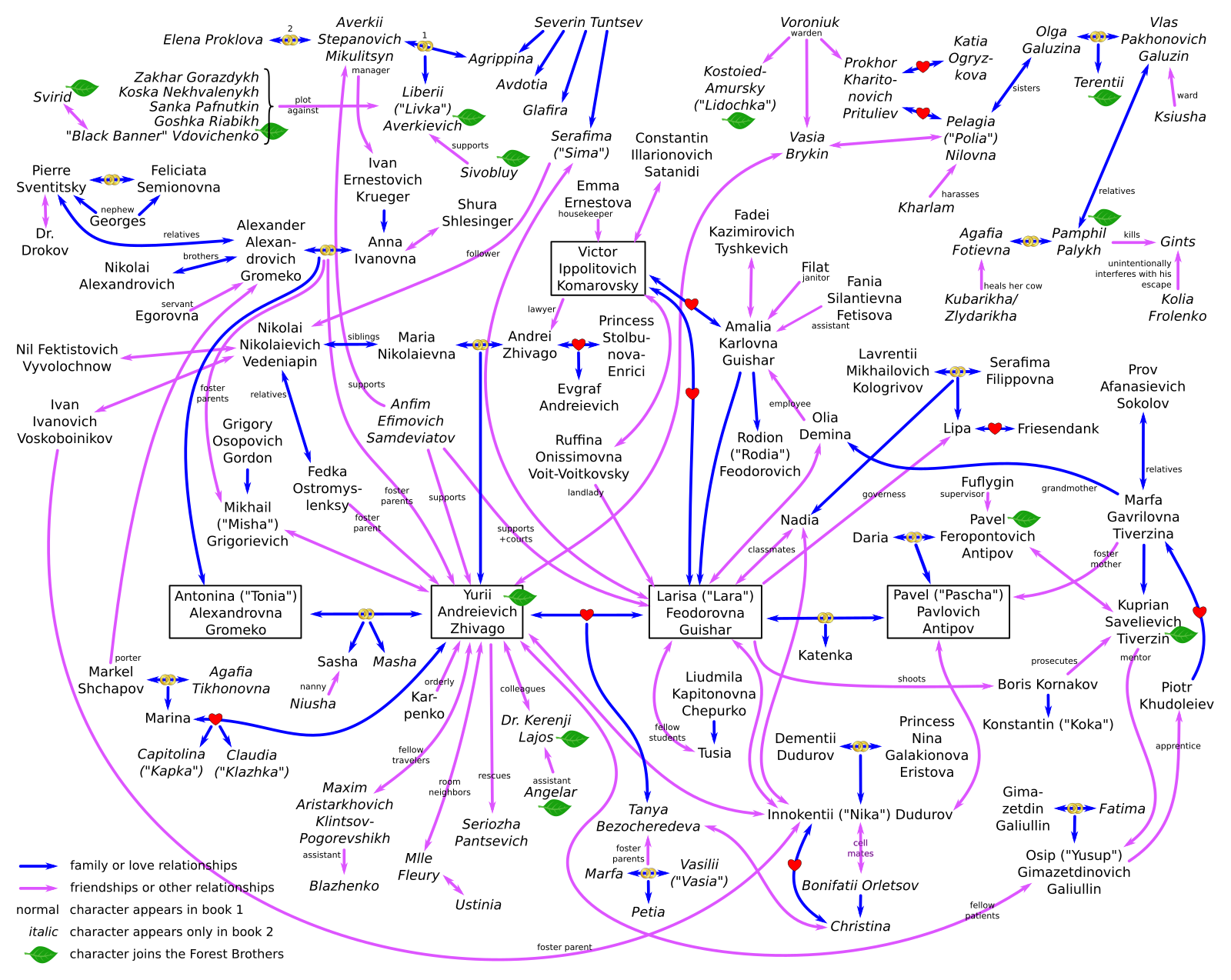
Doctor Zhivago (novel)
''Doctor Zhivago'' ( ; rus, До́ктор Жива́го, p=ˈdoktər ʐɨˈvaɡə) is a novel by Boris Pasternak, first published in 1957 in Italy. The novel is named after its protagonist, Yuri Zhivago, a physician and poet, and takes place between the Russian Revolution of 1905 and World War II. Owing to the author's independent-minded stance on the October Revolution, ''Doctor Zhivago'' was refused publication in the USSR. At the instigation of Giangiacomo Feltrinelli, the manuscript was smuggled to Milan and published in 1957. Pasternak was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature the following year, an event that embarrassed and enraged the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. The novel was made into a film by David Lean in 1965, and since then has twice been adapted for television, most recently as a miniseries for Russian TV in 2006. The novel ''Doctor Zhivago'' has been part of the Russian school curriculum since 2003, where it is read in 11th grade. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |