|
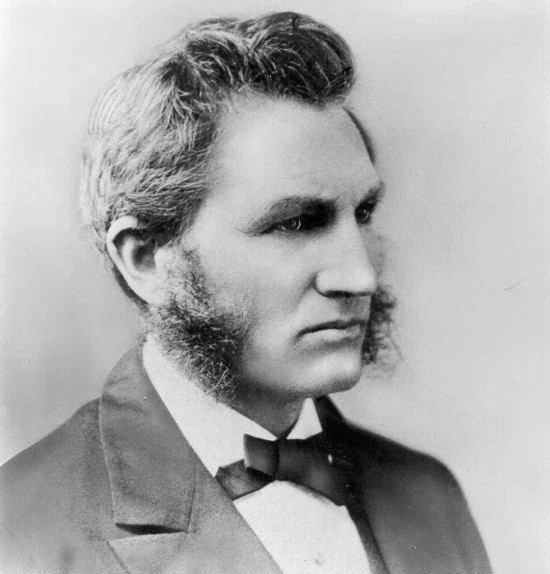
Ira De A. Reid
Ira De Augustine Reid (July 2, 1901 – August 15, 1968) was a prominent sociologist and writer who wrote extensively on the lives of black immigrants and communities in the United States. He was also influential in the field of educational sociology. He held faculty appointments at Atlanta University, New York University, and Haverford College, one of very few African American faculty members in the United States at white institutions during the era of " separate but equal." Biography Personal life Reid was born in Clifton Forge, Virginia, the son of a Baptist minister, but grew up in Harrisburg and Germantown, Philadelphia. He attended integrated public schools. While at the University of Pittsburgh, Reid met and wed Gladys Russell Scott, with whom he adopted a child. In 1950, Reid and his wife joined the Society of Friends, in which Reid was very active with educational works. Gladys Russell Scott died in 1956 and Reid remarried, to Anna "Anne" Margaret Cooke in 1958. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntington, West Virginia
Huntington is a city in Cabell and Wayne counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. It is the county seat of Cabell County, and the largest city in the Huntington–Ashland metropolitan area, sometimes referred to as the Tri-State Area. A historic and bustling city of commerce and heavy industry, Huntington has benefited from its location on the Ohio River at the mouth of the Guyandotte River. It is home to the Port of Huntington Tri-State, the second-busiest inland port in the United States. As of the 2020 census, its metro area is the largest in West Virginia, spanning seven counties across three states and having a population of 359,862. Huntington is the second-largest city in West Virginia, with a population of 46,842 at the 2020 census. Both the city and metropolitan area declined in population from the 2010 census, a trend that has been ongoing for six decades as Huntington has lost over 40,000 residents in that time frame. Surrounded by extensive natural resources, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen H
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Attorney For The District Of Maryland
The U.S. Attorney for the District of Maryland is the chief federal law enforcement officer for the State of Maryland. Since October 2021, the United States Attorney for the District of Maryland is Erek Barron. The United States District Court for the District of Maryland has jurisdiction over all cases prosecuted by the U.S. Attorney. Organization The Office is organized into divisions handling civil, criminal, and civil rights matters. U.S. Attorneys for the District of Maryland *Richard Potts 1789–1792 *Zebulon Hollingsworth 1792–1806 *John Stephen 1806–1810 *Thomas Beale Dorsey 1810–1812 * Elias Glenn 1812–1824 *Nathaniel Williams 1824–1841 * Zaccheus Collins Lee 1841–1845 *William L. Marshall 1845–1850 * Zaccheus Collins Lee 1850–1853 *William M. Addison 1853–1862 *William Price 1862–1865 *William J. Jones 1865–1866 *William Price 1866–1867 *Andrew Sterett Ridgley 1867–1869 *Archibald Stirling Jr. 1869–1886 * Thomas Gordon Hayes 1886–1890 *Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown V
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors Orange (colour), orange and black. In the RGB color model used to project colors onto television screens and computer monitors, brown combines red and green. The color brown is seen widely in nature, wood, soil, human brown hair, hair color, eye color and Human skin color, skin pigmentation. Brown is the color of dark wood or rich soil. According to public opinion surveys in Europe and the United States, brown is the least favorite color of the public; it is often associated with plainness, the rustic, feces, and poverty. More positive associations include baking, warmth, wildlife, and the autumn. Etymology The term is from Old English , in origin for any dusky or dark shade of color. The first recorded use of ''brown'' as a color name in English was in 1000. The Common Germanic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schomburg Center For Research In Black Culture
The Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture is a research library of the New York Public Library (NYPL) and an archive repository for information on people of African descent worldwide. Located at 515 Malcolm X Boulevard (Lenox Avenue) between West 135th and 136th Streets in the Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, it has, almost from its inception, been an integral part of the Harlem community. It is named for Afro-Puerto Rican scholar Arturo Alfonso Schomburg. The resources of the center are broken up into five divisions, the Art and Artifacts Division, the Jean Blackwell Hutson General Research and Reference Division, the Manuscripts, Archives and Rare Books Division, the Moving Image and Recorded Sound Division, and the Photographs and Prints Division. In addition to research services, the center hosts readings, discussions, art exhibitions, and theatrical events. It is open to the general public. Early history 135th Street branch In 1901, Andrew Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Public Library
The New York Public Library (NYPL) is a public library system in New York City. With nearly 53 million items and 92 locations, the New York Public Library is the second largest public library in the United States (behind the Library of Congress) and the fourth largest in the world. It is a private, non-governmental, independently managed, nonprofit corporation operating with both private and public financing. The library has branches in the boroughs of the Bronx, Manhattan, and Staten Island and affiliations with academic and professional libraries in the New York metropolitan area. The city's other two boroughs, Brooklyn and Queens, are not served by the New York Public Library system, but rather by their respective borough library systems: the Brooklyn Public Library and the Queens Public Library. The branch libraries are open to the general public and consist of circulating libraries. The New York Public Library also has four research libraries, which are also open to the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nations, its primary duties are advising the U.S. president on international relations, administering diplomatic missions, negotiating international treaties and agreements, and representing the United States at the United Nations conference. Established in 1789 as the first administrative arm of the U.S. executive branch, the State Department is considered among the most powerful and prestigious executive agencies. It is headed by the secretary of state, who reports directly to the U.S. president and is a member of the Cabinet. Analogous to a foreign minister, the secretary of state serves as the federal government's chief diplomat and representative abroad, and is the first Cabinet official in the order of precedence and in the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McCarthy Era
McCarthyism is the practice of making false or unfounded accusations of subversion and treason, especially when related to anarchism, communism and socialism, and especially when done in a public and attention-grabbing manner. The term originally referred to the controversial practices and policies of U.S. Senator Joseph McCarthy, and has its origins in the period in the United States known as the Second Red Scare, lasting from the late 1940s through the 1950s. It was characterized by heightened political repression and persecution of left-wing individuals, and a campaign spreading fear of alleged communist and socialist influence on American institutions and of espionage by Soviet agents. After the mid-1950s, McCarthyism began to decline, mainly due to Joseph McCarthy's gradual loss of public popularity and credibility after several of his accusations were found to be false, and sustained opposition from the U.S. Supreme Court led by Chief Justice Earl Warren on human rights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Sociological Association
The American Sociological Association (ASA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to advancing the discipline and profession of sociology. Founded in December 1905 as the American Sociological Society at Johns Hopkins University by a group of fifty people, the first president of the association would be Lester Frank Ward. Today, most of its members work in academia, while around 20 percent of them work in government, business, or non-profit organizations. ASA publishes ten academic journals and magazines, along with four section journals. Among these publications, the ''American Sociological Review'' is perhaps the best known, while the newest is an open-access journal titled Socius: Sociological Research for a Dynamic World'. '' Contexts'' is one of their magazines, designed to share the study of sociology with other disciplines as well as the public. The ASA is currently the largest professional association of sociologists in the world, even larger than the International So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Sociological Society
Eastern Sociological Society is a non-profit organization with a mission of "promoting excellence in sociological scholarship and instruction". It publishes a peer-reviewed journal (Sociological Forum) and holds a yearly academic conference An academic conference or scientific conference (also congress, symposium, workshop, or meeting) is an event for researchers (not necessarily academics) to present and discuss their scholarly work. Together with academic or scientific journals an ..., the Annual Meeting of Eastern Sociological Society. External linksHomepage Sociological organizations Academic organizations based in the United States Organizations established in 1930 {{socio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Sociological Review
The ''American Sociological Review'' is a bi-monthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering all aspects of sociology. It is published by SAGE Publications on behalf of the American Sociological Association. It was established in 1936. The editors-in-chief are Arthur S. Alderson (Indiana University-Bloomington) and Dina G. Okamoto (Indiana University-Bloomington). History For its first thirty years, the American Sociological Society (now the American Sociological Association) was largely dominated by the sociology department of the University of Chicago, and the quasi-official journal of the association was Chicago's '' American Journal of Sociology''. In 1935, the executive committee of the American Sociological Society voted 5 to 4 against disestablishing the ''American Journal of Sociology'' as the official journal of society, but the measure was passed on for consideration of the general membership, which voted 2 to 1 to establish a new journal independent of Chicago: the ''Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |