|
Iota Persei
ι Persei, Latinized as Iota Persei, is a single star in the northern constellation Perseus. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.1. It is located 34 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +49 km/s. Iota Persei has a relatively high proper motion across the sky. This is a late F- or early G-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of around G0V. It is about 3–4 billion years old and is spinning slowly with a projected rotational velocity of 4 km/s. The star has 1.4 times the mass of the Sun and 1.4 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating more than double the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 5,963 K. There is a 12.4-magnitude line-of-sight companion star that is not believed to be gravitationally associated with Iota Persei. This object i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
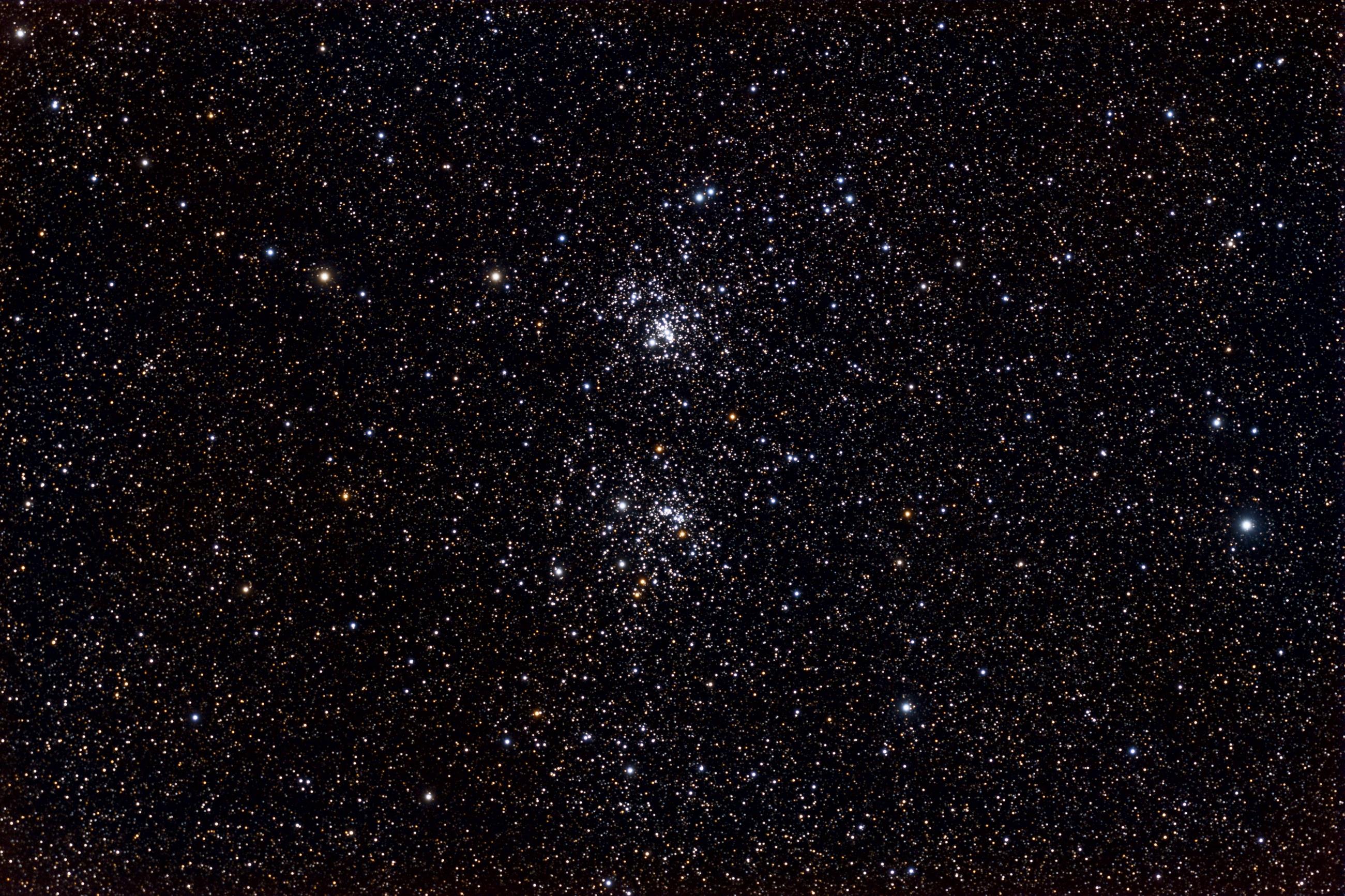
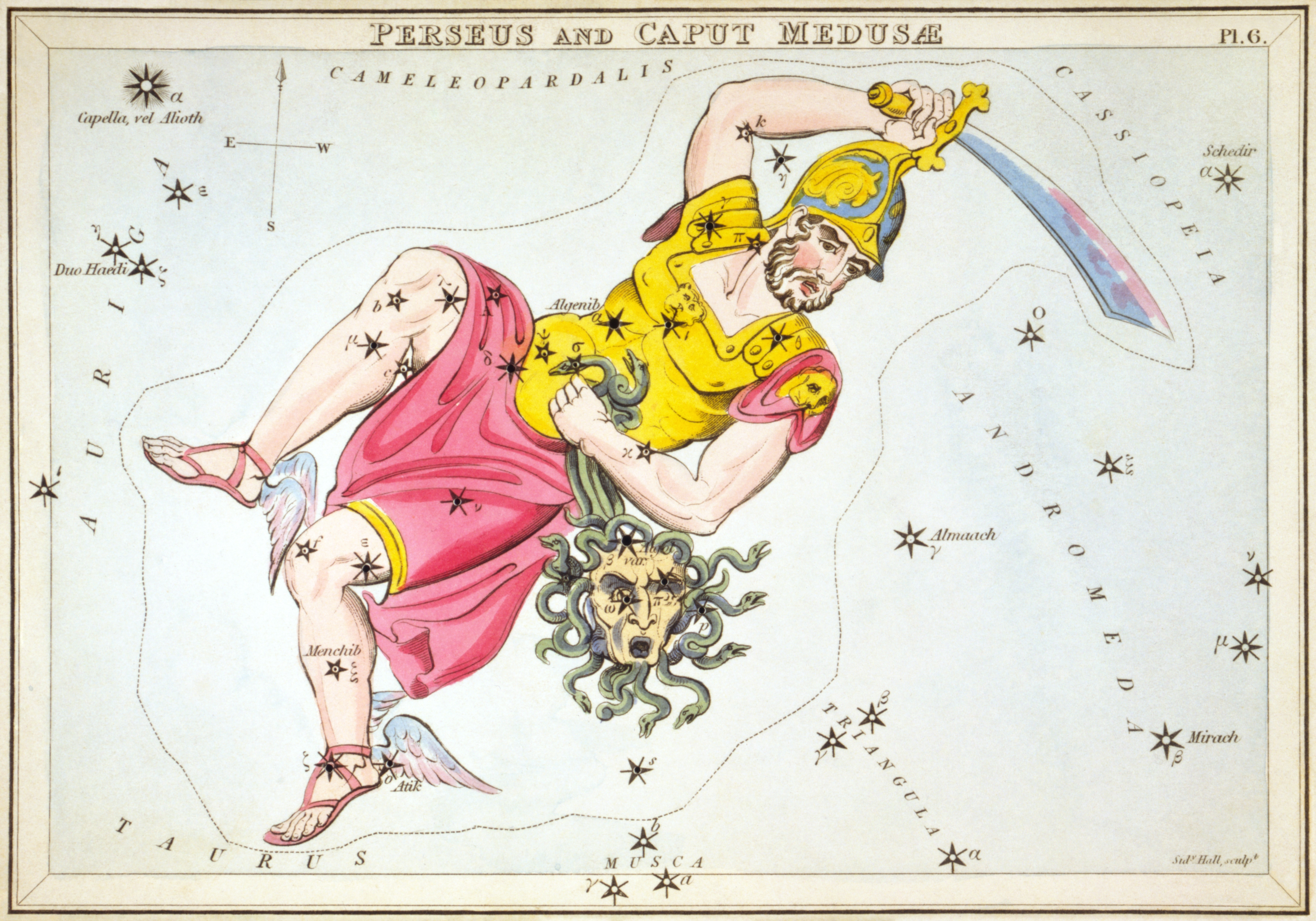
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the Northern celestial hemisphere, northern sky, being named after the Greek mythology, Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia (constellation), Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries (constellation), Aries and Taurus (constellation), Taurus to the south, Auriga (constellation), Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some Celestial cartography, star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose Asterism (astronomy), asterism was named together as ''Perseus e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16 Persei
16 Persei is a single, suspected variable star in the northern constellation of Perseus (constellation), Perseus, located approximately 121 light years away based on parallax. It is visible to the naked eye as a yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.22. This object is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +14 km/s. It displays a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of per year. Based upon a stellar classification of F2 III, this matches an aging giant star that has exhausted the hydrogen at its stellar core, core and is stellar evolution, evolving away from the main sequence. It is a possible pulsating Delta Scuti variable, although there is some uncertainty about this classification. However, Kunzli and North (1998) found no variation. The star is 1.44 billion years old with 1.8 times the mass of the Sun and 3.2 times the Sun's radius. It shows a high rotation rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Persei
Rho Persei, Latinized from ρ Persei, is a star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has the traditional name Gorgonea Tertia , being the third member of the quartet called the Gorgonea in reference to the Gorgons from the legend of Perseus. An apparent visual magnitude of +3.39 makes it visible to the naked eye, but a challenge to view from a well-lit urban environment. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of roughly from Earth. Rho Persei is a semiregular variable star, whose apparent magnitude varies between 3.3 and 4.0 with periods of 50, 120 and 250 days. The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch of its evolution. It is a bright giant star with a stellar classification of M4 II. The outer envelope has an effective temperature of 3,479 K, giving it the red-orange hue of an M-type star. This star has a mass 1.9 times the mass of the Sun, while its radius has expanded to 143 times solar. It is radiating so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algol
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources for more than thirty years. In the sense that the syntax of most modern languages is "Algol-like", it was arguably more influential than three other high-level programming languages among which it was roughly contemporary: FORTRAN, Lisp, and COBOL. It was designed to avoid some of the perceived problems with FORTRAN and eventually gave rise to many other programming languages, including PL/I, Simula, BCPL, B, Pascal, and C. ALGOL introduced code blocks and the begin...end pairs for delimiting them. It was also the first language implementing nested function definitions with lexical scope. Moreover, it was the first programming language which gave detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Persei
Kappa Persei or κ Persei, is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Perseus. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 28.93 mas, it is located at a distance of 113 light-years from the Sun. The system consists of a spectroscopic binary, designated Kappa Persei A, which can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.80. The third star, designated Kappa Persei B, is of magnitude 13.50. Kappa Persei A's two components are designated Kappa Persei Aa (officially named Misam , the traditional name of the entire system) and Ab. Nomenclature ''κ Persei'' ( Latinised to ''Kappa Persei'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as ''Kappa Persei A'' and ''B'', and those of ''A's'' components - ''Kappa Persei Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Persei
Tau Persei (τ Per), also known as 18 Persei, is a binary star in the constellation of Perseus. The system is fairly close, and is located about 254 light-years (78 parsecs) away, based on its parallax. Tau Persei is an eclipsing binary, which means the two stellar components orbit each other in such an orientation that they periodically eclipse each other, while blocking the other's light. Unlike many eclipsing binaries that have short orbital periods, Tau Persei has an orbital period of 4.15 years. With a semi-major axis of 0.055 arcseconds, this is one of the few eclipsing binaries whose components can be resolved with interferometry. The primary component of Tau Persei is a red giant with a spectral type of G8III. It has a radius 16 times that of the Sun, and is about 390 million years old. Its companion is an A-type main-sequence star. In 1989, the primary star eclipsed the secondary, allowing for the stellar parameters to be derived via its light curve. Namin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9 Persei
9 Persei is a single variable star in the northern constellation Perseus, located around 4,300 light years away from the Sun. It has the Bayer designation i Persei; ''9 Persei'' is the Flamsteed designation. This body is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of about 5.2. It is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −15.2 km/s. The star is a member of the Perseus OB1 association of co-moving stars. This is a blue supergiant with a stellar classification of A2 Ia, a massive star that has used up its core hydrogen and is now fusing heavier elements. It is an Alpha Cygni variable (designated V474 Persei), a type of non-radial pulsating variable. It ranges in magnitude from 5.15 down to 5.25. The star has 10.5 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 89 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating over 12,000 times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach (Chinese Constellation)
The Stomach mansion (胃宿, pinyin: Wèi Xiù) is one of the twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger The white tiger or bleached tiger is a leucistic pigmentation variant of the Mainland tiger. It is reported in the wild from time to time in the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, in the Sunderbans region and .... Asterisms {{DEFAULTSORT:Stomach (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Position Angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial pole (NCP), turning positive into the direction of the right ascension. In the standard (non-flipped) images, this is a counterclockwise measure relative to the axis into the direction of positive declination. In the case of observed visual binary stars, it is defined as the angular offset of the secondary star from the primary relative to the north celestial pole. As the example illustrates, if one were observing a hypothetical binary star with a PA of 135°, that means an imaginary line in the eyepiece drawn from the north celestial pole to the primary (P) would be offset from the secondary (S) such that the angle would be 135°. When graphing visual binaries, the NCP is, as in the illustration, normally drawn from the center point (origin) that is the Primary downward&nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Separation
Angular distance \theta (also known as angular separation, apparent distance, or apparent separation) is the angle between the two sightlines, or between two point objects as viewed from an observer. Angular distance appears in mathematics (in particular geometry and trigonometry) and all natural sciences (e.g. astronomy and geophysics). In the classical mechanics of rotating objects, it appears alongside angular velocity, angular acceleration, angular momentum, moment of inertia and torque. Use The term ''angular distance'' (or ''separation'') is technically synonymous with ''angle'' itself, but is meant to suggest the linear distance between objects (for instance, a couple of stars observed from Earth). Measurement Since the angular distance (or separation) is conceptually identical to an angle, it is measured in the same units, such as degrees or radians, using instruments such as goniometers or optical instruments specially designed to point in well-defined directions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |