|
Ionometer
The term ionometer was originally applied to a device for measuring the intensity of ionising radiation. Examples of radiation detectors described as ionometers can be found through to the 1950s but the term more often now means a device for measuring the chemical ion concentration of a fluid. Ionometer (radiation) An early ionometer is due to the Swiss physicist Heinrich Greinacher in 1913. However, Greinacher was not the first to build an ionometer, he credits one Bronson with building an instrument upon which Greinacher's was an improvement. Greinacher states the advantage of his instrument over Bronson's being in not requiring the quadrant electrometer (invented by Lord Kelvin). Greinacher also had to invent the practical voltage doubler circuit in order to provide the 200-300 V he needed for the ionometer as the 110 V AC supplied by the Zurich power stations of the time were insufficient. Ionometer (ion concentration) Possibly the first use of ionometer with thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Greinacher
Heinrich Greinacher (May 31, 1880 in St. Gallen – April 17, 1974 in Bern) was a Swiss physicist. He is regarded as an original experimenter and is the developer of the magnetron and the Greinacher multiplier. Greinacher was the only child of master shoemaker Heinrich Greinacher and his wife Pauline, born Münzenmayer. He went to school in St. Gallen and studied physics at both Zurich, Geneva and Berlin. He also trained as a pianist at the Geneva Conservatory of Music. Originally a German citizen, he was naturalized in 1894 as a Swiss citizen. In Berlin, Greinacher attended the lectures of Max Planck and received a doctorate in 1904 under Emil Warburg. He did his habilitation in 1907 at the University of Zurich, and in 1912, he moved to Zurich on a permanent basis. From 1924 to 1952, he was full professor of Experimental Physics at the University of Bern and the director of the Physical Institute (formerly Physics ''Cabinett''). In 1912, Greinacher developed the magnetron an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionising Radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation, whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, nearly all types of laser light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area is not sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts between 10 electronvolts (eV) and 33 eV. Typical ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Doubler
A voltage doubler is an electronic circuit which charges capacitors from the input voltage and switches these charges in such a way that, in the ideal case, exactly twice the voltage is produced at the output as at its input. The simplest of these circuits are a form of rectifier which take an AC voltage as input and outputs a doubled DC voltage. The switching elements are simple diodes and they are driven to switch state merely by the alternating voltage of the input. DC-to-DC voltage doublers cannot switch in this way and require a driving circuit to control the switching. They frequently also require a switching element that can be controlled directly, such as a transistor, rather than relying on the voltage across the switch as in the simple AC-to-DC case. Voltage doublers are a variety of voltage multiplier circuit. Many, but not all, voltage doubler circuits can be viewed as a single stage of a higher order multiplier: cascading identical stages together achieves a grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its contemporary form. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883, was its president 1890–1895, and in 1892 was the first British scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords. Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in his honour. While the existence of a coldest possible temperature ( absolute zero) was known prior to his work, Kelvin is known for determining its correct value as approximately −273.15 degrees Celsius or −459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. The Joule–Thomson effect is also named in his honour. He worked closely with mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdish Mehra
Jagdish Mehra (April 8, 1931 – September 14, 2008) was an Indian-American historian of science. Academic career Mehra was educated at Allahabad University, the Max Planck Institut für Physik and the University of California at Los Angeles and obtained a Ph.D. in theoretical physics at the University of Neuchatel. He subsequently taught at Purdue University, Southeastern Massachusetts University, the University of Geneva, the Solvay Institute in Brussels, Rice University, the University of Houston and the International Center for Theoretical Physics. He is particularly well known for a book in 6 volumes on The Historical Development of Quantum Theory,Mehra, J. and Rechenberg, H. The Historical Development of Quantum Theory, Volumes 1-6. New York: Springer-Verlag which he wrote with Helmut Rechenberg. He also wrote a biography of Richard Feynman. He also wrote a book on the controversy surrounding the exact role David Hilbert played in the development of the gravitation th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmut Rechenberg
Helmut Rechenberg (born November 6, 1937, in Berlin; died November 10, 2016, in Munich) was a German physicist and science historian. Rechenberg studied mathematics, physics and astronomy at the University of Munich and graduated in 1964. At Munich, his work was in experimental physics, studying the magnetism of solids. He moved to the Max Planck Institute for Physics in Munich, where he became Werner Heisenberg's doctoral student. In 1968, he graduated with a doctorate on quantum field theory. From 1970 to 1972 he worked at the University of Texas at Austin, collaborating with George Sudarshan on quantum field theory and with Jagdish Mehra on science history. He then returned to Germany and the Max Planck Institute, from which he officially retired in 2002. His six-volume work with Jagdish Mehra on the history of quantum mechanics has been described as "an extraordinary amount of painstaking scholarship". Rechenberg also co-edited Werner Heisenberg's collected works and from 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
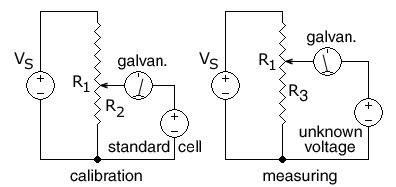
Potentiometer (measuring Instrument)
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the unknown voltage. Since the reference voltage can be produced from an accurately calibrated voltage divider, a potentiometer can provide high precision in measurement. The method was described by Johann Christian Poggendorff around 1841 and became a standard laboratory measuring technique. In this arrangement, a fraction of a known voltage from a resistive slide wire is compared with an unknown voltage by means of a galvanometer. The sliding contact or wiper of the potentiometer is adjusted and the galvanometer briefly connected between the sliding contact and the unknown voltage. The deflection of the galvanometer is observed and the sliding tap adjusted until the galvanometer no longer deflects from zero. At that point the galvanometer d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Detectors
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic particles like powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulate'' is most frequently used to refer to pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere, which are a suspension of unconnected particles, rather than a connected particle aggregation. Conceptual properties The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |