|
Invest (meteorology)
An invest in meteorology (short for ''investigative area'', alternatively written INVEST) is a designated area of disturbed weather that is being monitored for potential tropical cyclone development. Invests are designated by three separate United States forecast centers: the National Hurricane Center, the Central Pacific Hurricane Center, and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Invests (also called ''areas of interest'') are designated by three separate forecast centers located in the United States: the National Hurricane Center in Miami, Florida, overseeing the North Atlantic and North Eastern Pacific basins (east of the 140°W meridian); the Central Pacific Hurricane Center in Honolulu, Hawaii, monitoring the North Central Pacific basin (between the International Date Line and the 140°W meridian); and the military Joint Typhoon Warning Center in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii (formerly located in the island of Guam), serving U.S. government interests elsewhere (i.e. the North Western Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for almost one-third of the world's annual tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centers for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii (the Joint Typhoon Warning Center), the Philippines, and Hong Kong. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year. Within most of the northwestern Pacific, there are no official typhoon seasons as tropical cyclones form thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Analysis Branch
The United States Satellite Analysis Branch, part of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service's Satellite Services Division, is the operational focal point for real-time imagery products within NESDIS. It is also responsible for doing Dvorak technique intensity fixes on tropical cyclones. Its roots lie in the establishment of the Meteorological Satellite Section by January 1959. Its primary mission is to "operate new proof of concept satellite analysis techniques needed to support disaster mitigation and warning services" for the U.S. government and its agencies. It also distributes real-time satellite imagery from geostationary satellites. The SAB also produces graphics for Tropical Rainfall Potential forecasts for all tropical systems in the Western Hemisphere and many in the Eastern Hemisphere. Away from tropical cyclones, the SAB functions as the Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Tropical-like Cyclone
Mediterranean tropical-like cyclones, often referred to as medicanes (a portmanteau of Mediterranean hurricanes) but sometimes also as Mediterranean cyclones or as Mediterranean hurricanes, are meteorological phenomena occasionally observed over the Mediterranean Sea. On a few rare occasions, some storms have been observed reaching the strength of a Category 1 hurricane, on the Saffir–Simpson scale, and one storm has been recorded reaching Category 2 intensity. The main societal hazard posed by medicanes is not usually from destructive winds, but through life-threatening torrential rains and flash floods. The occurrence of medicanes has been described as not particularly rare. Tropical-like systems were first identified in the Mediterranean basin in the 1980s, when widespread satellite coverage showing tropical-looking low pressures which formed a cyclonic eye in the center were identified. Due to the dry nature of the Mediterranean region, the formation of tropical, subtropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. It was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological development and prototyping. The laboratory's specialties include plasma physics, space physics, materials science, and tactical electronic warfare. NRL is one of the first US government scientific R&D laboratories, having opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison, and is currently under the Office of Naval Research. As of 2016, NRL was a United States Navy Working Capital Fund, Navy Working Capital Fund activity, which means it is not a line-item in the US Federal Budget. Instead of direct funding from Congress, all costs, including overhead, were recovered through sponsor-funded research projects. NRL's research expenditures were approximately $1 billion per year. Research The Naval Research Laboratory conducts a wide v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
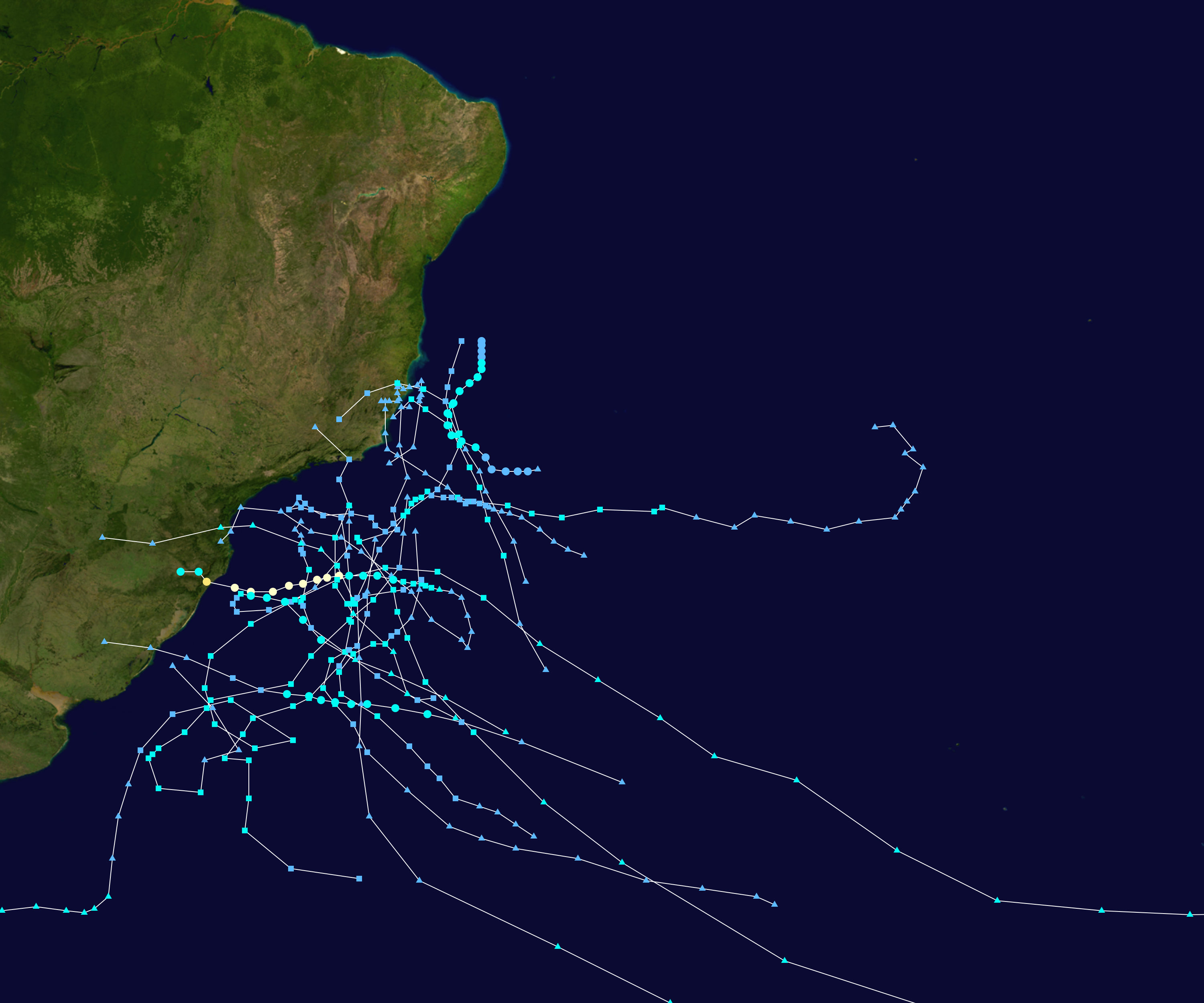
South Atlantic Tropical Cyclone
South Atlantic tropical cyclones are unusual weather events that occur in the Southern Hemisphere. Strong wind shear, which disrupts the formation of cyclones, as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South Atlantic Ocean, make any strong tropical system extremely rare, and Hurricane Catarina in 2004 is the only recorded South Atlantic hurricane in history. Storms can develop year-round in the South Atlantic, with activity peaking during the months from November through May. Since 2011, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center has assigned names to tropical and subtropical systems in the western side of the basin, near the eastern coast of Brazil, when they have sustained wind speeds of at least , the generally accepted minimum sustained wind speed for a disturbance to be designated as a tropical storm in the North Atlantic basin. Below is a list of notable South Atlantic tropical and subtropical cyclones. Theories concerning infrequency of occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pacific Tropical Cyclone
A South Pacific tropical cyclone is a non-frontal, low pressure system that has developed, within an environment of warm sea surface temperatures and little vertical wind shear aloft in the South Pacific Ocean. Within the Southern Hemisphere there are officially three areas where tropical cyclones develop on a regular basis, these areas are the South-West Indian Ocean between Africa and 90°E, the Australian region between 90°E and 160°E and the South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. The South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W is officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service and New Zealand's MetService, while others like the Australian Bureau of Meteorology and the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration also monitor the basin. Each tropical cyclone year within this basin starts on July 1 and runs throughout the year, encompassing the tropical cyclone season which runs from November 1 and lasts until April 30 each season. Within the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Region Tropical Cyclone
An Australian region tropical cyclone is a non-frontal, low-pressure system that has developed within an environment of warm sea surface temperatures and little vertical wind shear aloft in either the Southern Indian Ocean or the South Pacific Ocean. Within the Southern Hemisphere there are officially three areas where tropical cyclones develop on a regular basis: the South-West Indian Ocean between Africa and 90°E, the Australian region between 90°E and 160°E, and the South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. The Australian region between 90°E and 160°E is officially monitored by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, the Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency, and the Papua New Guinea National Weather Service, while others like the Fiji Meteorological Service and the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration also monitor the basin. Each tropical cyclone year within this basin starts on 1 July and runs throughout the year, encompas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South-West Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclone
In the south-west Indian Ocean, tropical cyclones form south of the equator and west of 90° E to the coast of Africa. Warnings and nomenclature In 1946, Réunion's first airstrip opened, then called Gillot, and now called Roland Garros Airport. In 1950, the first meteorological station on the island opened at the airport, operated by Météo-France (MFR). The agency began publishing annual reviews in the 1962–63 season. Each year, the Météo-France office (MFR) based on Réunion island issues warnings on tropical cyclones within the basin, which is defined as the waters of the Indian Ocean from the coast of Africa to 90° E, south of the equator. The agency issues the warnings as part of its role as a Regional Specialized Meteorological Center, designated as such in 1993 by the World Meteorological Organization. Intensities are estimated through the Dvorak technique, which utilizes images from satellites by the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Peninsula, on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives, on the southwest by Somalia, and on the east by India. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 meters (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf. Name The sea is named after Arabia, the historic name of the region to the west of the sea. The Arabian Sea's name in Arabic is ; in Persian it is دریای عرب; in Urdu it is بحیرہ عرب; in Hindi it is अरब सागर; in Gujarati it is અરબી સમુદ્ર; in Marathi it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the north westernmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the existence of British India, it was named as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region. At the time, the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges– Hooghly, the Padma, the Brahmaputra–Yamuna, the Barak� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclone
In the Indian Ocean north of the equator, tropical cyclones can form throughout the year on either side of India, although most frequently between April and June, and between October and December. Sub-basins The North Indian Ocean is the least active basin, contributing only seven percent of the world's tropical cyclones. However the basin has produced some of the deadliest cyclones in the world, since they strike over very densely populated areas. The Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and it is responsible to monitor the basin, issues warning and name the storms. The basin is divided into two sub-basins the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. The Bay of Bengal, located in the northeast of the Indian Ocean. The basin is abbreviated ''BOB'' by the India Meteorological Department (IMD). The United States's Joint Typhoon Warning Center unofficially designates as ''B'' to classify storms formed in the Bay of Bengal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |