|
Inverted Index
In computer science, an inverted index (also referred to as a postings list, postings file, or inverted file) is a database index storing a mapping from content, such as words or numbers, to its locations in a table, or in a document or a set of documents (named in contrast to a forward index, which maps from documents to content). The purpose of an inverted index is to allow fast full-text searches, at a cost of increased processing when a document is added to the database. The inverted file may be the database file itself, rather than its index. It is the most popular data structure used in document retrieval systems, used on a large scale for example in search engines. Additionally, several significant general-purpose mainframe-based database management systems have used inverted list architectures, including ADABAS, DATACOM/DB, and Model 204. There are two main variants of inverted indexes: A record-level inverted index (or inverted file index or just inverted file) conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Engine Indexing
Search engine indexing is the collecting, parsing, and storing of data to facilitate fast and accurate information retrieval. Index design incorporates interdisciplinary concepts from linguistics, cognitive psychology, mathematics, informatics, and computer science. An alternate name for the process, in the context of search engines designed to find web pages on the Internet, is ''web indexing''. Popular engines focus on the full-text indexing of online, natural language documents. Media types such as pictures, video, audio, and graphics are also searchable. Meta search engines reuse the indices of other services and do not store a local index whereas cache-based search engines permanently store the index along with the corpus. Unlike full-text indices, partial-text services restrict the depth indexed to reduce index size. Larger services typically perform indexing at a predetermined time interval due to the required time and processing costs, while agent-based search engines ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Algorithms
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the search space of a problem domain, with either discrete or continuous values. algorithms are Although search engines use search algorithms, they belong to the study of information retrieval, not algorithmics. The appropriate search algorithm often depends on the data structure being searched, and may also include prior knowledge about the data. Search algorithms can be made faster or more efficient by specially constructed database structures, such as search trees, hash maps, and database indexes. Search algorithms can be classified based on their mechanism of searching into three types of algorithms: linear, binary, and hashing. Linear search algorithms check every record for the one associated with a target key in a linear fashion. Binary, or half-interval, searches repeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource. Concept The concept of data management arose in the 1980s as technology moved from sequential processing (first punched cards, then magnetic tape) to random access storage. Since it was now possible to store a discrete fact and quickly access it using random access disk technology, those suggesting that data management was more important than business process management used arguments such as "a customer's home address is stored in 75 (or some other large number) places in our computer systems." However, during this period, random access processing was not competitively fast, so those suggesting "process management" was more important than "data management" used batch processing time as their primary argument. As application software evolved into real-time, interactive usage, it became obvious that both management processes were important. If the data was not well defined, the data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosetta Code
Rosetta Code is a wiki-based programming website with implementations of common algorithms and solutions to various programming problems in many different programming languages. It is named for the Rosetta Stone, which has the same text inscribed on it in three languages, and thus allowed Egyptian hieroglyphs to be deciphered for the first time. Website Rosetta Code was created in 2007 by Michael Mol. The site's content is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License 1.2, though some components may be dual-licensed under more permissive terms. The Rosetta Code web repository illustrates how desired functionality is implemented very differently in various programming paradigms, and how "the same" task is accomplished in different programming languages. , Rosetta Code has: ::* 1,121 computer programming tasks (or problems) ::* 303 additional draft programming tasks ::* 810 computer programming languages that are used to solve tasks ::* 83,043 computer programmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, claiming nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science ( informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading, Massachusetts
Reading ( ) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, north of central Boston. The population was 25,518 at the 2020 census. History Settlement and American independence Many of the Massachusetts Bay Colony's original settlers arrived from England in the 1630s through the ports of Lynn and Salem. In 1639 some citizens of Lynn petitioned the government of the colony for a "place for an inland plantation". They were initially granted six square miles, followed by an additional four. The first settlement in this grant was at first called "Lynn Village" and was located on the south shore of the "Great Pond", now known as Lake Quannapowitt. On June 10, 1644 the settlement was incorporated as the town of Reading, taking its name from the town of Reading in England. The first church was organized soon after the settlement, and the first parish separated and became the town of "South Reading" in 1812, renaming itself as Wakefield in 1868. Thomas Parker was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison-Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson PLC, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison-Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison-Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison-Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include ''The Art of Computer Programming'', ''The C++ Programming Language'', ''The Mythical Man-Month'', and ''Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison-Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison-Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first computer book was ''Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
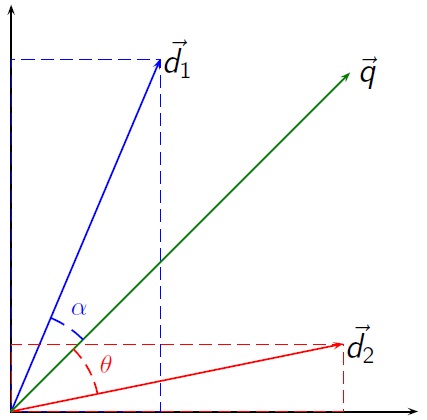
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (and any objects, in general) as vectors of identifiers (such as index terms). It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ''term'' depends on the application. Typically terms are single words, keywords, or longer phrases. If words are chosen to be the terms, the dimensionality of the vector is the number of words in the vocabulary (the number of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Index
Database management systems provide multiple types of indexes to improve performance and data integrity across diverse applications. Index types include b-trees, bitmaps, and r-trees. In database management systems, a reverse key index strategy reverses the key value before entering it in the index. E.g., the value 24538 becomes 83542 in the index. Reversing the key value is particularly useful for indexing data such as sequence numbers, where each new key value is greater than the prior value, i.e., values monotonically increase. Reverse key indexes have become particularly important in high volume transaction processing systems because they reduce contention for index blocks. Creating data Reversed key indexes use b-tree structures, but preprocess key values before inserting them. Simplifying, b-trees place similar values on a single index block, e.g., storing 24538 on the same block as 24539. This makes them efficient both for looking up a specific value and for finding valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitmap Index
A bitmap index is a special kind of database index that uses bitmaps. Bitmap indexes have traditionally been considered to work well for ''low- cardinality columns'', which have a modest number of distinct values, either absolutely, or relative to the number of records that contain the data. The extreme case of low cardinality is Boolean data (e.g., does a resident in a city have internet access?), which has two values, True and False. Bitmap indexes use bit arrays (commonly called bitmaps) and answer queries by performing bitwise logical operations on these bitmaps. Bitmap indexes have a significant space and performance advantage over other structures for query of such data. Their drawback is they are less efficient than the traditional B-tree indexes for columns whose data is frequently updated: consequently, they are more often employed in read-only systems that are specialized for fast query - e.g., data warehouses, and generally unsuitable for online transaction processing ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Assembly
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology might not be able to 'read' whole genomes in one go, but rather reads small pieces of between 20 and 30,000 bases, depending on the technology used. Typically, the short fragments (reads) result from shotgun sequencing genomic DNA, or gene transcript ( ESTs). The problem of sequence assembly can be compared to taking many copies of a book, passing each of them through a shredder with a different cutter, and piecing the text of the book back together just by looking at the shredded pieces. Besides the obvious difficulty of this task, there are some extra practical issues: the original may have many repeated paragraphs, and some shreds may be modified during shredding to have typos. Excerpts from another book may also be added in, and some shreds may be completely unrecognizable. Genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |