|
Inuit Words For Snow
The claim that Eskimo words for snow (specifically Yupik and Inuit words) are unusually numerous, particularly in contrast to English, is often used to support the controversial linguistic-relativity hypothesis or "Whorfianism". That strongest interpretation of this hypothesis, which posits that a language's vocabulary (among other features) shapes or defines its speakers' view of the world, has been largely discredited, though a 2010 study supports the core notion that these languages have many more words for "snow" than the English language. The original claim is based in the work of anthropologist Franz Boas and was particularly promoted by his contemporary, Benjamin Lee Whorf, whose name is connected with the hypothesis. Overview Franz Boas did not make quantitative claims but rather pointed out that the Eskimo–Aleut languages have about the same number of distinct word roots referring to snow as English does, but the structure of these languages tends to allow more va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yupik Languages
The Yupik languages () are a family of languages spoken by the Yupik peoples of western and south-central Alaska and Chukotka. The Yupik languages differ enough from one another that they are not mutually intelligible, although speakers of one of the languages may understand the general idea of a conversation of speakers of another of the languages. One of them, Sirenik, has been extinct since 1997. The Yupik languages are in the family of Eskimo–Aleut languages. The Aleut and Eskimo languages diverged around 2000 BC (contemporaneous with the split of Indo-Iranian); within the Eskimo classification, the Yupik languages diverged from each other and from the Inuit language around 1000 AD. List of languages # Naukan Yupik (also Naukanski): spoken by perhaps 100 people in and around Lavrentiya, Lorino, and Uelen on the Chukotka Peninsula of Eastern Siberia. # Central Siberian Yupik (also Yupigestun, Akuzipigestun, Akuzipik, Siberian Yupik, Siberian Yupik Eskimo, Centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Snow
Classifications of snow describe and categorize the attributes of snow-generating weather events, including the individual crystals both in the air and on the ground, and the deposited snow pack as it changes over time. Snow can be classified by describing the weather event that is producing it, the shape of its ice crystals or flakes, how it collects on the ground, and thereafter how it changes form and composition. Depending on the status of the snow in the air or on the ground, a different classification applies. Snowfall arises from a variety of events that vary in intensity and cause, subject to classification by weather bureaus. Some snowstorms are part of a larger weather pattern. Other snowfall occurs from lake effects or atmospheric instability near mountains. Falling snow takes many different forms, depending on atmospheric conditions, especially vapor content and temperature, as it falls to the ground. Once on the ground, snow crystals metamorphose into different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Brown (psychologist)
Roger William Brown (April 14, 1925 – December 11, 1997) was an American psychologist. He was known for his work in social psychology and in children's language development. Brown taught at Harvard University from 1952 until 1957 and from 1962 until 1994, and at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) from 1957 until 1962. His scholarly books include ''Words and Things: An Introduction to Language'' (1958), ''Social Psychology'' (1965), ''Psycholinguistics'' (1970), ''A First Language: The Early Stages'' (1973), and ''Social Psychology: The Second Edition'' (1985). He authored numerous journal articles and book chapters. He was the doctoral adviser or a post-doctoral mentor of many researchers in child language development and psycholinguistics, including Jean Berko Gleason, Susan Ervin-Tripp, Camile Hanlon, Dan Slobin, Ursula Bellugi, Courtney Cazden, Richard F. Cromer, David McNeill, Eric Lenneberg, Colin Fraser, Eleanor Rosch (Heider), Melissa Bowerman, Steven Pink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
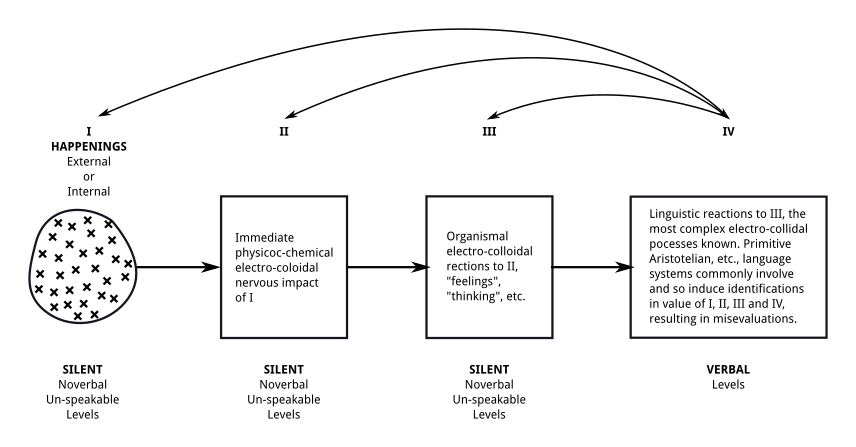
General Semantics
General semantics is concerned with how events translate to perceptions, how they are further modified by the names and labels we apply to them, and how we might gain a measure of control over our own cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses. Proponents characterize general semantics as an antidote to certain kinds of delusional thought patterns in which incomplete and possibly warped mental constructs are projected onto the world and treated as reality itself. After partial launches under the names ''human engineering'' and ''humanology'', Polish-American originator Alfred Korzybski (1879–1950) fully launched the program as ''general semantics'' in 1933 with the publication of ''Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics''. In ''Science and Sanity'', general semantics is presented as both a theoretical and a practical system whose adoption can reliably alter human behavior in the direction of greater sanity. In the 1947 preface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Whorf
Benjamin Lee Whorf (; April 24, 1897 – July 26, 1941) was an American linguist and fire prevention engineer. He is known for "Sapir–Whorf hypothesis," the idea that differences between the structures of different languages shape how their speakers perceive and conceptualize the world. This principle has been named after him and his mentor Edward Sapir, which was initially called linguistic relativity by Whorf because he saw the idea as having implications similar to Einstein’s principle of physical relativity. The idea, however, follows from post-Hegelian 19th-century philosophy, especially from Wilhelm von Humboldt; and from Wilhelm Wundt's Völkerpsychologie. Throughout his life Whorf was a chemical engineer by profession, but as a young man he took an interest in linguistics. At first this interest drew him to the study of Biblical Hebrew, but he quickly went on to study the indigenous languages of Mesoamerica on his own. Professional scholars were impressed by his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Sapir
Edward Sapir (; January 26, 1884 – February 4, 1939) was an American Jewish anthropologist-linguist, who is widely considered to be one of the most important figures in the development of the discipline of linguistics in the United States. Sapir was born in German Pomerania, in what is now northern Poland. His family emigrated to the United States of America when he was a child. He studied Germanic linguistics at Columbia, where he came under the influence of Franz Boas, who inspired him to work on Native American languages. While finishing his Ph.D. he went to California to work with Alfred Kroeber documenting the indigenous languages there. He was employed by the Geological Survey of Canada for fifteen years, where he came into his own as one of the most significant linguists in North America, the other being Leonard Bloomfield. He was offered a professorship at the University of Chicago, and stayed for several years continuing to work for the professionalization of the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sastrugi
Sastrugi, or zastrugi, are features formed by erosion of snow by wind. They are found in polar regions, and in snowy, wind-swept areas of temperate regions, such as frozen lakes or mountain ridges. Sastrugi are distinguished by upwind-facing points, resembling anvils, which move downwind as the surface erodes. These points usually lie along ridges perpendicular to the prevailing wind; they are steep on the windward side and sloping to the leeward side. Smaller irregularities of this type are known as ripples (small, ~10 mm high) or wind ridges. Large sastrugi are troublesome to skiers and snowboarders. Traveling on the irregular surface of sastrugi can be very tiring, and can risk breaking equipment—ripples and waves are often undercut and the surface is hard and unforgiving, with constant minor topographic changes between ridge and trough. Etymology The words ''sastrugi'' and ''zastrugi'' are Russian-language plurals; the singular is ''zastruga''. The form ''sastrug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penitente (snow Formation)
Penitentes, or nieves penitentes (Spanish for " penitent snows"), are snow formations found at high altitudes. They take the form of elongated, thin blades of hardened snow or ice, closely spaced and pointing towards the general direction of the sun. The name comes from the resemblance of a field of penitentes to a crowd of kneeling people doing penance. The formation evokes the tall, pointed habits and hoods worn by brothers of religious orders in the Processions of Penance during Spanish Holy Week. In particular, the brothers' hats are tall, narrow, and white, with a pointed top. These spires of snow and ice grow over all glaciated and snow-covered areas in the Dry Andes above . They range in length from a few centimetres to over . First description Penitentes were first described in scientific literature by Charles Darwin in 1839. On March 22, 1835, he had to squeeze his way through snowfields covered in penitentes near the Piuquenes Pass, on the way from Santiago de Chile t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Névé
Névé is a young, granular type of snow which has been partially melted, refrozen and compacted, yet precedes the form of ice. This type of snow is associated with glacier formation through the process of ''nivation''. Névé that survives a full season of ablation turns into firn, which is both older and slightly denser. Firn eventually becomes glacial ice – the long-lived, compacted ice that glaciers are composed of. Glacier formation can take days to years depending on freeze-thaw factors. Névé is annually observed in skiing slopes, and is generally disliked as an icy falling zone. Névé has a minimum density of 500 kg/m3, which is roughly half of the density of liquid water at 1 atm. Névé can also refer to the alpine Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to: Places Europe * Alps, a European mountain range ** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range Australia * Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village * Alpine Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firn
__NOTOC__ Firn (; from Swiss German "last year's", cognate with ''before'') is partially compacted névé, a type of snow that has been left over from past seasons and has been recrystallized into a substance denser than névé. It is ice that is at an intermediate stage between snow and glacial ice. Firn has the appearance of wet sugar, but has a hardness that makes it extremely resistant to shovelling. Its density generally ranges from 0.35 g/cm3 to 0.9 g/cm3, and it can often be found underneath the snow that accumulates at the head of a glacier. Snowflakes are compressed under the weight of the overlying snowpack. Individual crystals near the melting point are semiliquid and slick, allowing them to glide along other crystal planes and to fill in the spaces between them, increasing the ice's density. Where the crystals touch they bond together, squeezing the air between them to the surface or into bubbles. In the summer months, the crystal metamorphosis can occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifications Of Snow
Classifications of snow describe and categorize the attributes of snow-generating weather events, including the individual crystals both in the air and on the ground, and the deposited snow pack as it changes over time. Snow can be classified by describing the weather event that is producing it, the shape of its ice crystals or flakes, how it collects on the ground, and thereafter how it changes form and composition. Depending on the status of the snow in the air or on the ground, a different classification applies. Snowfall arises from a variety of events that vary in intensity and cause, subject to classification by weather bureaus. Some snowstorms are part of a larger weather pattern. Other snowfall occurs from lake effects or atmospheric instability near mountains. Falling snow takes many different forms, depending on atmospheric conditions, especially vapor content and temperature, as it falls to the ground. Once on the ground, snow crystals metamorphose into different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)

_D130902_3.jpg)

