|
Intertemporal Choice
Intertemporal choice is the process by which people make decisions about what and how much to do at various points in time, when choices at one time influence the possibilities available at other points in time. These choices are influenced by the relative value people assign to two or more payoffs at different points in time. Most choices require decision-makers to trade off costs and benefits at different points in time. These decisions may be about saving, work effort, education, nutrition, exercise, health care and so forth. Greater preference for immediate smaller rewards has been associated with many negative outcomes ranging from lower salary to drug addiction. Since early in the twentieth century, economists have analyzed intertemporal decisions using the discounted utility model, which assumes that people evaluate the pleasures and pains resulting from a decision in much the same way that financial markets evaluate losses and gains, exponentially 'discounting' the value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saver
Saver or savers may refer to: * ''Saver'' (manhwa), a Korean manhwa by Eun-Young Lee *''The Saver'', 2015 Canadian drama film, written and directed by Wiebke von Carolsfeld * Saver return, a type of train ticket in the United Kingdom *Kaman KSA-100 SAVER (Stowable Aircrew Vehicle Escape Rotorseat), a gyroplane * Savers, a U.S. thrift store chain *Savers (UK retailer), a U.K. discount store chain * Cheongju KB ''Savers'', a South Korean women's basketball team See also *''Captain Saver'', a 1992 Taito videogame *Savères, a commune in Haute-Garonne department, France *Savior (other) *Savor (other) *SAVR (other) SAVR or ''Savr'' may refer to: * surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) * Alto Río Senguer Airport (ICAO airport code: SAVR), Alto Río Senguer, Chubut, Argentina * Savr Shalburov, a Russian wrestler who competed against Kurban Shiraev See als ... * Save (other) * * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Behaviour
Consumer behavior is the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and all the activities associated with the purchase, use and disposal of goods and services. Consumer behaviour consists of how the consumer's emotions, attitudes, and preferences affect buying behaviour. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, ethnology, marketing, and economics (especially behavioural economics). The study of consumer behaviour formally investigates individual qualities such as demographics, personality lifestyles, and behavioural variables (such as usage rates, usage occasion, loyalty, brand advocacy, and willingness to provide referrals), in an attempt to understand people's wants and consumption patterns. Consumer behaviour also investigates on the influences on the consumer, from social g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
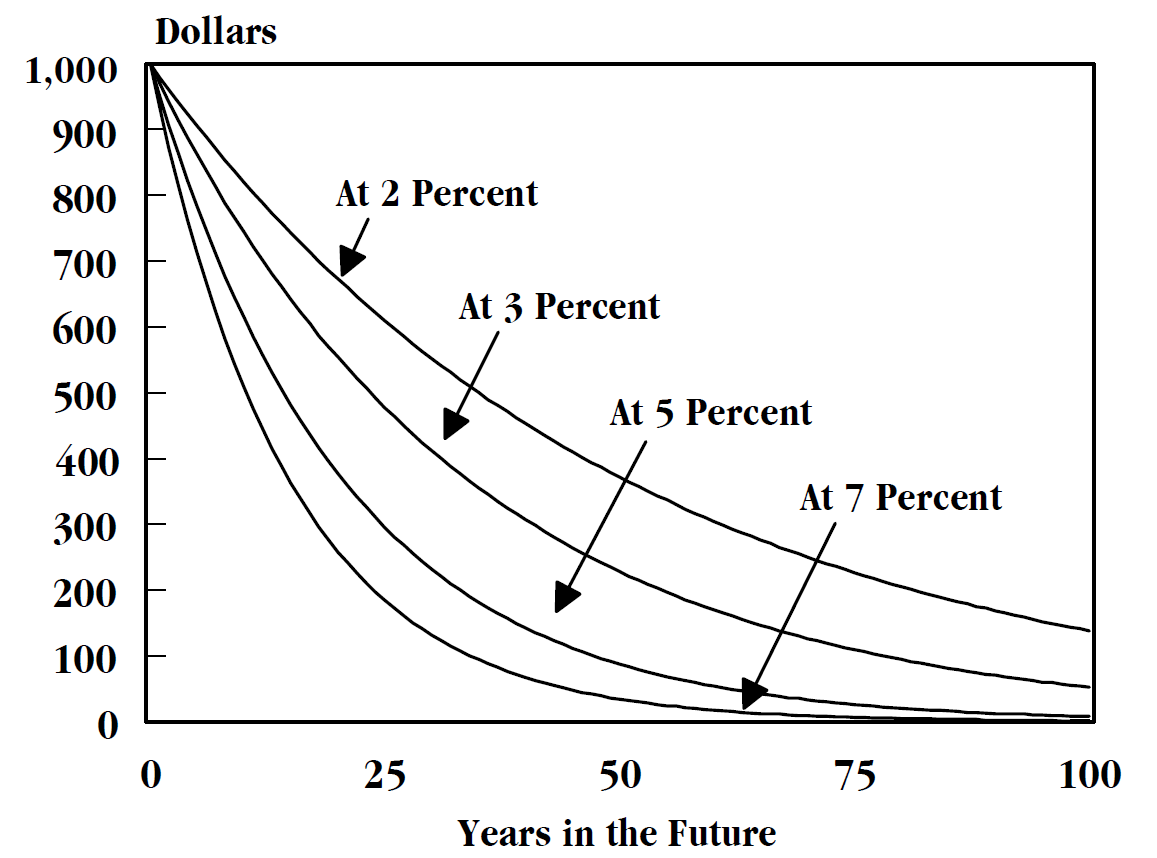
Temporal Discounting
In economics, time preference (or time discounting, delay discounting, temporal discounting, long-term orientation) is the current relative valuation placed on receiving a good or some cash at an earlier date compared with receiving it at a later date. Time preferences are captured mathematically in the discount function. The higher the time preference, the higher the discount placed on returns receivable or costs payable in the future. One of the factors that may determine an individual's time preference is how long that individual has lived. An older individual may have a lower time preference (relative to what they had earlier in life) due to a higher income and to the fact that they have had more time to acquire durable commodities (such as a college education or a house). Example A practical example: Jim and Bob go out for a drink but Jim has no money so Bob lends Jim $10. The next day Jim visits Bob and says, "Bob, you can have $10 now, or I will give you $15 when I get p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynes–Ramsey Rule
In macroeconomics, the Keynes–Ramsey rule is a necessary condition for the optimality of intertemporal consumption choice. Usually it is express as a differential equation relating the rate of change of consumption with interest rates, time preference, and (intertemporal) elasticity of substitution. If derived from a basic Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans model, the Keynes–Ramsey rule may look like :\dot(t) = \frac \cdot (r - \rho) \cdot c(t) where c(t) is consumption and \dot(t) its change over time (in Newton notation), \rho \in (0,1) is the discount rate, r \in (0,1) is the real interest rate, and \sigma > 0 is the (intertemporal) elasticity of substitution. The Keynes–Ramsey rule is named after Frank P. Ramsey, who derived it in 1928, and his mentor John Maynard Keynes, who provided an economic interpretation. Mathematically, the Keynes–Ramsey rule is a necessary first-order condition for an optimal control problem, also known as an Euler–Lagrange equation. See also * Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertemporal Budget Constraint
In economics and finance, an intertemporal budget constraint is a constraint faced by a decision maker who is making choices for both the present and the future. The term intertemporal is used to describe any relationship between past, present and future events or conditions. In its general form, the intertemporal budget constraint says that the present value of current and future cash outflows cannot exceed the present value of currently available funds and future cash inflows. Typically this is expressed as :\sum_^T \frac \le \sum_^T \frac , where x_t is expenditure at time ''t'', w_t is the cash that becomes available at time ''t'', ''T'' is the most distant relevant time period, 0 is the current time period, and \frac{1+r} is the discount factor computed from the interest rate ''r''. Complications are possible in various circumstances. For example, the interest rate for discounting cash receipts might be greater than the interest rate for discounting expenditures, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discounted Utility
In economics, discounted utility is the utility (desirability) of some future event, such as consuming a certain amount of a good, as perceived at the present time as opposed to at the time of its occurrence. It is calculated as the present discounted value of future utility, and for people with time preference for sooner rather than later gratification, it is less than the future utility. The utility of an event ''x'' occurring at future time ''t'' under utility function ''u'', discounted back to the present (time 0) using discount factor \beta, Is :\beta ^t u(x_t). Since more distant events are less liked, 0 < \beta < 1. Discounted utility calculations made for events at various points in the future as well as at the present take the form : where is the utility of some choice at time and ''T'' is the time of the most distant future satisfaction event. Here, since utility comparis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discount Function
A discount function is used in economic models to describe the weights placed on rewards received at different points in time. For example, if time is discrete and utility is time-separable, with the discount function f(t) having a negative first derivative and with c_t (or c(t) in continuous time) defined as consumption at time ''t'', total utility from an infinite stream of consumption is given by :U(\_^\infty)=\sum_^\infty . Total utility in the continuous-time case is given by :U(\_^\infty)=\int_^\infty {f(t)u(c(t)) dt} provided that this integral exists. Exponential discounting and hyperbolic discounting are the two most commonly used examples. See also *Discounted utility *Intertemporal choice *Temporal discounting In economics, time preference (or time discounting, delay discounting, temporal discounting, long-term orientation) is the current relative valuation placed on receiving a good or some cash at an earlier date compared with receiving it at a later .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Discounting
In economics, hyperbolic discounting is a time-''inconsistent'' model of delay discounting. It is one of the cornerstones of behavioral economics and its brain-basis is actively being studied by neuroeconomics researchers. According to the discounted utility approach, intertemporal choices are no different from other choices, except that some consequences are delayed and hence must be anticipated and discounted (i.e., reweighted to take into account the delay). Given two similar rewards, humans show a preference for one that arrives sooner rather than later. Humans are said to ''discount'' the value of the later reward, by a factor that increases with the length of the delay. In the financial world, this process is normally modeled in the form of exponential discounting, a time-''consistent'' model of discounting. Many psychological studies have since demonstrated deviations in instinctive preference from the constant discount rate assumed in exponential discounting. Hyperbolic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discount Factor
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of mortality effects, impatience effects, and salience effects. The discount, or charge, is the difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Discounting
In economics, hyperbolic discounting is a time-''inconsistent'' model of delay discounting. It is one of the cornerstones of behavioral economics and its brain-basis is actively being studied by neuroeconomics researchers. According to the discounted utility approach, intertemporal choices are no different from other choices, except that some consequences are delayed and hence must be anticipated and discounted (i.e., reweighted to take into account the delay). Given two similar rewards, humans show a preference for one that arrives sooner rather than later. Humans are said to ''discount'' the value of the later reward, by a factor that increases with the length of the delay. In the financial world, this process is normally modeled in the form of exponential discounting, a time-''consistent'' model of discounting. Many psychological studies have since demonstrated deviations in instinctive preference from the constant discount rate assumed in exponential discounting. Hyperbolic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Galeries_Royales_St_Hurbert%2C_Brussels.jpg)